![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the alternative name for neuropathic ulcers?
|
diabetic ulcerations
|
|
|
What is the incidence of neuropathic ulcerations ?
|
15-25%
|
|
|
How many amputations annually is diabetes responsible for?
|
over 600,000 -50% will have contralateral ulcer within 18 months -50% will have second amputation within 3-5 years |
|
|
What is the etiology of diabetes?
|
-Disorder of carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism related to alterations in the body's ability to produce or use insulin
|
|
|
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
|
-children or young adults -result from immune mediated destruction or pancreatic beta cells |
|
|
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
|
-middle age or later -aprox. 80% of diagnosed are over weight -genetic predisposition to developing type 2 |
|
|
What are the percentage amounts of Type 1 vs. Type 2?
|
10% type 1 insulin dependent 90% type 2 |
|
|
What is hyperglycemia?
|
-changes in RBC's, platelets, and capillaries -alters blood flow -increases microvascular pressure (tissue damage related to diabetes) |
|
|
What causes tissue damage related to diabetes?
|
-hyperglycemia -glycosylated proteins -accumulation of sorbitol, due to breakdown of glucose |
|
|
What are the risk factors contributing to NU and delayed healing?
|
-vascular disease -neuropathy -mechanical stress -abnormal foot function and inadequate footwear -impaired healing and immune response -poor vision -ulcer characteristics -disease characteristics -inadequate care and education |
|
|
Describe vascular disease as a risk factor for NU:
|
-risk for PVD greater in pt. with diabetes -accelerated atherosclerosis -thickening of basement membrane -once though to be the major contributing factor , now known to be neuropathy |
|
|
Describe neuropathy as a risk factor fro NU:
|
-most common complication in diabetes -causes (neural ischemia, segmental demyelination) -symmetrical, distal -affects sensory, motor, and autonomic system |
|
|
Describe sensory neuropathy as a risk factor for NU:
|
-50% of pt. unaware they have lost protective sensation -lack of protective sensation = lack of early detection to irritation or trauma -paresthesias -if unable to perceive 10 g of pressure, at risk for ulceration |
|
|
Describe motor neuropathy as a risk factor for NU:
|
-intrinsic muscle weakness/atrophy -decreases foot stability -leads to deformities -increased pressure and shear forces to foot |
|
|
Describe autonomic neuropathy as a risk factor for NU:
|
-dry, cracked skin due to decreased ability to sweat -increased rate of callus formation -arteriovenous shunting leads to decreased perfusion -uncontrolled vasodialation leads to osteopenia |
|
|
Describe mechanical stress as risk factor for NU:
|
-abnormal or excessive forces predispose to ulceration -high plantar pressures overload tissue's ability to repair itself |
|
|
Describe impaired healing and immune response as a risk factor for NU:
|
-decreased ability to build new tissue and fight infection -decreased ability to fight infection -increased frequency of osteomyelitis, soft tissue, infections, candida -impairs all 3 phases of wound healing |
|
|
Describe abnormal foot function and inadequate footwear as a risk factor for NU:
|
-impaired ROM -great toe ext, DF, subtalar joint -increase vertical pressure and horizontal shear -Foot deformities -PF contracture, varus/valgus, charcot foot -Prior ulcer/amputation -Poor footwear -does not protect foot, decreases pressure/sear, or accommodate deformities |
|
|
Describe poor vision as a risk factor for NU:
|
-diabetes is leading cause of retinopathy, glaucoma, cataracts -increases risk to trauma -decreases ability to perform adequate foot care |
|
|
Describe ulcer characteristics as a risk factor for NU:
|
-larger and deeper wounds take longer to heal -wounds present for longer time take longer to heal |
|
|
Describe disease characteristics as a risk factor for NU:
|
-poor glycemic control associated with increased risk of long-term complications -complications can be improved/reversed with improved glycemic control |
|
|
Describe inadequate care and education as a risk factor for NU:
|
-lack of cutting-edge knowledge -delayed referrals -poor adherence to clinical guidlines -minor short-term complications but major long-term complications -pt. do not understand link between euglycemia and long term complications -absence of pain or short-term effects decreases pt. adherence |
|
|
What are the PT tests and measures for NU?
