![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Does zygosity change |
No |
|
|
|
Zygosity depends on |
How many eggs are fertilized (1 or 2) |
|
|
|
Dyzygotic come from |
2 eggs |
|
|
|
Dizygotic aka |
Fraternal twins |
|
|
|
Most common type of twins |
Dizygotic |
|
|
|
What are the genders in dizygotic twins |
Same or different -2 types |
|
|
|
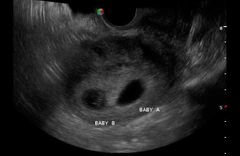
Dizygotic twins have |
2 of everything-placenta may be fused
And thick membrane between sacs |
|
|
|
How can dizygotic twins be confirmed |
With different genders |
|
|
|
Dizygotic twins are always |
Dichorionic diamniotic |
|
|
|
Monozygotic twins aka |
Identical twins |
|
|
|
Monozygotic twins |
1 egg that divides |
|
|
|
What are the genders at monozygotic twins |
Always the same -mono gender |
|
|
|
How many chorions amnions and placenta are there with monozygotic twins? |
Depends on when the egg divides |
|
|
|
Monozygotic twins can be |
Di/di Mono/di Mono/mono |
|
|
|
When can monozygotic pregnancy give di/di type |
When the morula divides during the first 4 days |
|
|
|
When can monozygotic pregnancy give mono/di type |
When morula dividesduring first week |
|
|
|
When can a monozygotic pregnancy give mono/mono type |
When morula divides during the second week |
|
|
|
What happens if morula divides after day 13? |
Conjoined twins |
|
|
|
In what type of twins placenta may be fused |
Both types of di/di We have 2 placentas only in this pregnancy |
|
|
|
Can we tell from US if di/di type comes from dizygotic or monozygotic |
They look exactly the same except if the fetuses have different gender that means its a dizygotic pregnancy |
|
|
|
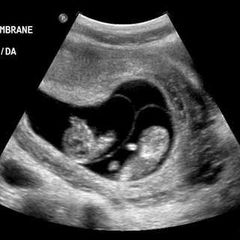
Monochorionic/ diamniotic will habe |
One sac/ chorion One placenta 2 amnions-thin 2 yolk sacs |
|
|
|
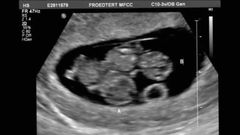
Monochorionic monoamniotic will have |
1 sac 1amnion 1placenta 1yock sack |
|
|
|
Most common type of monozygotic twins |
Mono/di |
|
|
|
Least common monozygotic twins |
Mono/mono |
|
|
|
US sign for dichorionic pregnancy |
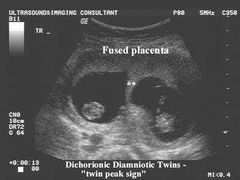
Lambda Delta Twin peak |
|
|
|
Clinicals sign for multiple gestation |
Increased hCG Increased maternal serum AFP Increased uterine size-large for dates |
|
|
|
Eval of chorionicity and amnionicity is best done in |
First trimester |
|
|
|
Vanishing twin US findings |
Faiure to demonstrates multiple sacs on seria sonograms Failure of sac growing in twin gestation Irregular marginated sac
|
|
|
|
What is TTTS |
Abnormal vascular anastamoses in the shared placenta that shunt blood away from the donor to the recipient twin |
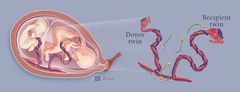
|
|
|
TTTS AKA |
Poly-Oli sequence |
|
|
|
TTTS has increased morbidity for |
Mom And both twins |
|
|
|
Treatments for TTTS |
