![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amalgam and a full metal crown can be distinguished from each other radiographically by their:
a. degree of radiopacity b. shape of margins c. location in the mouth d. use of retention pins |
b. shape of margins
* Ref. pp. 291-292 *
- Metal crowns will most often appear to have smooth margins, whereas amalgam restorations have irregular margins. |
|
|
Which of these dental restorative materials appear most radiopaque?
a. Amalgam b. Porcelain c. Silicate d. Acrylic resin |
a. Amalgam
* Ref. p. 291 *
- Amalgam = Radiopaque - Porcelain = Slightly Radiopaque - Silicate = Less Radiopaque / Radiolucent - Acrylic resin = Less Radiopaque / Radiolucent |
|
|
Which of these dental materials is most likely to mimic decay radiographically?
a. Gold b. Stainless steel c. Amalgam d. Composite |
d. Composite
* Ref. pp. 291-292 *
- Gold, Stainless steel and amalgam are all metal dental restorations and appear radiopaque. - Composite varies in appearance from radiopaque to radiolucent. When radiolucent, composite may mimic caries. |
|
|
Dens in dente appears radiographically as a:
a. Tiny tooth b. Large tooth c. Twin tooth d. Tooth within a tooth |
d. Tooth within a tooth
* Ref. p. 295 *
Dens in dente is literally a tooth within a tooth, an invagination of the enamel within the body of the tooth (most frequently in maxillary lateral incisors). |
|
|
A sharp bend in the root is called:
a. taurodontosis b. hypercementosis c. dilaceration d. exostosis |
c. dilaceration
* Ref. pp. 295, 296 & 300 *
- Taurodontosis is characterized by an elongated pulp chamber and very short roots. - Hypercementosis is excessive cementum on the roots often causing a bulbous enlargement along the root surface, with the area near the apex appearing most bulbous. - Delaceration is when the root is misshapen with a sharp bend. - Exostosis is a localized overgrowth of bone. |
|
|
Radiographically, it is not possible to accurately differentiate between a periapical abscess, a granuloma, and a cyst. Radiographically, it is not possible to accurately differentiate between carcinoma and sarcoma.
a. Both statements are true. b. Both statements are false. c. The first statement is true; the second statement is false. d. The first statement is false; the second statement is true. |
a. Both statements are true.
* Ref. pp 300-301 *
- Periapical abscesses, granulomas and cysts all appear radiolucent and cannot be distinguished from each other radiographically. - Carcinomas are malignant tumors of epithelial origin, and sarcomas are malignant tumors of connective tissue origin. The radiographic appearance of these tumors is radiolucent with regular and poorly defined borders. |
|
|
Which of these appears radiolucent on a radiograph?
a. Sialolith b. Abscess c. Torus d. Odontoma |
b. Abscess.
* Ref. pp. 296-297 & 299-300 *
- Sailoliths are depositions of calcium salts in the salivary glands and ducts that appear radiopaque. - Abscess is first a barely discernible radiographically when acute, and become more radiolucent as it becomes chronic. - Torus is an asbestosis near the midline of the palate or on the lingual surface of the mandible, which appear as areas of increased radiopacity - Odontoma is a tumor consisting of a radiolucent fibrous cyst-like capsule around small, radiopaque misshapen teeth structures. |
|
|
A large radiolucency surrounding the corwn only of an unerupted tooth is most likely what type of cyst?
a. Dentigerous b. Radicular c. Residual b. Pariapical |
b. Detigerous
* Ref. 297 *
- Detigerous or follicular cyst form around the crowns of imparted or unerupted teeth. - Peripaical cyst is around the end of the tooth root, and is also known as a radicular cyst. If the cyst is not completely removed, it is then called a residual cyst. |
|
|
The evidence of resorption that appears to shorten the tooth is called:
a. internal resorption b. external resorption c. primary resoption d. secondary resorption
|
b. external resorption
* Ref. pp. 297-298 *
-Internal resorption typically appears as a radiolucent widening of the root chanal. - External resorption is most often characterized by root-end resorption where the root of the teeth appear shorter than normal. - There is no primary or secondary resorption in this chapter. |
|
|
The radiographic appearance of a small ovoid radiopacity in the pulp chamber of the tooth is called a:
a. rhinolith b. phlebolith c. pulp stone d. pulp cap. |
c. pulp stone
* Ref. p 299
- Rhinoliths are stones within the maxillary sinuses - Phleboliths, or calcified thrombi, are calcified masses observed as round or oval bodies in the soft tissues of the cheeks. - Pulp stones are small nodules of calcification in the dental pulp. - There is no pulp cap in this chapter. |
|
|
Which of the following appears as radiolucent in its early stages as a radiopaque mass in its later stages?
