![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 5 basic radiographic densities?
|
Air-black
Bone-White Metal-Bright White Fat-light gray Liquid-dark gray |
|
|
when you order a xray for an abdomen, what view do you want?
|
person lying on their back, flat plate, AP view
|
|
|
what is the rule of 3s of the small intestine?
|
Gas less than 3cm (if greater, it is dilated/distended)
Intestinal wall should not be more than 3mm thick plicae should never be more than 3mm (if they are, indicative of inflammation) |
|
|
3 characteristics of the small bowel?
|
1. Central
2. No>3cm 3. Mucosal folds |
|
|
What is the most common cause of obstruction of the bowel?
|
Prior surgery
adhesions develop causing occlusion (can occur as fast as 3 days) |
|
|
'stair stepping' seen on xray is associated with what? seen where?
|
post surgical obstruction
always on the left |
|
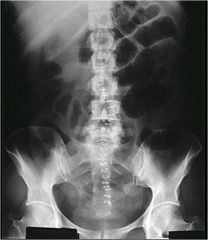
sign?
|
stair stepping
shows obstruction |
|
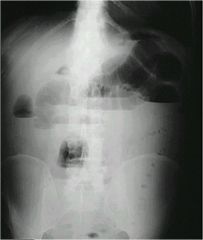
sign?
|
Stair step in upper left quadrant
(technically Asynchronis-different levels) |
|
|
what are the 2 types of stair stepping?
|
Synchronis- same level
Asynchronis- different levels (air fluid levels stair step upwards (different levels)) |
|
|
what is Adynamic ileus? how do you distinguish it from Obstruction?
|
acts like an obstruction, but just a small intestinal dilitation, just quits working, won’t hear anything on auscultation
Obstruction auscultation gives a high pitched sounds |
|
|
what is the string of pearls sign?
|
you see bubbles of air where the intestine segments itself to squeeze by the obstruction/ileus to keep working
associated with adynamic ileus |
|
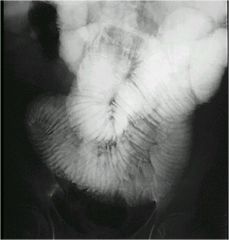
Is the barium
in large or small bowel? |
barium in small bowel
see the plicae circularis going all the way across, seen across the entire intestinal lumen |
|
|
in the workup of abdominal pain, what 3 views should you order?
|
upright PA chest (PE can cause belly pain), one supine abdomen, one upright abdomen
|
|
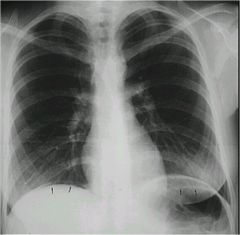
what is going on?
|
air under hemidiaphragm...allows you to see the liver separate from the diaphragm
|
|
|
4 most common causes of free air in abd?
|
diverticulitis with perforation,
duodenal ulcer that has perforated, gastric ulcer that has perforated; most common cause overall is post surgical |
|
|
What is the Rigler's Sign?
|
abdomen- have bowel wall that you see on both sides; you typically only see one side of bowel wall because it is the inside wall that is visible
|
|
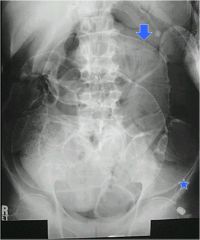
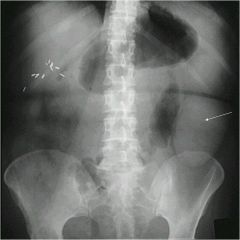
2 signs shown?
|
arrow: Rigler’s sign
star: football sign |
|
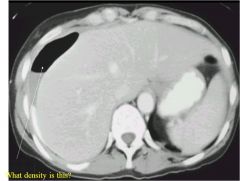
|
this is air, but look at the bottom and you can see fluid (because they are laying down)
this Perihepatic ascities most commonly due to diverticulitis with rupture |
|
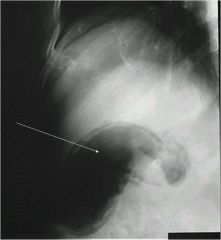
What structure is this? What is going on?