|
-circulation -sensory integrity |
|
|
How do we test circulation?
|
-pulses -Doppler ultrasound -ankle-brachial index (ABI) |
|
|
What are the indications for circulation tests?
|
-all open wounds -decreased or absent pulses -signs and symptoms of arterial insufficiency -history of PVD |
|
|
Describe capillary refilll indications, and when you would refer:
|
Indications: -digital ulcer -abnormal Doppler or ABI Refer: -arteriography or transcutaneous oxygen measurements if fail to respond -refer to vascular specialist if very low ABI |
|
|
What is the test we use to test sensory integrity and how is it done?
|
Semmes-Weinstein Monofilaments -occlude pt. vision -begin with 5.07 monofilament -avoid calloused areas -each location tested randomly 3x |
|
|
What are the indications for Semmes-Weinstein Monofilaments?
|
-all neuropathic ulcers -all pt. with diabetes -all pt. with plantar foot ulcers |
|
|
What are the locations to perform monofilament testing on the foot?
|
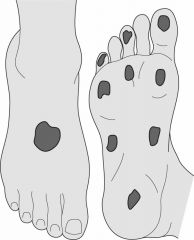
-one on top -bottom digits 1,3,5 -bottom corresponding heads -2 mid foot -1 on heel |
|
|
Interpretation of Sensory Testing:
|
Monofilament 4.17 = 1 g pressure = decreased sensation 5.07 = 10 g pressure = loss of protective sensation 6.10 = 75 g pressure = absent sensation |
|
|
What are the grades of NU on the Wagner classification system?
|
Grade 0 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 |
|
|
Describe Wagner classification system Grade 0:
|
-no open lesions -may have deformity or cellulitis |
|
|
Describe Wagner classification system Grade 1:
|
-superficial ulcer |
|
|
Describe Wagner classification system Grade 2:
|
-deep ulcer to tendon -capsule -bone |
|
|
Describe Wagner classification system Grade 3:
|
-deep ulcer with abscess -osteomyelitis -joint sepsis |
|
|
Describe Wagner classification system Grade 4:
|
-localized gangrene |
|
|
Describe Wagner classification system Grade 5:
|
Gangrene of entire foot
|
|
|
Use the 5PT Method to check NU:
|
-pain -position -presentation -periwound -pulses -temperature |
|
|
Describe pain of NU:
|
-lack of pn. complaint due to neuropathy -possible paresthesias |
|
|
Describe Position for NU:
|
-plantar foot -plantar aspect of metatarsal heads -plantar aspect of midfoot if charcot deformity -may occur under calluses -may occur in areas of pressure/friction from inappropriate footwear |
|
|
Describe Temperature for NU:
|
-normal -may be increases in areas of reactive hyperemia or infection |
|
|
Describe Presentation for NU:
|
-round, punched-out lesions -callused rim -minimal drainage unless infected -eschar or necrotic material uncommon unless infected |
|
|
Describe Periwound and Structural changes for NU:
|
-skin is dry, cracked -callus present -structural deformities (claw toes, rocker-bottom foot, prior amputation) |
|
|
Describe pulses for NU:
|
-normal -may be accentuated with vessel calcification |
|
|
When can you expect good healing for NU?
|
-smaller, superficial (wagner grade 1 or 2) -present for <2 months -ulcers decreasing in size within 4 wks of tx |
|
|
When can you expect poor healing for NU?
|
-large size -risk of amputation 154x greater with infected ulcers -if 20-50% decrease in size not noted in first month of tx. |
|
|
What is the average healing time of NU?
|
12-14 wks
|
|
|
What should the pt. related instructions include?
