![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
energy that you can see |
light |
|
|
"To take in" the process by which some materials take in light energy and change it to heat energy |
absorption |
|
|
"bounce off" the bouncing of light off a surface |
reflection |
|
|
"Reflects light" - a smooth surface that forms images by reflecting light |
mirror |
|
|
"flat mirror" - a mirror that is flat |
plane mirror |
|
|
"Curves inward" - a mirror that curves inward like a bowl and is thicker at the edges |
concave mirror |
|
|
a mirror that curves outward and is thicker in the middle |
Convex mirror |
|
|
the bending of light when it passes from one material into another |
Refraction |
|
|
a clear, or see through, object that separates white light into all the colors of the rainbow |
prism |
|
|
a clear material that has at least one curved surface. It refracts light. |
lens |
|
|
These people wear convex lens in their glasses. They can not see up close. |
Farsighted People |
|
|
These people wear concave lenses in their glasses. They can not see far away. |
Nearsighted People |
|
|
Allows MOST light to pass through |
transparent |
|
|
Some light passes through |
translucent |
|
|
No light can pass through |
opaque |
|
|
Have the ability to give off light energy |
luminous |
|
|
the transfer of heat from a warmer object to a cooler object |
conduction |
|
|
negative or positive force that results from the gain or loss of electricity |
charged |
|
|
a looping path of material that conducts electricity |
circuit |
|
|
a complete system of electrical parts that are unbroken |
closed circuit |
|
|
transfers heat and electricity easily - These will heat up easily |
Conductors |
|
|
movement in electrons through conductors such as wire |
current |
|
|
energy of moving charges in atoms |
electricity |
|
|
metal objects, wrapped in wire, that become magnetic by receiving electrical charge |
electromagnets |
|
|
negatively charged particles that move in an orbit outside an atoms' nucleus |
electrons |
|
|
doesn't transfer heat or electricity easily. These objects keep heat in. |
Insulators |
|
|
system of electricity that are broken or incomplete |
open circuit |
|
|
type of electrical circuit where there are more than one path for travel |
parallel circuit |
|
|
electrical circuit where current travels only on a single path |
series circuit |
|
|
charge that builds up when two things rub together "Friction" |
static electricity |
|
|
the transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another |
heat |
|

|
Closed Circuit Image |
|
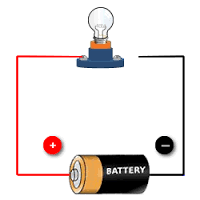
|
Open Circuit Image |
|

|
Parallel Circuit Image |
|

|
Series Circuit Image |

