![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
White Fiber |
Type 2 a & b skeletal fiber, engaged in anaerobic exercise |
|
|
Red fiber |
Type 1 skeleton fiber, engaged during anaerobic exercise. |
|
|
Lypolysis |
Breakdown and release of fatty acids from stored triglycerides |
|
|
Anaerobic exercise |
Sugar burning exercise, no oxygen. All out sprint or 4-6 rep exercise is this |
|
|
Aerobic exercise |
With oxygen. 90% of ATP is produced in mitochondria from beat oxidation of fatty acids...only possible if oxygen present. Example: incline tredmil walking while holding conversation |
|
|
Glycolysis |
Breakdown of glucose through 10 step process to pyruvic acid. Occurs during anerobic exercise (sugar burning, intense short exercise) |
|
|
High intensity cardio exercise |

|
|
|
Low intensity cardio |
Intensity too low to help, minimal fat burning. |
|
|
THR |
Target heart rate. Max HR: (220-age) Target HR (moderate) = 50-70% of max Target HR (intense) = 70-85% of max |
|
|
Interval training |
Red line (~170bpm) hr, completely recover to 110bpm hr. Repeat for 30min. Optimal fast-twitch (white, or type 2a and b, fiber) |
|
|
Slow twitch fiber training |
Treadmill in incline, stair stepper, deep sand walking. Make sure not to be out of breath, minimum of 30min exercise. The more muscles you move, the more fuel must be used by fat |
|
|
Free radicals |
Reactive atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons making unstable molecule. Normal biproduct of metabolism...also obtained by cigarette smoke, smog, etc. |
|
|
Antioxident |
Molecule (mostly vitamin A, C and E) that donates an electron to neutralize the free radical and provide stabalization. Bodyguards! |
|
|
Vitamins |
Organic substance essential to sustain human life, must be regularly supplied in small amounts. 2 types: water soluble (vitamin B and C) and fat soluble (A,D,E,K) |
|
|
Minerals |
Nutrients in body and food. Inorganic elements essential for mental and physical health, essential to survive |
|
|
R.D.A |
Recommended daily allowance of essential nutrients of protien, vitamins and minerals.
Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academy of Sciences National Research Council.
Split into: 1) infants 2) children 3) adults 4) pregnant and lactating women Set so to provide sufficient intake of nutrients so the average person in US can survive for brief period of nutrient inadequacy. |
|
|
Vitamin C |
Water soluble. Occasionally a coenzyme.
Mostly facilitates production and maintenance of protien collagen. Collagen forms all connective tissues in the body, and is scar tissue over wounds and reinforced fractures. It also produces white blood cells. |
|
|
Endocrine system |
Hormones. Made up primarily of: hypothalamus.pituitary gland.thyroid.parathyroids.adrenal glands.pineal body.reproductive glands (which include the ovaries and testes)pancreas. |
|
|
Hypoglycemia |

Low blood sugar below 70mg/dl clinically, below 50-60mg/dl, but too low for optimal homeostasis.
Side effects: nervousness, hunger, headaches, weakness.
Body stores fat (fat --> energy takes time and energy) and burnes other stored fuel, like amino acids in muscle! |
|
|
Hyperglycemia |

Blood sugar above 120mg/dl. Clinically, above 140mg/dl, which is too high for optimal homeostasis.
Side effects: gain fat, sleepiness, lethargy.
|
|
|
Glucagon |
a hormone formed in the pancreas that promotes the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver.
Glycogen is stored glucose. |
|
|
Glycogen |
a substance deposited in bodily tissues as a store of carbohydrates. It is a polysaccharide that forms glucose on hydrolysis. |
|
|
HCl |
Hydrocholoric Acid. Clear corrosive liquid in stomach, release when we eat. Breaks down food & releases other enzymes to help digestion |
|
|
Hypothalamas |
Thermostat. controller of pituitary gland, which directs the functions of the other glands in the endocrine system. Secreates: TRH GnRH GHRH CRH |
|
|
TRH |
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Hypothalamus - TRH - Pituitarry- TSH - Thyroid -T3,T4 - Metabolism |
|
|
GnRH |
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Hormones in reproduction. All start with hypothalmus-GnRH-PituitaryMale: hypothalmus-GnRH-Pituitary Male: -LH-Testes-Testostrone-growth Female FSH-Follicle-Estrogens LH-Corpus Luteum- Progesrerone |
|
|
GHRH |
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone. Stimulates creation and secretion of growth hormone for: Bone growth Muscle building Developing Hypothalamus - GHRH -Pituitary -GH - Liver - IGH-I |
|
|
CRH |
Cortictrophin Releasing Hormone Leads to chain neccessary for proper adrenal gland function. Energy and stress control Hypothalamus - CRH - Pituitary - ACTH - Adrenal Gland (cortex) - cortisol or adrenal gland (medulla) - epineephrine (adrenaline) and Norepinephrine. |
|
|
Pineal Gland |
Sleep controller. Synthezises and secretes melatonin. More in dark environments; light inhibits its secretion. |
|
|
Thyroid Gland |
The Metabolism. Synthesizes and stores hormones to regulate: Heart Rate Blood pressure Body temperature Rate at which food is converted to energy |
|
|
Adrenal gland |
Control heart rate, blood pressure and how body uses food for energy. Releases cortisol (stress fighting and antiinflame hormone), adrenaline and its opposite |
|
|
Pancreas |
Blood sugar stabilizer. Exocrine tissue secretes digestive enzymes for nutrients, endocrine tissue secretes insulin and glucagon. |
|
|
Insulin |
Lowers blood sugar levels using it as energy & storing, by opening cells to let in glucose.
- stimulating liver and muscles to store glucose as glycogen and make protiens from amino acids (anabolism) - stimulating fat cells to form fats from fatty acids and glycerol - inhibits liver and kidney from making glucose (Gluconeogenesis) |
|
|
Glucagon |
Increases blood sugar levels by acting on the same cells as insulin with the opposite effects: - stimulates liver and muscles to break down stored glycogen for use (Glycogenolysis). - stimulates Liver and kidney to make glucose (gluconeogenisis) |
|
|
Nervous system |

|
|
|
Digestive System |
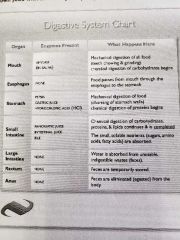
|
|
|
Triglycerides |
Type of fat; made of glycerol (fat backbone) and 3 fatty acids. Opposed to cholesterol |

