![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the four bones of pelvis |
Sacrum Coccyx 2 innominate Ilium and ischium |
|
|
Name the 3 layers of the uterus |
Serosa (perimetrium) Myometrium Endometrium |
|
|
What is the normal size of the ovary in a woman in her reproductive years |
3x2x1 cm |
|
|
Identify the portions of the Fallopian tubes |
Interstitial Isthmus Ampulla Infundibulum |
|
|
The part of the Fallopian tube most lateral to the uterus called |
Infundibulum |
|
|
The mature follicle is known as |
Graafian follicle |
|
|
Patient prep for transabdominal pelvic ultrasound |
32 oz of water finished 1 hour prior to exam |
|
|
What is sonohystography |
Technique in which infusion of 25-30 ml of sterile saline into endometrial cavity enhances visualization by either transabdominal or endovaginal |
|
|
When would perineal ultrasound be useful |
When endovaginal is contraindicated |
|
|
When is endovaginal ultrasound contraindicated |
If patient has never been sexually active |
|
|
What is the diagnostic purpose of 3D imaging |
Evaluate 1st trimester embryo Provides detail topographical image Face, digits, limbs and neural tube defects |
|
|
From where to where do we measure the uterus when in sag |
Anterior to posterior Fundus to cervix |
|
|
The part of Fallopian tube closest to uterus is called |
Interstitial (intramural) |
|
|
Which vessels are useful in identification of the ovaries |
Iliac |
|
|
Where are the iliac vessels located to ovaries |
Posterior |
|
|
Which ligament anchors uterine cervix to sacrum |
Uterosacral ligament |
|
|
What is the widest and longest part of the Fallopian tube called |
Ampulla |
|
|
Where does fluid first collect in the pelvic cavity |
Pouch of Douglas |
|
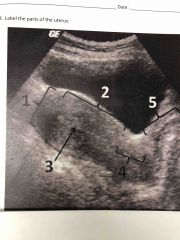
Front (Term) |
1 fundus 2 body 3 endometrium 4 cervix 5 vaginal fold |
|
|
6 different parts of the female pelvic anatomy |
Uterus Fallopian tubes Surrounding spaces Ligaments Bony pelvis Ovaries |
|
|
4 regions of uterus |
Fundus Corpus Isthmus Cervix |
|
|
Explain nulliparous |
Someone who has never been pregnant |
|
|
Normal nulliparous uterine measurement |
8x5x3 cm |
|
|
Name the junction of the cervical canal and the vagina is called what |
External OS |
|
|
What part of Fallopian tube is most lateral to the uterus |
Infundibulum |
|
|
What is aka for interstitial |
Intramural |
|
|
What’s the name of the Fallopian tube closest to uterus |
Interstitial |
|
|
Name the tortuous and longest part of the Fallopian tube |
Ampulla |
|
|
Normal measurement of ovary |
3x2x1 cm |
|
|
List reasons for bladder filling |
Pushes bladder superiorly Decreases angle of incidence Pushes loops of bowels out of view Provides acoustic window for uterus and adnexa |
|
|
List reasons for bladder emptying |
Transvaginal |
|
|
3 phases of menstrual cycle |
Menstrual (1-5) Proliferative (6-14) Secretory (15-28) |
|
|
Which phase of menstrual cycle is mainly under the influence of estrogen |
Proliferative phase |
|
|
What does GnH stand for |
Gonad releasing hormone |
|
|
Which gland secretes GnH |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
With a rise in GnH what other gland is stimulated and what hormone does it release |
Anterior pituitary FSH |
|
|
Which hormone cause ovulation to occur |
LH |
|
|
What hormone does the corpus luteum cyst produce |
Progesterone |
|
|
Days between ____-____ of menstrual cycle that the endometrium is at its thickest |
Secretory phase days 15-28 |
|
|
What’s the name of the dominant follocle |
Graafian follicle |
|
|
Diethylstilbestrol (DES) taken by a pregnant mother is known to put daughters of those patients at higher risk for what |
T-shaped uterus Ectopic pregnancy Premature labor Uterine anomalies |
|
|
What’s normal endometrium thickness in proliferative phase |
5-11 mm |
|
|
How do you measure the uterus in sag |
Anterior to posterior Cervix to fundus |
|
|
Birconuate uterus happens with the lack of fusion of what |
Müllerian ducts |
|
|
