![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phenylketonuria |
Elevation of serum phenylalanine.
Results in mental retardation Children are tested at birth Autosomal recessive trait most common in whites Tx - dietary restriction of phenylalanine |
|
|
Tay-Sachs Disease
|
Autosomal recessive disease resulting in missing enzyme that leads to accumulation of gangliosides -> child develops symptoms at 6 months, missing developmental milestones - > dies usually by age 5
|
|
|
Mitochondrial Disorders
|
Over 100 forms, each with different levels of disability.
Genetic or spontaneous mutations in DNA lead to impaired mitochondria. s/s - loss of muscle coordination, muscle weakness, visual and hearing problems, learning disabilities, heart, liver, kidney diease, respiratory neuro, GI disorders, dementia. |
|
|
Wilson's disease
|
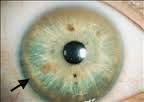
Rare inherited disorder - autosomal recessive
Defect in body's ability to metabolize copper Accumulates within brain, liver, cornea, kidney, and other tissues. Symptoms normally appear by age 6 with a ring around iris. |
|
|
Medical conditions which may cause low bone mass
|
Cushing's syndrome, osteomalacia, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyrdoism, celiac disease, RA, renal failure, hypogonadism, osteogenesis imperfecta
|
|
|
Cushing's Syndrome
|
Too much cortisol
Adrenal dysfunction s/s - hyperglycemia, growth failure, truncal obesity, purple abdominal striae, moon shaped face, buffalo hump posteriorly at the base of the neck, weakness, acne, hypertension, male gyno. Mental changes include depression, poor concentration, memory loss Tx - pharmacological intervention, radiation, chemo, surgery |
|
|
Paget's Disease
|
Heightened osteoclast activity. Excessive bone formation lacks true structural integrity.
Large, weak bone Tx - pharmacology; weight control, exercise, cardiac fitness |
|
|
Metabolic Alkalosis
|
pH >7.45
Commonly occurs after continuous vomiting, ingestion of antacids or other alkaline substances, duiretic therapy.. s/s - nausea, diarrhea, prolonged vomiting, confusion, muscle fasciculations, cramping, convulsions Tx - manage underlying cause, give pt potassium chloride |
|
|
Metabolic Acidosis
|
pH <7.35
Commonly occurs with renal failure, lactic acidosis, starvation, diabetic or alcoholic ketoacidosis, severe diarrhea, or poisoning. s/s hyperventilation, vomiting, headache, weakness/malaise, can induce coma/death if untreated Tx - manage underlying cause; correct electrolyte imbalances, administer sodium bicarbonate |
|
|
Islets of Langerhans
|
Hormone-producing cells of the pancreas
|
|
|
Measureing bone mineral density
|
Measured by dual energy xray absorptiometry.
Expressed as t-score (compared to healthy adult) and z-score (compared to age adjusted adult of the same gender) T score = -1 to -2.5 SD - osteopenia = -2.5 or lower = osteoporosis = as above with hx of fractures = Severe osteoporosis |
|
|
Addison's Disease
|
Hypofunction of adrenal cortex -> too little cortisol and aldosterone
s/s include widespread metabolic dysfunction and electrolyte imbalance. Weight loss, hypotension, shock, death |
|
|
Grave's disease
|
Most common cause of hyperthyroidism
- Autoimmune disease where antibodies stimulate thge thyroid gland - s/s include enlargement of thyroid gland (goiter), heat intolerance, nervousness, weight less, tremor, palpitations - tx - pharmacology, radiation or surgical removal of thyroid |
|
|
DM type 1
|
Pancreas fails to produce enough insulin.
Normally diagnosed in childhood but can occur at any age Also known as insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes Ketoacidosis more common in type 1 than type 2 |
|
|
DM type 2
|
Typical onset is over 40
Body has a resistance to insulin Obesity is common |
|
|
Normal blood glucose
|
70-130 g/dl before meal
<180 after meal |
|
|
Ketoacidosis
|
More common in DM type 1.
