![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
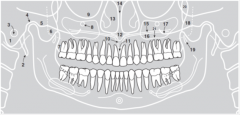
1 |
|
|
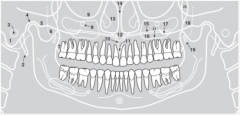
2 |
|
|
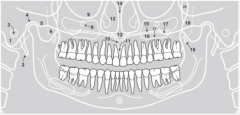
3 |
|
|
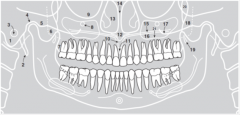
4 |
|
|
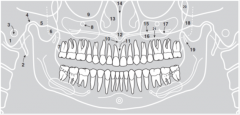
5 |
|
|
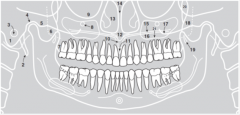
6 |
|
|
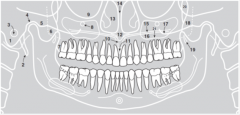
7 |
|
|
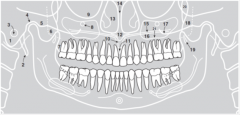
8 |
|
|
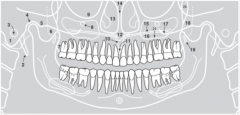
9 |
|
|
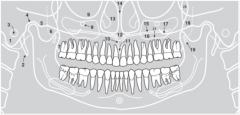
10 |
|
|
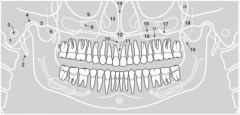
11 |
|
|
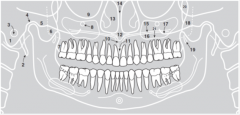
12 |
|
|
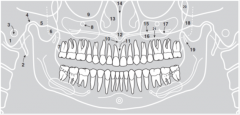
13 |
|
|
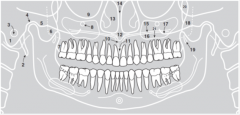
14 |
|
|
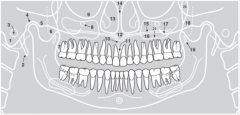
15 |
|
|
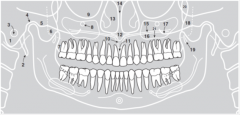
16 |
|
|
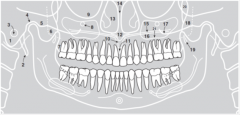
17 |
|
|
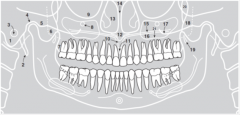
18 |
|
|
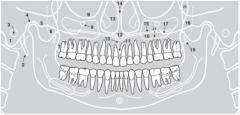
19 |
|
|
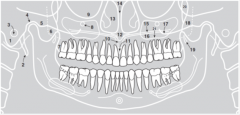
20 |
|
|
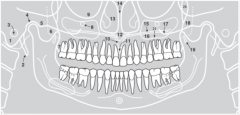
21 |
|
|
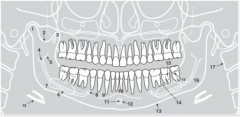
1 |
|
|
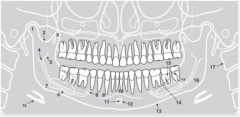
2 |
|
|
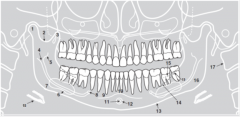
3 |
|
|
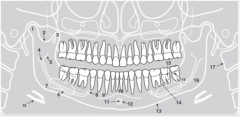
4 |
|
|
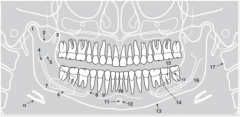
5 |
|
|
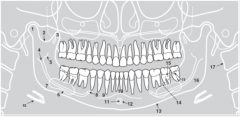
6 |
|
|
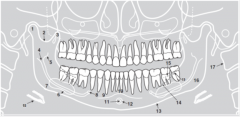
7 |
|
|
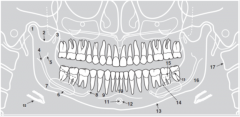
8 |
|
|
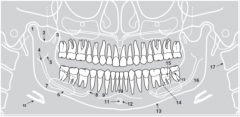
9 |
|
|
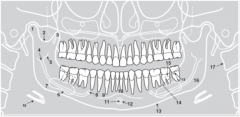
10 |
|
|
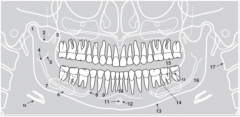
11 |
|
|
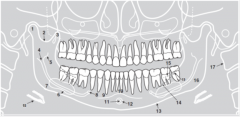
12 |
|
|
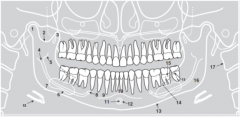
13 |
|
|
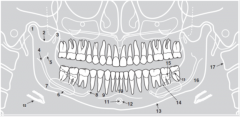
14 |
|
|
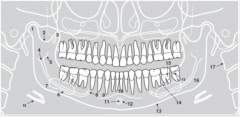
15 |
|
|
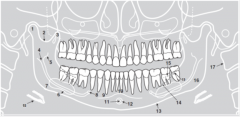
16 |
|
|
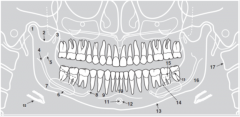
17 |
|
|
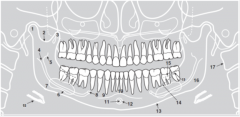
18 |
|
|
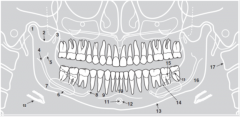
19 |
|
|
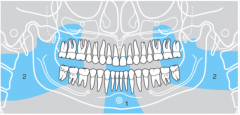
1 |
|
|
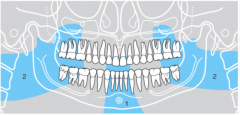
2 |
|
|
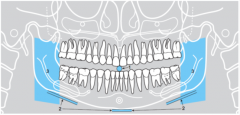
1 |
|
|
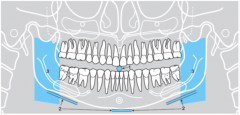
2 |
|
|
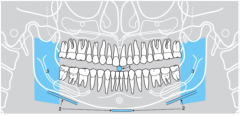
3 |
|
|
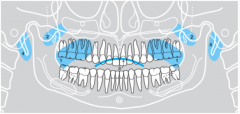
1 |
|
|
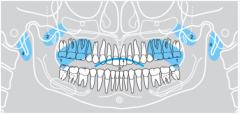
2 |
|
|
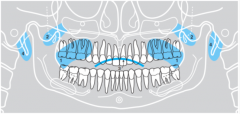
3 |
|
|
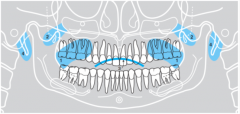
4 |
|
|
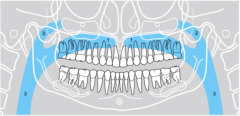
1 |
|
|
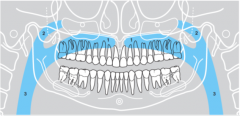
2 |
|
|
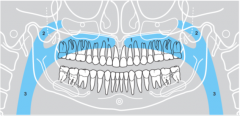
3 |
|

