![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PT comes in with headache or other acute neuro findings in the ER
What is the first imaging study you want to use? ****** |
NON CONTRAST CT
|
|
|
What is one key reason why CT is better than MRI?
*** |
it is good for quick evaluation of acute bleeding: Excellent for acute intracranial hemorrhage
(also, MRI might require pre-approval for access) |
|
|
where do epidural bleeds most commonly occur
|
fronto-temporal area
|
|
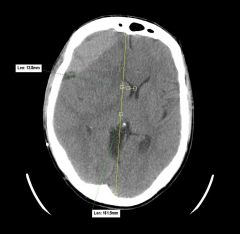
What is this? Where is it occuring
|
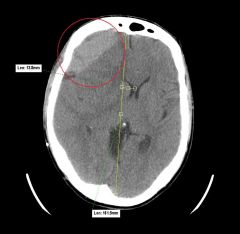
Epidural bleed
frontal lobe |
|
|
what are the Hounsfield units for:
water bone air blood Fat |
0 = water density
+ 1000 = bone -1000 = air + 60 – +80 = blood - 5 to –12 = fat |
|
|
T1 vs T2 on MRI?
|
T1 = the “anatomic” sequence
T2 = the “pathology” sequence On T1 water is dark black On T2 water is bright white |
|

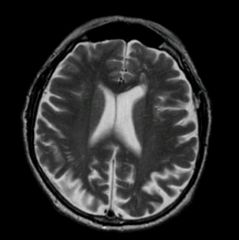
T1 or T2?
What 4 things are black on this type of image? |
T1
Cortical bone Bone Moving blood Fluid |
|
T1 or T2
|
T2
|
|
|
Which study, MRI or CT can detect ischemic injusry 24-36 hours earlier than CT?
|
MRI
|
|
|
This imaging study has no bone artifact (especially in the posterior fossa), and is better at assessment of tumors, white matter, and disease/early edema?
|
MRI
|
|
|
Which imaging study (CT or MRI) has unchanged multi-planar capability?
** |
MRI
|
|
|
A 26 y/o patient presents to the ED after being struck by a softball bat. You want to rule our intracranial hemorrhage. You order:
A. CT B. MRI |
CT (no contrast)
Cranial bone will be white |
|
|
Which modality is best for evaluating white matter disease?
A. CT B. MRI |
MRI
|
|
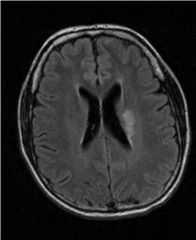
CT or MRI?
|
MRI
|
|
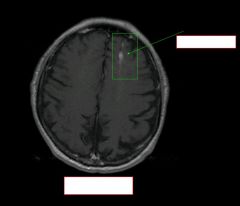
type of image? Path?
|
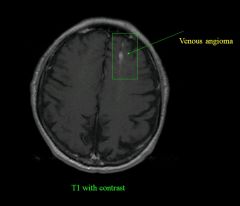
|
|
|
what normally causes an epidural hematoma?
Subdural? |
epi: skull fracture
sub: direct blow to the head w change in lvl of conciousness |
|
|
What happens in shear injuries?
|
diffuse axonal injury
can be due to rotational injury (not necessarily blow to a head) |
|
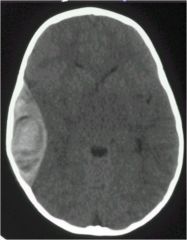
path?
will it cross sutural lines? what blood vessel causes it? |
epidural hematoma
DOESN'T CROSS SUTURAL LINES assoc with skull fracture due to arterial tear (middle meningeal artery) |
|
|
epidural hematoma vs subdural hematoma
which crosses suture lines? |
epidural hematoma :DOESN'T CROSS SUTURAL LINES
Sub: does |
|
|
for an epidural hematoma, at what amount of bleeding do you have to consider operative tx?
|
less than 5mm: NON OPERATIVE
greater than 5mm: drain |
|

|
epidural hematoma in kid
|
|
|
describe some of the characteristics of subdural hematomas (shape, blood source, who it happens to)
|
crecentic,
bridging veins, old people who fall |
|
|
SDH more common with ____ while
EDH more common with _____ (cause of injury) |
SDH more common with falls
EDH more common with MVA |
|
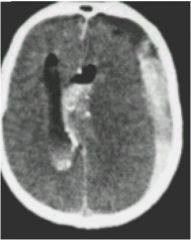
|
Subdural Hematoma
|
|
|
this type of bleed is Spread over a larger area, limited by the falx and the tentorium
|
Subdural Hematoma
|
|
|
there are 3 densities seen on CT with a SDH..what are they and what are the time frames assoc with them
|
Acute 0 to 3-4 days hyperdense
Subacute 3 to 20 days isodense Chronic > 20 days hypodense |
|
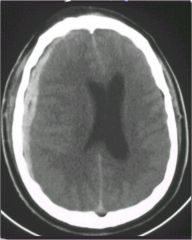
|
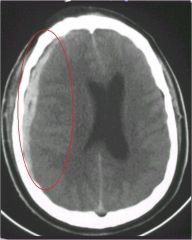
SDH
|
|
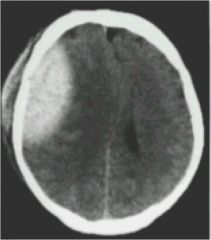
|
epidural hematoma
|
|
|
this type of injury Occur with rapid acceleration/deceleration
Usually involves large WM tracts: corpus callosum, brainstem and deep white matter Occurs at gray-white matter interface due to slight differences in mass Minor differences in tissue inertia |
Shear Injuries
|
|
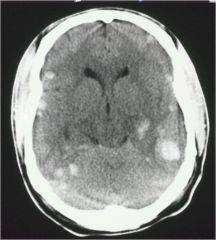
|
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage from shear injuries
|
|

|
MRI showing
intra parenchymal hemorrrhage |
|
|
Left Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction with midline shift:
what is the most useful landmark for measuring midline shift? |
Most useful landmark for measuring midline shift: Septum Pellucidum
note:This type of edema is called cytotoxic edema cytotoxic edema visible on CT and MRI |
|
|
what is key to remember about cytotoxic edema?
|
Affects both gray and white matter
|
|

History: stroke symptoms
|
cytotoxic edema
|
|
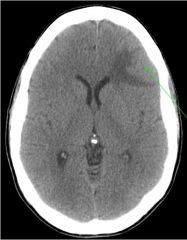
44 y/o female
New onset seizures Fell, hit head hemorrhage or tumor? |
This is an enhancing
tumor with edema confined to the white matter (vasogenic edema) |
|
|
vasogenic edema is found where?
cytogenic? causes? *** |
vasogenic edema: CONFINED TO WHITE MATTER (tumor or infection)
where cytogenic could be in white or gray (infarct or stroke) |
|
|
SUMMARY SLIDE
CT is 1st in the emergent setting to rule out hemorrhage. MRI is more sensitive for edema, tumors, infections and white matter disease. Be able to distinguish SDH from EDH. Be able to distinguish cytotoxic (stroke) from vasogenic (tumor or infection) |
CT is 1st in the emergent setting to rule out hemorrhage.--FAST
MRI is more sensitive for edema, tumors, infections and white matter disease.--CONTRAST MAKES IT EVEN MORE SENSITIVE Be able to distinguish SDH from EDH.--SDH more cresentic, covers further distance, not confined by sutures Be able to distinguish cytotoxic (stroke-effects both grey and white matter) from vasogenic (tumor or infection--just in white matter) |