Hyperglycemic reaction When blood glucose is >180-200, s/s appear including thirst and frequent urination. Progresses to life-threatening condition (ketoacidosis) with s/s including fruiting breath, dry mouth, dyspnea, nausea/vomiting, confusion, eventual LOC |
|
|
Hypoglycemia
|
When blood glucose <70 mg/dl, pt will c/o hunger, sweating, dizziness, clumsiness, headache that will progress to LOC.
May occur during exercise Give pt glucose or other carb-rich substance |
|
|
Which structure produces bile?
Stores bile? |
Produces - liver
Stores - gallbladder |
|
|
Rehab considerations for GI patients
|
Recognize electrolyte imbalances.
Increased risk of muscle cramping. Orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
Kehr's sign
|
he occurrence of acute pain in the tip of the shoulder due to the presence of blood or other irritants in the peritoneal cavity when a person is lying down and the legs are elevated. Kehr's sign in the left shoulder is considered a classical symptom of a ruptured spleen.[1] May result from diaphragmatic or peridiaphragmatic lesions, renal calculi, splenic injury or ruptured ectopic pregnancy
|
|
|
Diverticulitis
|
Pouch like protrusions in the colon
Bloating, cramping, constipation |
|
|
Hepatitis A
|
Transmitted by close personal contact.
Presents with flu-like symptoms. Does not progress to chronic disease or cirrhosis of the liver. |
|
|
Hepatitis B
|
Virus that affects the liver and its function. 10% of cases become chronic.
Transmitted by needles, intercourse, blood/semen exposure, maternal-fetal. Immunization available |
|
|
Hepatitis C
|
Leads to chronic liver disease and eventual failure (in 50% of cases.
Transmitted by needles, intercourse, blood/semen exposure, maternal-fetal. No immunization |
|
|
Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis
|
Gallstones
R upper quadrant pain Often symptomatic |
|
|
Pharmalogical intervention for GERD / dyspepsia
|
Antacids
H2 Receptor Blockers - bind specifically to histamine receptors Proton Pump Inhibitors |
|
|
Anticholinergics
|
Given for gastric ulcers
-Decrease release of gastric acid |
|
|
Left upper quadrant pain - etiologies
|
Gastric ulcer
Perforated colon Pneumonia Spleen injury/rupture Aortic aneurysm |
|
|
Right upper quadrant pain - etiologies
|
Hepatomegaly
Duodenal ulcer Cholecystitis Pneumonia Hepatitis Biliary stones (gallstones) |
|
|
Left lower quadrant pain - etiologies
|
Perforated colon
Ileitis Sigmoid diverticulitis Kidney stone Ureteral stone Intestinal obstruction |
|
|
Right lower quadrant pain - etiologies
|
Kidney stone
Ureteral stone Meckel diverticulum Appendicitis Cholecystitis Intestinal obstruction |
|
|
Transmission of visceral pain
|
Transmitted by ANS. Helps differentiate musculoskeletal pain from visceral pain if accompanied by nausea, vomiting, pallor, sweating.
|
|
|
Endometriosis
|
Development of endometrial tissue (normally lines uterus) in extrauterine locations.
Moderate to severe lower abdominal pain Tx - myofascial release, relaxation exercises, TENS; surgery, total hysterectomy, oral contraceptives |
|
|
Renal failure
|
Typically occurs secondary to DM or hypertension.