a. condensing osteitis b. periapical granuloma c. Osteosclerosis d. Oeriapical cemental dysplasia (PCD) |
d. Oeriapical cemental dysplasia (PCD)
* Ref. pp. 297 & 299 *
- Condensing osteitis occurs when sclerotic (hardened) bone is formed as a result of infection and is increased radiopacity. - Periapical Granuloma is a mass of granulated tissue usually surrounded by a fibrous sac continuous iwthin the PDL space and may form a cyst, which is radiolucent. - Osteosclerosis occurs when regions of abnormally dense bone form NOT as a result of infection and is increased radiopacity. - Oeriapical cemental dysplasia (PCD), sometimes called cementomas, is a boney displacia derived from the PDL of fully developed/erupted teeth and appears radiolucent early and radiopaque later. |
|
|
Which of the following tumors appears radiolucent radiographically?
a. Torus palatinus b. Odontoma c. Sarcoma |
c. Sarcoma
* Ref. pp. 299-301 *
- Torus Palatinus appears radiopaque. - Odontoma appears as a radiolucent fibrous capsul around a varous number of radiopaque mishapen toothlike structures. - Sacromas are milignant tumors of connective tissue that appears radiolucent. |
|
|
Radiographic evidence of a bone fracture appears as radiolucent line that may resemble a:
a. nutrient canal b. cyst c. tumor d. retained root tip |
a. nutrient canals
* Ref. p. 301 *
Fractures may on occasion have a similar appearance to the nutrient canals described in chapter 22.
|
|
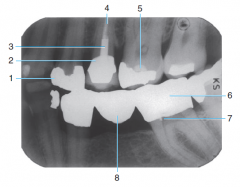
1 |
Amalgam |
|
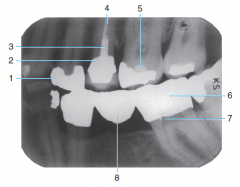
2 |
Porcelain-fused-to-metal crown |
|
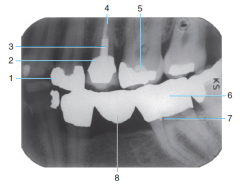
3 |
Post and core |
|
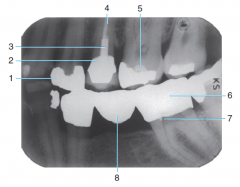
4 |
Gutta percha |
|
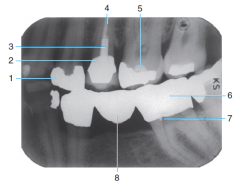
5 |
Base material |
|
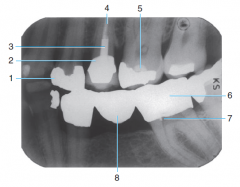
6 |
Full metal Crown |
|
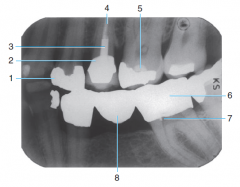
7 |
Retention pin |
|

8 |
