![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 5 targets of the nervous system?
Which are innervated by ANS? |
Skeletal muscle
Sensory structures Smooth muscle* Cardiac muscle* Secretory glands* *Innervated by the ANS |
|
|
What is the structure which sits superior to the foramen magnum?
What is it called when this structure herniates through the formen magnum? |
Tonsil (of the cerebellum)
Tonsilar herniation |
|
|
What are the three parts of the brainstem from cranial to caudal?
|
Midbrain
Pons Medulla |
|
|
Which part of the brain stem is involved in wakefulness?
|
Reticular Formation
|
|
|
Damage to which two parts of the brain can lead to a coma?
|
Reticular Formation (of the brain stem)
Large areas of the cerebral cortex |
|
|
What are the four parts of the diencephalon?
|
Thalamus
Hypothalamus Epithalamus Subthalamus |
|
|
What separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe?
|

Lateral sulcus
|
|
|
What separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe?
|

Central sulcus
|
|
|
What are the 2 functions of the thalamus?
|
1. Processes all sensory information (except olfactory)
2. Integrates motor functions of the cortex with the cerebellum and basal nuclei |
|
|
Where does olfactory sensory information go?
|
Directly to the cortex of the anterior temporal lobe (uncus)
|
|
|
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
|
Regulates homeostasis, reproductive functions, circadian rhythm, sleep, and autonomic functions
|
|
|
From what structure do the mamillary bodies and the attachment of the pituitary stalk arise from?
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
What connects the two cerebral hemispheres?
What sort of matter is this structure made of? |
Corpus callosum
White matter |
|
|
What part of the brain is located just rostral of the central sulcus?
What is the function of this area of the brain? |
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor cortex |
|
|
What is the ventral, caudal gyrus of the frontal lobe responsible for?
What is the area called? |
Speech motor control
Broca's area |
|
|
What is the dorsal, caudal gyrus of the temporal lobe responsible for?
What is this area called? |
Speech comprehension and composition
Wernicke's area |
|
|
95-99% of right-handed people have speech dominant in which side of the brain?
|
Left
|
|
|
What are basal nuclei?
What are their functions? |
Large collections of gray matter located within the subcortical white matter
Regulation of motor functions by modification of voluntary movements initated by the motor cortex |
|
|
What sort of cells line the ventricles?
|
Ependymal cells
|
|
|
What is the structure called which makes CSF?
Where is this structure located? |
Choroid plexus
Lateral ventricles, interventricular foramina, roof of the 3rd ventricle, part of the 4th ventricle |
|
|
What is the ventral fissure of the "Y" in the caudal part of the brain called?
What is its function? |

Calcarine sulcus
Primary visual cortex |
|
|
Where is the central visual field cortex located?
|
Posterior calcarine sulcus
|
|
|
Where is the peripheral visual field cortex located?
|
Anterior calcarine sulcus
|
|
|
What is the superior, rostral fissure of the "Y" in the caudal part of the brain called?
|

Parietal-occipital sulcus
|
|
|
What 2 structures make up the primary motor cortex?
|
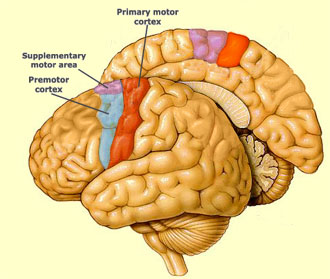
Precentral gyrus
Paracentral lobule (anterior part) |
|
|
What 2 structures make up the primary sensory cortex?
|

Postcentral gyrus
Paracentral lobule (posterior part) |
|
|
What is the function of the superior parietal lobule?
|
General sensory association cortex
|
|
|
What is the function of the inferior parietal lobule?
|
Multimodal association cortex
|
|
|
What separates the superior parietal lobule from the inferior parietal lobule?
|

Intraparietal sulcus
|
|
|
Which part of the brain is used for object identification without the use of vision?
Where is it located? |
General sensory association cortex
Superior parietal lobule |
|
|
Which part of the brain is used to integrate general sensations with special sensations, such as audition and vision?
Where is it located? |
Multimodal association cortex
Inferior parietal lobule |
|
|
What is the the function of the superior temporal gyrus?
|

Primary auditory cortex
|
|
|
Where is the primary auditory cortex located?
|

Superior temporal gyrus
|
|
|
What is the function of the middle and inferior temporal gyri?
|

Visual association cortices
|
|
|
What is the location of the visual association cortices?
|

Middle and inferior temporal gyri
|
|
|
What is the function of the lateral occipital lobe?
|
Primary visual cortex
|
|
|
Where is the primary visual cortex located?
|
Lateral occipital lobe
|
|
|
What is the function of the hippocampal formation?
What are the three cortical areas? |

Consolidation of new memories
Hippocampus, dentate gyrus, subiculum |
|
|
What part of the brain is responsible for consolidation of new memories?
|