s/s include nausea, vomiting, lethargy, weakness, anorexia, GI ulcer, sleep disorders, headache, peripheral neuropathy, anemia, pruritus (itching), osteomalacia, ecchymosis, pulmonary edema, seizures, coma May require dialysis |
|
|
Rehab considerations for patients with renal failure / dialysis
|
- Modify tx based on fluid and electrolyte status
- Recognize patient's abilities post-dialysis and potential for dehydration and hypotension - Monitor vital signs closely - Energy conservation techniques should be incorporated |
|
|
Bladder irritants
|
Carbonated, caffeinated, and alcoholic beverages
Spicy foods Citric juices Artificial sweeteners |
|
|
Stress Urinary Incontinence
|
Loss of urine during activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure
Risk factors include pregnancy, hx of vaginal delivery, epesiotomy, prostate/pelvic surgery, aging, DM, recurrent UTI, obesity (increased IAP) 8-12 weeks of physical therapy recommended 50% of nursing home admissions have direct relationship to unresolved urinary incontinence |
|
|
Urge Urinary Incontinence
|
Loss of urine after a sudden intense urge to void.
The most common type of incontinence in elderly. Triggered by conditioned reflex such as water running or "key-in-the-lock" when coming home. Behavior modification is primary tx including scheduled voiding |
|
|
Overflow Urinary Incontinence
|
Loss of urine when pressure in bladder exceeds urethra's capacity to stay closed.
Caused by outflow obstruction. These pts also often have difficulty initiating urine stream, with post-void dribble (neat) |
|
|
Functional Urinary Incontinence
|
Can't or wont get to the potty
|
|
|
Physical Therapy for Incontinence
|
0/5-2/5 on muscle test:
- biofeedback, e-stim, bladder re-training, therex, pelving floor strengthening includes tapping of pelvic floor muscles, overflow exercises using buttocks, adductors, lower abdominals; Kegel exercises - 3/5-5/5: above plus weighted vaginal cones, pelvic floor muscle exercise during activitiy |
|
|
Obstetric Musculoskeletal Pathology
|
Coccydynia (becomes hypermobile and painful)
Diastasis Recti Piriformis Syndrome Symphysis Pubis Pain (complications or large infant can lead to soft tissue injury around joint) |
|
|
Diastasis Recti
|
Diagnosed by 3 or more fingers separation when patient lifts her head.
Tx - stabilization exercises, postural awareness exercises, body mechanics training |
|
|
Physiological and Postural Changes During Pregnancy
|
- Weight gain between 25-35 pounds; anemia may occur
- Uterus ascents into abdominal cavity becoming an abdominal organ - Ribs expand to accommodate the uterine ascent; respiratory diaphragm elevates four centimeters - Increased depth of respiration, tidal volume, and minute ventilation - Increased oxygen consumption (15-20%), blood volume (45-50%), and cardiac output (30-60%) - Hypotension in supine position during pregnancy from pressure on inferior vena cava - Abdominals become overstretched; ligaments become lax secondary to hormonal changes - Joints may become hypermobile |
|
|
Exercise & Pregnancy
|
50-60% max HR for ~30 min per session
At least 3x per week Stop exercising when fatigued NWB preferred Loose clothing advised Adequate fluids No supine after first trimester Pelvic floor muscle exercises (80-100 contractions per day combining quick, long hold, and functional contractions) |
|
|
Contraindications for Exercise during pregnancy
|
Absolute:
- Hemodynamically significant heart disease - Restrictive lung disease - Incompetent cervix/cerclage (risk of miscarriage) - Multiple gestation at risk for premature labor - Persistent second or third trimester bleeding - Placenta previa after 26 weeks of gestation - Premature labor during the current pregnancy - Ruptured membranes - Preeclampsia / pregnancy-induced hypertension Relative: - Severe anemia - Unevaluated maternal cardiac dysrhythmia - Chronic bronchitis - Poorly controlled type 1 diabetes - Extreme morbid obesity - Extremely underweight (BMI <12) - History of extremely sedentary lifestyle - Intrauterine growth restriction in current pregnancy - Poorly controlled hypertension - Poorly controlled hyperthyroidism - Heavy smoker |
|
|
Best position for high-risk pregnancy
|
L side-lying
|
|
|
% of pregnant women who experience back pain
|
70%
|
|
|
PT for high-risk pregnancy
|
Often on bed rest
Left sidelying is best position D/c abdominal exercises Allow minimal exertion only Avoid valsalva Provide instruction on proper body mechanics Educate about c-section rehab Monitor & report any uterine contraction, bleeding, amniotic fluid loss |
|
|
Anuria
|