Amnioreduction Fetoscopic lases photocoagulation of chorionic plate vessels |
|
|
|
What is the difference in weight in TTTS |
20% in weight Or AC difference of >20mm
Mnemonic starts with T |
|
|
|
What do we see in the donor twin |
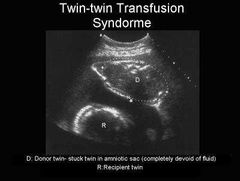
Oligo Small for dates Stuck twin -no fluid |
|
|
|
What do we see in the recipient twin |
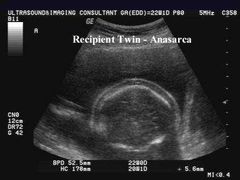
Poly Poly Hydrops edema Large for dates |
|
|
|
In what pregnancy does TTTS happen |
Monochorionic( that share one placenta) |
|
|
|
Conjoined twins happen |
If morula divides after day 13 |
|
|
|
Thoracopagus |
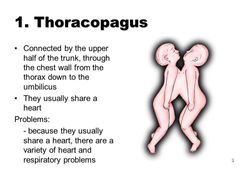
Joined at thorax- most common |
|
|
|
Omphalopagus |
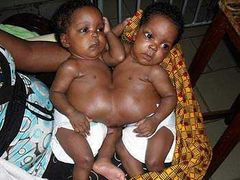
Xiphoid to umbilicus |
|
|
|
Pyopagus |
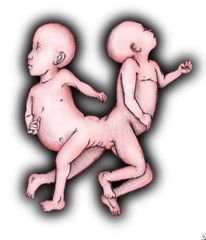
Sacrum |
|
|
|
Ischiopagus |
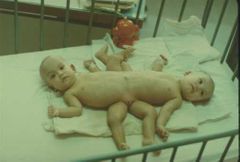
Ischium/pelvis |
|
|
|
Craniophagus |
Head |
|
|
|
Most common form of conjoined twins |
Thoracopagus |
|
|
|
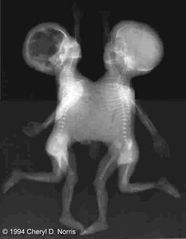
Thoraco-omphalopagus |
|
|
|
|
TRAP sequence is |
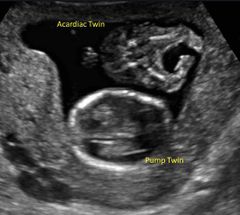
Twin reversed arterial perfusion
Acardiac twinning Parabiotic twining |
|
|
|
TRAP |
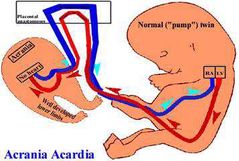
Abnorma anastomoses in shared placenta Artery will supply blood to acardiac twin |
|
|
|
Acardiac twin will |
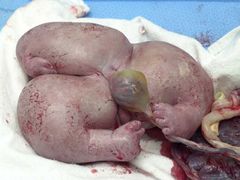
Move Have no heart No head Severe hydrops Edema
Mass of tissue |
|
|
|
Donor twin in TRAP |
Will pump hard for the acardiac twin and will suffer from congenital heart failure |
|
|
|
Fetus papyraceus |
Dead fetus in first trimester and maintained in uterus throughout pregnancy |
|
|
|
Vanishing twin |
Death of one twin and reabsorption |
|
|
|
Death of one twin usually affects the other twin in |
Monochorionic twins |
|
|
|
Early death of one twin in monochorionic twins will cause |
Death of the other twin usually |
|
|
|
Late death of one twin in monochorionic twins can cause |
Life threatening issues for the other twin such as twin embolization syndrome |
|
|
|
Twin embolization syndrome |
Vascular products that travel from demized twin to the surviving twin and causes abnormalities in CNS, GU, GI |
|
|
|
Which term relates to nr of placentas |
Chorionicity Placentation |
|
|
|
TRAP and TTTS are both from |
Abnormal connections in the shared placenta in monochorionic twins |
|
|
|
Zygosity shows only |
How many eggs do we start with |
|
|
|
Chorionicity shows |
How many houses will we have (Remember each house will also have the curtains too=amnion) |
|
|
|
Nr of chorions will equal |
Nr of placentas -may be fused |
|
|
|
Nr of yolk sacs equals |
Nr of amnions |
|
|
|
Twin peak sign is |
Extension of the placenta separating the chorions |
|