Metal Pontic (Part of the three-unit bridge) |
|
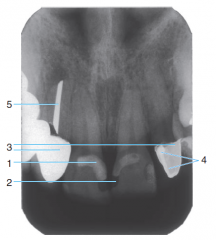
1 |
Radiopaque composite |
|
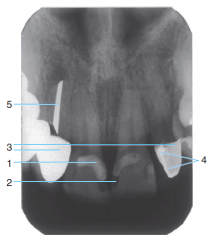
2 |
Radiolucent Composite |
|
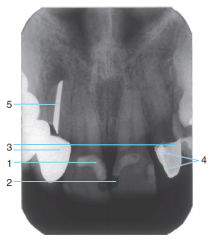
3 |
Porcelain-fused-to-metal crowns |
|
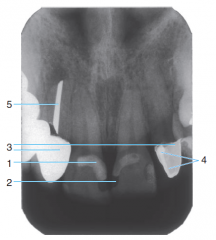
4 |
Cement under a crown |
|
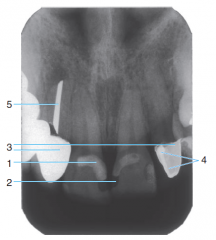
5 |
Silver point endodontic filler |
|
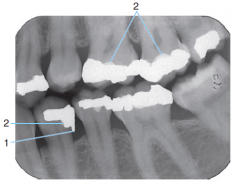
1 |
Amalgam Overhang |
|
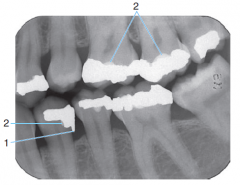
2 |
Base Material |
|
|
Amalgam fragment embedded in soft tissue |
|
|
Stainless steel crown |
|
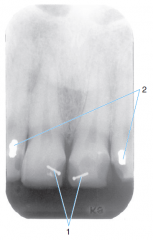
1 |
Retention pins |
|
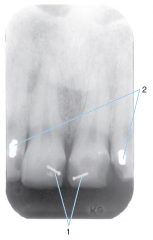
2 |
Small amalgam restorations |
|
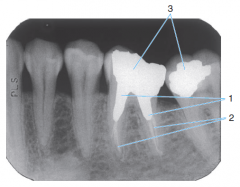
1 |
Endodontic Treatment |
|
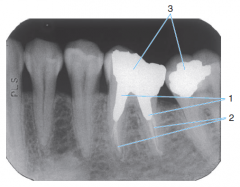
2 |
Gutta percha |
|
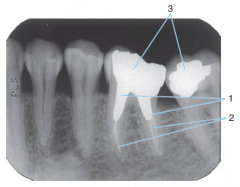
3 |
Amalgam Restorations |
|
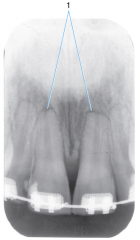
|
External root resorption from trauma due to orthodontic treatment |
|
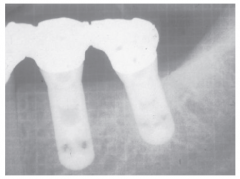
|
Implants |
|
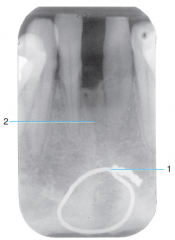
1 |
Surgical Wire |
|
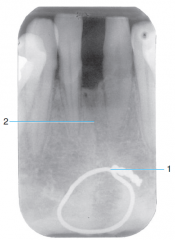
2 |
Fracture line |
|
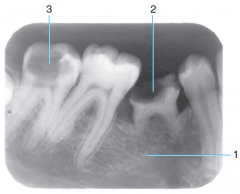
1 |
Congenitally missing tooth - second premolar didn't develop under primary second molar |
|
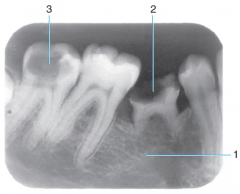
2 & 3 |
Severe Caries |
|

|
Mesiodens - small supernumerary tooth |
|
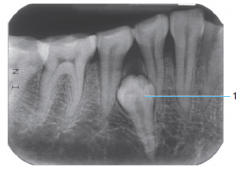
|
Imparted supernumerary premoalr |
|
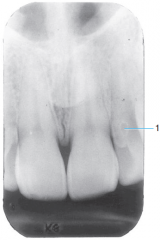
|
Dens in dente |
|
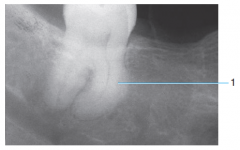
|
Hypercementosis |
|
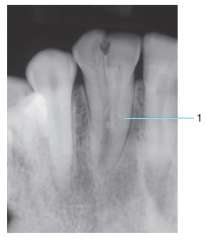
|
Fusion of teeth from gemination |
|
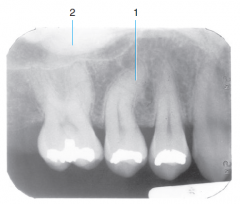
1 |
Dilaceration |
|
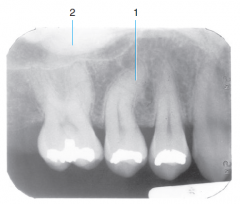
2 |
Torus palatinus |
|
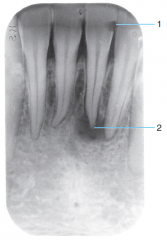
