![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Animals are classed as ......... or ......... . |
1. ectotherms 2. endotherms |
|
|
Give two examples of ectotherms. |
Reptiles and fish.
|
|
|
Give two examples of endotherms. |
Mammals and birds. |
|
|
How do ectotherms control their body temperature compared to endotherms. |
|
|
|
What are ectotherms and endotherms internal body temperature dependant on? |
|
|
|
Explain if temperature levels affect activity levels in ectotherms and endotherms.
|
|
|
|
State three mechanisms to reduce body temperature. |
|
|
|
How does sweating lower body temperature? |
|
|
|
How do hairs lying flat lower body temperature? |
|
|
|
How does vasodilation lower body temperature? |
|
|
|
State five mechanisms to increase body temperature. |
|
|
|
How does shivering increase body temperature? |
|
|
|
How does less sweat increase body temperature? |
|
|
|
How do hairs stand up increase body temperature? |
|
|
|
How does vasoconstriction increase body temperature? |
|
|
|
How do hormones increase body temperature? |
|
|
|
In endotherms, the body ......... in mammals is maintained at a ......... level by a part of the brain called the .......... |
1. temperature 2. constant 3. hypothalamus |
|
|
The hypothalamus receives information about ........ from the .......... . |
1. temperature 2. thermoreceptors |
|
|
Thermoreceptors in the ......... detect internal temperature. |
hypothalamus |
|
|
Thermoreceptors in the ......... detect external temperature. |
skin |
|
|
What are thermoreceptors in the skin called? |
Peripheral temperature receptors |
|
|
Give a basic overview of the path of the impulse from the thermoreceptors. |
|
|
|
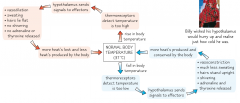
Draw a homeostasis cycle for the control of body temperature. |
|