Explain hematocolos |
Accumulation of menstrual blood in vagina |
|
|
What plane is most helpful to assess patient with bicornis uterus |
Transvaginal in coronal plane |
|
|
What does adenomyosis invade |
Myometrium |
|
|
What can cervical fibroids be mistaken for |
Cervical carcinoma |
|
|
What does a subserosal leiomyoma distort |
Uterine contour |
|
|
What is the procedure that can be helpful in identification of endometrial polyps |
Sonohysterography |
|
|
Leiomyomas is found in which patient population |
Afro american |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of leiomyomas |
Pelvic pain Menorrhagia Asymptomatic Bladder or rectum pressure Infertility Spontaneous abortion Dysmenorrhea with heavy menses |
|
|
Adenomyosis is most commonly mistaken for or misdiagnosed as |
Leiomyoma |
|
|
What is a krukenberg tumor |
Carcinoma of ovary Secondary tumor of the ovary that has moved (METS) from GI tract |
|
|
If you find a mass, what is your responsibility as a sonographer |
Measure, describe, define location Provide thorough and systematic exams |
|
|
What are some characteristics of stein-leventhal syndrome |
Infertility Obesity Oligomenorrhea Hirsutism |
|
|
Explain dermoid tumor |
Cystic lesion w/echogenic components and internal nodularities Contains: fluid, fat, teeth or hair |
|
|
If you find a malignant tumor of the ovary, what else should you look for |
Gastrointestinal tract and breasts Other tumors, fluid in posterior cul de sac Matted loops of bowel |
|
|
Could you list 3 functional cysts of the ovary |
Corpus luteum Theca luteum cysts Graafian follicle |
|
|
In relation to screen orientation, in transvaginal us scanning, the top of the screen relates to ________ (body direction) |
Inferior |
|
|
With sonohysterography what is introduced into the endometrial cavity |
25-30 ml of sterile saline |
|
|
What does DUB stand for |
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
|
|
What does the term polymenorrhea mean |
Frequent menstrual bleeding less than 21 days apart |
|
|
What portion of the uterus can be well evaluated using transperineal scanning |
Lower uterine segment Cervix |
|
|
75 year old female patient presents for US with a hx of vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain for one week. Upon exam, sonographer visualizes uterus measuring 8.5x4.5x4.2 cm. The endometrium measures 10 mm in thickness. This is suggestive of what pathology |
Endometrial carcinoma |
|
|
57 year old female patient presents with vague gastrointestinal symptoms, pelvic pain, and a lower backache. On US, a cystic mass with septations and low level echoes measuring 10 cm is visualized in left adnexal area. Most likely interpretation of these findings would be |
Serous cystadenocarcinoma |
|
|
9 year old female is admitted to ER complaining of nausea and acute onset of pain in RLQ. Pain commenced one hour ago just after gymnastics class. What is strong possibility dx |
Ovarian torsion |
|
|
Signs and symptoms for hematocolpos |
Amenorrhea Pelvic pain |
|
|
signs and symptoms of Endometrial carcinoma |
Bleeding or discharge after menopause |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of torsion of the ovaries |
Lower abdominal pain more than 48 hours, fever, lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of Serous cystadenocarcinoma |
Abdominal pain, distension, gastrointestinal symptoms, abdominal girth, pelvic pressure |
|
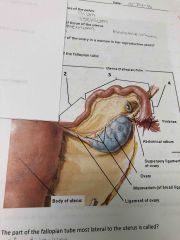
|
1. Interstitial 2. Isthmus 3. Ampulla 4. Infundibulum |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of Stein-Leventhal Syndrome |
Obesity Menstrual abnormalities (absent period or infrequent) Virulization with hirsutism Infertility |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of ovarian torsion |
Acute onset of pelvic pain Nausea Vomiting *most commonly found in gymnast |
|
|
“Under goes rapid growth spurt” |
Leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
What days is endometrial lining thickest |
14-28 |