Inadequate urine output; less than 100 ml
- Severe dehydration, shock, end-stage renal disease |
|
|
Cystocele
|
Bulging of bladder into vagina
|
|
|
Ectopic
|
Implantation of a fetalized ovum outside of the uterus (most commonly fallopian tube)
|
|
|
Endometrium
|
Inner lining of uterus that is shed monthly
|
|
|
Glomerulus
|
Specialized tuft of capillaries that are needed for the filtration of fluid as blood passes through the arterioles of the kidneys
|
|
|
Hematuria
|
Blood in urine
- cancer, faulty catheterization, serious disease |
|
|
Impotence
|
Impairment of ejaculation, orgasm, erection, and/or libido
|
|
|
Myometrium
|
Muscular outer layer of uterus
|
|
|
Nephrolithiasis
|
Kidney stones
|
|
|
Nocturia
|
Frequency at night
- DM, CHF |
|
|
Oliguria
|
Urine output less than 400 ml
|
|
|
Polyuria
|
Large volumes of urine
|
|
|
Perimetrium
|
The serous peritoneal coat of the uterus
|
|
|
Radical mastectomy
|
Surgical procedure in which the entire breast, pectoral muscles, axillary lymph nodes, and some skin are remove secondary to breast cancer
|
|
|
Rectocele
|
Bulging of anterior wall of rectum into the vagina secondary to weakneing of pelvic support structures
|
|
|
Seminiferous tubules
|
Coiled tubes found in each lobe of testes where spermatogenesis takes place
|
|
|
Urea
|
Major nitrogen-containing end product of protein metabolism normally cleared from the blood by the kidney into the urine
|
|
|
Urinary frequency
|
Voiding more than 8 times in a 24 hour period.
- Overactive bladder, reduced bladder capacity, painful bladder syndrome, increase urine output caused by uncontrolled DM |
|
|
Urinary urgency
|
The sudden desire to urinate that is stronger than usual and difficult to defer.
- Detrusor overactivity, bladder infection, inflammation or presence of foreign body such as stones or tumors. |
|
|
General signs and symptoms of cancer
|
CAUTION
C - Change in bowel/bladder routine A - A sore that will not heal U - Unusual bleeding/discharge T - Thickening/lump develops I - Indigestion or difficulty swallowing O - Obvious change in wart/mole N - Nagging cough/hoarseness |
|
|
Cancer staging
|
0 - Early malignancy only present in layer of cells in which it began
1 - Limited to tissue of origin with no lymph involvement or metastasis 2 - Spreading to adjacent tissues; lymph nodes may shown signs of micrometastasis 3 - Spread to adjacent tissues showing sign of fixation to deeper structures. High likelihood of metastatic lymph node involvement 4 - Metastasis |
|
|
Exercise guidelines for patients undergoing cancer treatment
|
Side effects of tx include - pain, fatigue, depression, anxiety, altered body image, sleep disturbances, lymphedema, GI distress
- Check physician orders for WB status, especially with bone mets - Monitor blood values daily, especially platelet and hematocrit counts - Keep exercise at 40-65% max HR - RPE should not exceed 12 - Schedule visits when pt has most energy |
|
|
PT for patients undergoing chemo and radiation
|
- Massage and heat contraindicated for 12 months over irradiate areas
- Most heat and e-stim contraindicated over malignant areas - This may be overlook for palliative care for terminally ill patients - Cognitive changes are common |
|
|
Oncological pharmacology
|
Alkylating Agents
Antimetabolite Agents Antibiotic Agents Plant Alkaloid Agents (Mitotic Inhibitors) Biologic Response Modifier Agents Heavy Metal Compounds |
|
|
Adjuvant
|
treatment provided in addition to other cure-focused interventions
|
|
|
Benign neoplasm
|
Abnormal cell growth that is usually slow growing and harmless
|
|
|
Dysplasia
|
Abnormal development of cells or tissue that is often an early sign of neoplasia
|
|
|
Hyperplasia
|
Increase in cell number than may be normal or abnormal
|
|
|
Malignant neoplasm
|
Abnormal uncontrolled cell growth that invades and destroys adjacent tissues and may metastasize to other sites and systems in the body
|
|
|
Metaplasia
|
Change in a cell from one type to another that may be normal or abnormal
|
|
|
Neoadjuvant
|
Chemotherapy or radiation given prior to surgical oncology intervention
|
|
|
Neoplasm (tumor)
|
Abnormal new growth of tissue that increases the overall tissue mass. Tumors are benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) as well as primary or secondary. Primary tumors form from cells that belong to the area of the tumor. Secondary tumors grow from cells that have metastasized (spread) from another affected area within the body. Tumor classification is defined by cell type, tissue of origin, amount of differentiation, benign versus malignant, and anatomic site.