Hippocampal formation
|
|
|
What is the function of the anterior end of the parahippocampal gyrus?
What is it called? |
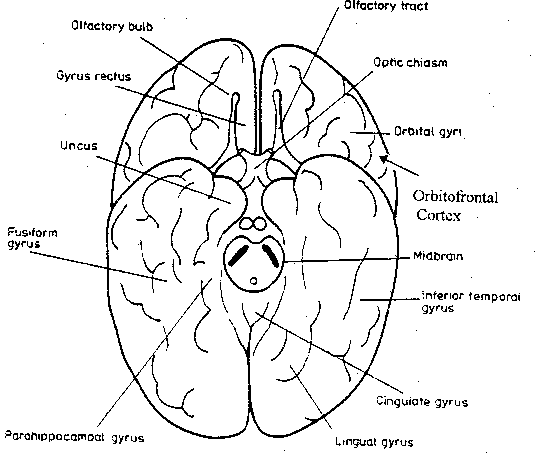
Primary olfactory cortex
Uncus |
|
|
What are the twelve pairs of cranial nerves?
|
I - Olfactory
II - Optic III - Oculomotor IV - Trochlear V - Trigeminal VI - Abducent VII - Facial VIII - Vestibulocochlear IX - Glossopharyngeal X - Vagus XI - Accessory XII - Hypoglossal |
|
|
What is the plate through which olfactory fibers penetrate?
|

Cribriform plate
|
|
|
What passes through the optic canal?
|

CN.II
Opthalmic artery |
|
|
What passes through the suerior orbital fissure?
|

CN.III
CN.IV CN.V<sub>1</sub> CN.VI |
|
|
What passes through the foramen rotundum?
|

CN.V<sub>2</sub>
|
|
|
What passes through the foramen ovale?
|

CN.V<sub>3</sub>
|
|
|
What passes through the foramen spinosum?
|

Middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
Rupture of the middle meningeal artery will lead to what sort of cranial hematoma?
|
Epidural hematoma
|
|
|
What passes through the carotid canal?
|
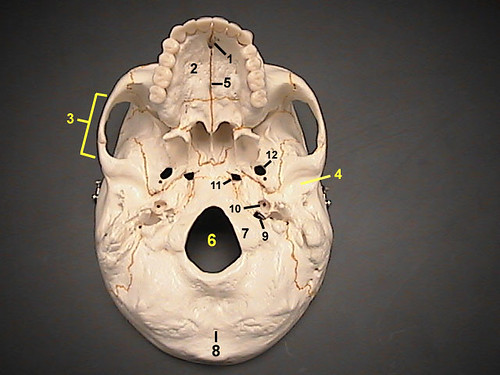
Internal carotid artery (11)
|
|
|
What passes through the hiatus of greater petrosal?
|
Greater petrosal nerve
|
|
|
What passes through the internal acoustic meatus?
|

CN.VII
CN.VIII |
|
|
What passes through the jugular foramen?
|
CN.IX
CN.X CN.XI |
|
|
What passes through the hypoglossal canal?
|
CN.XII
|
|
|
What passes through the formen magnum?
|
CN.XI
Vertebral artery |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.I?
|
CN.I - Olfactory
Special sensory Smell Cribriform plate |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.II?
|
CN.II - Optic
Special sensory Vision Optic Canal |
|
|
Which cranial nerves are associated with the anterior cranial fossa?
|
CN.I
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves are associated with the middle cranial fossa?
|
CN.II
CN.III CN.IV CN.V CN.VI |
|
|
Which cranial nerves are associated with the posterior cranial fossa?
|
CN.VII
CN.VIII CN.IX CN.X CN.XI CN.XII |
|
|
From which spinal cord segments do sympathetics to head and neck structures arise?
|
T1-T4/T5
|
|
|
What are the sympathetic functions of the head and neck?
|
1. Sweating of the face
2. Arterial constriction (pallor) 3. Innervation of the smooth muscle dilator of the pupil 4. Innervation of the smooth muscle superior tarsal muscle |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.III?
|
CN.III - Oculomotor
Somatomotor, Para/Pre Eye movement Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.IV?
|
CN.IV - Trochlear
Somatomotor Eye movement (Superior Oblique Muscle only) Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.V<sub>1</sub>?
|
CN.V<sub>1</sub> - Opthalmic
Somatosensory Sensory of the cornea, iris, ciliary body, lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, mucus membrane of nasal cavity, skin of eyelids, eyebrow, forehead, and nose Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.V<sub>2</sub>?
|
CN.V<sub>2</sub> - Maxillary
Somatosensory Sensory from the maxilla, palate, nasal cavity, sinus, and midface Foramen rotundum |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.V<sub>3</sub>?
|
CN.V<sub>3</sub> - Mandibular
Somatosensory, Somatomotor Sensory from lower face, buccal mucosa, anterior 2/3 of the tongue; Motor for mastication Foramen ovale |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.VI?
|
CN.VI - Abducent
Somatomotor Eye abduction (Lateral rectus) Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.VII?
|
CN.VII - Facial
SS, SM, Taste Sensory, Para/Pre Movement of facial muscles, sensations of tongue and oral cavity Internal auditory meatus |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.VIII?
|
CN.VIII - Vestibulocochlear
Balance/Hearing sensory Balance, hearing Internal auditory meatus |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.IX?
|
CN.IX - Glossopharyngeal
Visceroscensory, SM, Taste sensory, Para/Pre Sensory from tonsils, posterior 1/3 of tongue, parotid gland Jugular foramen |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.X?
|
CN.X - Vagus
Viscerosensory, SM, Taste sensory, Para/Pre Myriad Jugular foramen |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.XI?
|
CN.XI - Accessory
SM Trapezius and Sterno-Cleido-Mastoid innervation Foramen Magnum to Jugular foramen |
|
|
What is the name, nerve components, function, and pathway for CN.XII?
|
CN.XII - Hypoglossal
Somatomotor Tongue muscles ? |