1 |
Distal Caries |
|
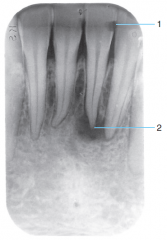
2 |
Periapical Lesion - abscess or granuloma |
|
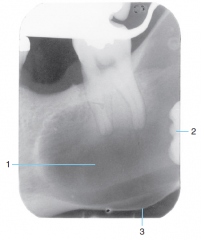
1 |
Dentigerous cyst |
|
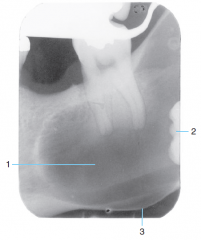
2 |
Impacted 3rd molar |
|
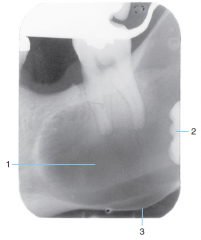
3 |
Expansion and thinning of the cortical bone of the mandible |
|
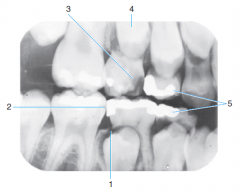
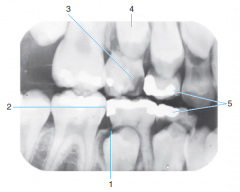
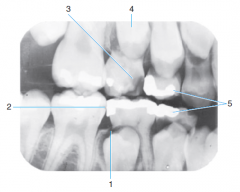
1 |
Follicular cyst around crown of unerupted second premolar |
|
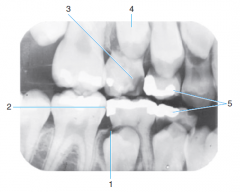
2 |
incipient caries on first permanent premolar |
|
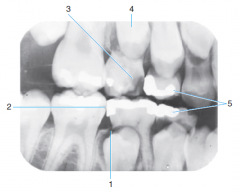
3 |
advanced caries on primary second molar |
|
4 |
erupting second premolar |
|
4 |
primary first molar about to be exfoliated |
|

|
Incisive canal cyst |
|
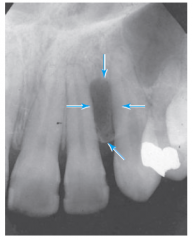
|
Internal resorption - widening of the pulp chamber |
|
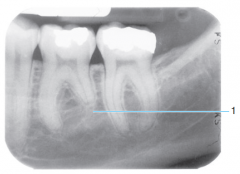
|
Globulomaxillary cyst |
|
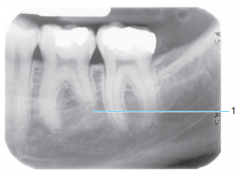
|
External (root) resorption |
|
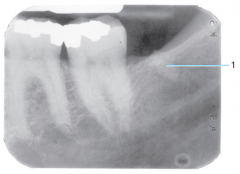
|
Retained root |
|
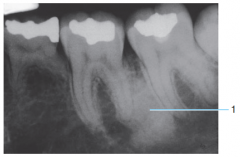
|
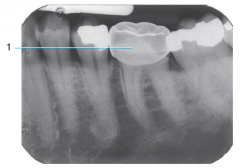
Condensing osteitis |
|
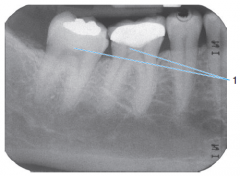
|
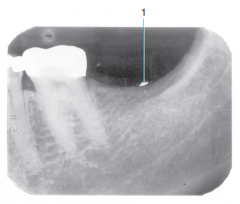
Pulp stones |
|
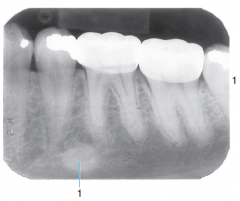
|
Osteosclerosis |
|

|
Sialolith |
|
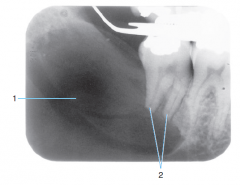
1 |
Ameloblastoma |
|
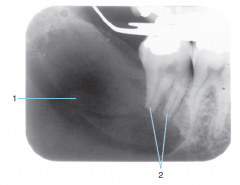
2 |
External Resorption (root) |
|
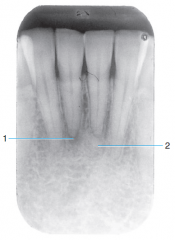
1 |
Periapical cemental dysplasia - Early stage development |
|
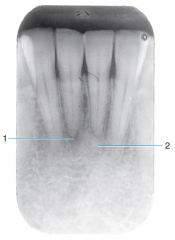
2 |
Periapical cemental dysplasia - Late stage development |
|
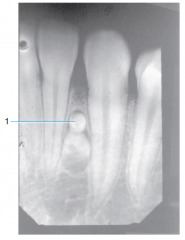
|
Odontoma |
|
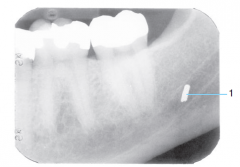
|
Foreign object - Broken Dental Bur |