|
-disease process/management of DM -role of exercise and safety guidelines -risk factor reduction -daily foot checks -foot care guidelines -proper footwear -toenail care -demonstrate what decreased protective sensation 'feels' like |
|
|
What are the precautions for PT interventions?
|
-May not show signs of infection due to decreased inflammatory response/PVD -Monitor blood sugar
|
|
|
Describe what should be done if not showing signs of infection?
|
~request culture and sensitivity for wounds that fail to respond to appropriate interventions ~osteomyelitis must be treated surgically |
|
|
Describe what should be done depending on what you find when monitoring blood sugar:
|
-hyperglycemia: common with infections and uncontrolled diabetes -hypoglycemia may occur |
|
|
What are the keys to local wound care?
|
-offload the NU -pare callus flush with epithelial surface -use petrolatum-based moisturizer daily -use toe spacers if enclosing toes in bandage -possible adjuncts ~negative pressure wound therapy ~ultrasound ~electrical stimulation ~growth factors |
|
|
What is total contact casting?
|
-Modified short leg casts used for Wagner grade 1 or 2 ulcers -Assists wound healing ~Cast is molded to foot and leg, dispersing weight-bearing forces over large area ~cast rigidity controls edema ~immobilization of foot protects from trauma and microorganisms ~assists with pt. adherence |
|
|
What are the contraindications of total contact casting?
|
-osteomyelitis -gangrene -fluctuating edema -active infection -ABI less than 0.45 |
|
|
What should be included in the gait and mobility training when using contact casting?
|
-PWB gait with assistive device -alter gait pattern to decrease plantar pressure -step-to pattern -slower steps -shuffling gait -footwear modifications |
|
|
What are the therapeutic exercises used for NU?
|
-ROM exercises (assess/address great toe extension, talocrural dorsiflexion, and subtalar joint motion; joint mobilizations may be helpful) -aerobic exercise (assist with glycemic control, assists with weight loss) |
|
|
What are some of the devices and equipment used for NU?
|
-temporary footwear -permanent footwear |
|
|
Describe temporary footwear for NU:
|
-options Felt or foam inserts Padded ankle-foot orthoses Walking shoes -provides safe ambulation, pressure reduction, room for bandages -can use when total contact cast is not an option |
|
|
Describe permanent footwear for NU:
|
-Shoes should be ~½ inch longer than the longest toe with snug heel fit -Shoe last should match foot shape -Extra-depth toe box -Heel height < 1 inch -Soft, moldable materials -Soft inserts may decrease pressure -Fit shoes at the middle of the day -Break in shoes gradually -Patients with severe foot deformities or amputations should be referred to an orthotist |
|
|
What are the medical interventions for NU?
|
-glycemic control -manage neuropathic pain/paresthesias -management of concomitant arterial insufficiency -antibiotic therapy -radiological assessment |
|
|
Describe how we medically manage glycemic control:
|
-even 1% decrease in hemoglobin A1c associated with improvements in many complications
|
|
|
Describe how we medically manage neuropathic pain/paresthesias:
|
-anticonvulsants, antidepressants, capsaicin
|
|
|
Describe how we medically manage with antibiotic therapy:
|
-cultures of neuropathic ulcers average 4-5 different microbes -most commonly group A Strep and Staph aureus |
|
|
Describe how we medically manage NU by using radiological assessment:
|
-fracture identification-charcot foot -presence of foreign bodies -bone scan for osteomyelitis |
|
|
What are the surgical interventions for NU?
|
-Debridement (necrotic tissue, osteomyelitis) -incision and drainage -antimicrobial bead implantation -incision and drainage -Surgery to address abnormal foot function or limited tissue perfusion (joint arthroplasty, tendon lengthening, stabilization of charcot deformities and reduction of abnormal biomechanics) -Revascularization surgery -Amputation (gangrene, wagner grade 4 or 5 ulcers) |

