![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the treatment for POAG? |
• Medical drugs • Incisional surgery • Laser surgery |
|
|
What are the types of drugs used to treat POAG? |
• Beta blockers (timolol) • Prostaglandin Analogues (Latanoprost) • Parasympathomimetics (Pilocarpine) • Adrenoceptor agonists (Brimonidine) • Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Acetazolamide) |
|
|
How do beta blockers work? |
• by blocking B2 receptors in the ciliary epithelium reducing aqueous humour production. |
|
|
Which beta blockers are regarded as non-selective? |
• Timolol • carteolol • levobunolol • metipranolol |
|
|
Which beta blocker is referred to as cardio-selective? |
Betaxolol |
|
|
What beta blockers have adverse reactions? |
• Few • Rare decreased corneal sensitivity • Rare conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis |
|
|
What are Beta blockers - adverse systemic reactions (cardiac)? |
• Blocking β-1 receptors may cause: – a reduction in heart rate – reduction in heart contractility – cardiac failure – arrhythmias – syncope – hypotension |
|
|
What are Beta blockers - adverse systemic reactions (bronchial)? |
Blocking beta-2 receptors: • constriction of the bronchioles resulting in - shortness of breath - wheezing - dyspnoea - bronchospasm |
|
|
What are Prostaglandin analogues mode of action? |
Latanoprost and travoprost: Increase in uveo-scleral outflow
Bimatoprost: increase in both trabecular and uveoscleral outflow |
|
|
What are Prostaglandin analogues adverse reactions? |
• Increase in brown pigment in the iris- permanent • darker, longer, curlier or thicker eye lashes • FB sensation • Conjunctival hyperaemia |
|
|
How do Parasympathomimetics (Cholinergic Agonists) (Miotics) work?
|
• Lower IOP by stimulating muscarinic receptors on the ciliary smooth muscle, thus opening the trabecular meshwork to increase aqueous outflow |
|
|
What are the adverse reactions to Parasympathomimetics? |
• ciliary spasm • headaches • vasodilation of conjunctival blood vessels • miotic causes dimming of vision • break down in the blood/aqueous barrier • need yearly dilation to prevent permanent miosis |
|
|
How do Adrenoceptor agonists work? |
Alpha-2 agonists lower IOP by reducing aqueous humour formatiom
• Brimonidine • Apracloidine |
|
|
What are the adverse reactions to Adrenoceptor agonists? |
• Conjunctival hyperaemia
|
|
|
How do Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors work? |
Lower IOP by blocking the enzyme carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary epithelial cells, thereby reducing aqueous humour formation |
|
|
Name some Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. |
• Acetazolamide • Brinzolamide • Dorzolamide |
|
|
What are the adverse reactions to Acetazolamide? |
• diuretic during the first few weeks of treatment • Paraesthesia (tingling in the extremities, especially hands and feet) • Taste disturbance • Headache • Fatigue
• dizziness • guessing or ringing in the ears |
|
|
What are the adverse reactions to Brinzolamide and Dorzolamide? |
– Foreign body sensation – Ocular hyperaemia – Bitter taste in the mouth |
|
|
What are the combination drugs available in the UK? |
Xalacom® – a combination of latanoprost with timolol0.5% Combigan® – a combination of brimonidine and timolol 0.5% Cosopt® – a combination of timolol 0.5% with dorzolamide 2% |
|
|
When is surgery offered to treat glaucoma? |
If the risk of losing sight through uncontrolled IOP is greater than the risk of sight loss through surgery, then surgery is offered |
|
|
What are the aims of surgical procedures? |
• To preserve (and if possible enhance) patients quality of life • Not going to bring back lost visual field, but if getting patient off topical treatment, that is an improved QoL |
|
|
What is filtration surgery? |
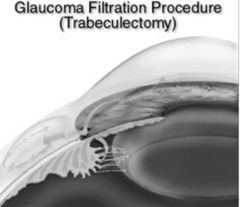
Creation of a new channel for aqueous outflow |
|
|
What are the glaucoma drainage devices? |
• Implanted devices that are designed to maintain an artificial drainage pathway
• This procedure is often chosen for patients at high risk of failure with trabeculectomy |
|
|
What types of laser treatment are used to treat gluacoma? |
• SLT (YAG) • Cyclodestruction • Penetrating Surgery • Non-penetrating surgery |
|
|
What is Angle Closure Glaucoma? |
• PACG – Acute, chronic, intermiitent
• Secondary – Pupil block – Anterior pulling – Posterior Pushing |
|
|
What is Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma? |
Significant obstruction of functional trabecular meshwork by peripheral iris* that results in optic neuropathy
*In absence of secondary pathological process |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of acute angle closure? |
• Symptoms sudden & severe • Marked pain, follows trigeminal distribution and associated with nausea, vomiting
• Ciliary flush and periph conj congestion (red eye)
• Blurry vision (corneal oedema)
• Mid-dilated pupil |
|
|
What is your management for acute angle closure? |
Immediate referral |
|
|
What is the clinical assessment for acute angle closure? |
• Pen torch? • Van-Herick • Gonioscopy |
|
|
How does PACG differ from PAC? |
• Can only be said to have glaucoma persè if there is evidence of optic nerve damage
• PAC is an ocular emergency and presents as an acute episode |
|
|
What is the classification for PACG? |
• Pupillary block
• Anterior non-pupillary block – Plateau iris syndrome/ peripheral iris crowding
• Lens-related
• Factors behind the lens |
|
|
What is the mechanism of pupil block? |
• most common form of PACG • Pressure of iris on anterior lens • impedance to flow of aqueous from posterior to anterior chamber • Iris bombé |
|
|
What is Plateau iris? |
• Smaller percentage of PACG • Flat iris extending into AC • Abnormal insertion of iris into ciliary body &/or anteriorly rotated ciliary body distorting peripheral iris • Wide open anterior chamber – Iris blocking trabecular meshwork |
|
|
What is pigment dispersion syndrome? |
• IOP elevation • GON • Melanin iris pigment epithelium • Aqueous • Deposit in TM |
|
|
What is Pseudoexfoliative glaucoma?
|
• Raised IOP and GON
• Secondary to PXF (syndrome) • Abnormal protein epithelium anterior segment (lems, CB, iris, S Canal, cornea endo)
• Iris atrophy |
|
|
What is the management for acute closure attacks? |
Lower IOP Miotic therapy- break pupillary block Surgery- iridoctomy |