|
|
|
Cancer
|
A group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation with mutation and spreading of the abnormal cells. The etiology is based on the type and location of the cancer. The most common causes include cigarette smoking, diet and nutrition, chemical agents, physical agents, environmental causes, viral causes, and genetics.
|
|
|
Affective Disorders
|
Depression, mania, bipolar
|
|
|
Neuroses
|
Maladaptive strategies in dealing with stressful or everyday stimuli.
OCD Anxiety disorder Phobia disorder |
|
|
Dissociative Disorders
|
Develop when a person unconsciously dissociates (separates) one part of the mind from the rest.
Psychogenic Amnesia - forgets past Multiple personality |
|
|
Somatization Disorder
|
Complaints of symptoms with no physiological basis
|
|
|
Conversion disorder
|
Physical complaints with no underlying cause
Most common - paralysis, deafness, blindness, parasthesia |
|
|
Hypochondriasis
|
Excessive fear of illness
Believes that minor illnesses or medical problems indicate a serious of life-threatening disease |
|
|
Types of schizophrenia
|
Catatonic - rigid posture and/or uncontrolled movements
Paranoid - Delusions of grandeur / persecution. May believe they have special powers Disorganized - Usually progressive and irreversible with inappropriate emotional responses, mumbled talking |
|
|
Psychopathic Personality
|
Low morality, poor sense of responsibility, no respect for others
Impulsive behavior for immediate gratification; high frustration Little guilt or remorse for all actions; inability to alter behavior, even with punishment Expert liar |
|
|
Antisocial behavior
|
Lacks responsibility and emotion stability but typically has some concern for others
|
|
|
Narcissistic Behavior
|
Incapable of loving others
Self-absorbed; obsessed with self and power Unrealistic perception of self-importance |
|
|
Borderline Behavior
|
Instability in all aspects of life
Uses projection, denial, defensiveness, unpredictable mood or behavior Intense or uncontrolled anger; chronic feelings of emptiness |
|
|
Interacting with escalating patient
|
- Be empathetic when setting boundaries
- Low, calm tone of voice - Do not respond defensively to patient comments - Offer choices, options, or small concessions - Allow patient to look away - Be respectful and acknowledge the patient's complaints or frustrations - Wait for patient to pause rather than raising your voice - Leave area if necessary - Avoid physical contact - Do not turn your back - Do not allow patient to block your exit route - Maintain more space than usual - Stand at an angle facing the patient so that it is easier to sidestep if needed - Stay at the same eye level as the patient (both standing or sitting etc) - Keep hands out of your pockets |
|
|
Child - overweight or obese?
|
BMI - 85th - 94th percentile = OVERWEIGHT
95 or higher - OBESE |
|
|
Female Athlete Triad Syndrome
|
Disordered eating
Amenorrhea Osteoporosis |