|
Hollow tubular structure in RUQ- gall bladder
This is an ER! Emphysematous cholicystitis! Significantly distended, will see air in the wall of the GB too (the wall shouldn’t be greater than 3mm) |
|
|
for solid structures what imaging modality is best? tubular?
|
solid: CT
tubular: Ultrasound |
|
|
first study you want to order if you suspect gall bladder disease
|
Ultrasound
|
|
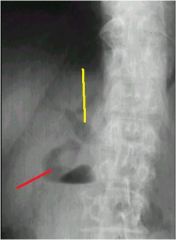
red? yellow?
|
red: biliary tree
yellow: biliary duct air can be put in there to help pass stones, but then the air can get in the tree |
|
|
enlarged spleen
|
|
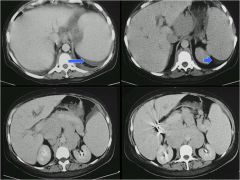
|
ascities
|
|
|
Phlebolith?
Appendicolith? Chronic pancreatitis? Porcelian GB? |
Phlebolith- ‘stone’ that has been there for years, or leucive center;
Appendicolith- calcified fecal debris within the appendix. Chronic pancreatitis- calcification Porcelian GB- wall of GB gets totally encrusted with calcification, found in older females, associated with increased risk of GB cancer |
|
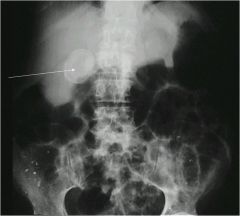
|
pancreatic calcification
|
|
|
GB calcification
|
|
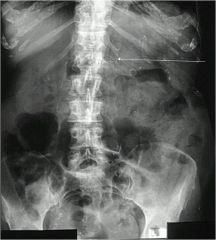
|
splenic artery calcification
Splenic artery is the first artery to develop visible calcification, extremely tortuous |
|
|
in the abdominal aorta, what thickness increases the risk of abdominal aortic anuerism?
|
3 cm
|
|
|
Best way to see air under hemidiaphragm is?
* |
upright abdominal film
|
|
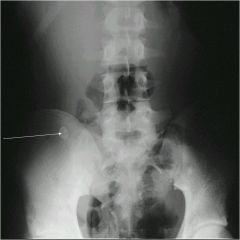
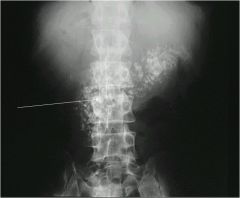
pt presents with RLQ pain at McBerneys point, pt is vomiting...you get this xray..what do they have?
|
appendicolith
|
|
|
describe what is seen in and upper, middle, and lower barium study, along with the required prep
|
Upper GI- only prep is not eating, so fairly easy; can even do them ER with no prep; generally looks at the esophagus down to duodenum
Middle-duodenum through the ileum Lower- requires more prep, no eating, same prep for colonoscopy |
|
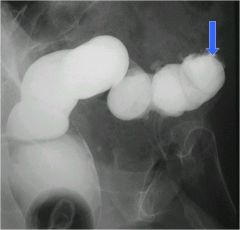
|
Arrow- Apple core lesion of the sigmoid colon--> adenocarcinoma
|
|
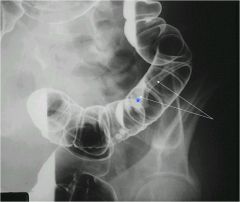
|
Arrows beginning of a polyp that has a long stalk (star on head)
|
|
|
most colon polyp adenomas are benign, but...
|
most colon carcinomas arise from adenomas
|
|
|
what type of contrast technique most you do to see colon polyps?
*** |
MULTIPLE CONTRAST
POLYPS CAN BE MISSED WITH SINGLE CONTRAST TECHNIQUE Maki (mmKay) suggests you use endoscopy over virtual colonoscopy (due to the radiation) |
|
|
Familial Polyposis has a high association with what?
|
malignancy
|
|
|
lead pipe appearance =
|
Ulcerative colitis
|
|
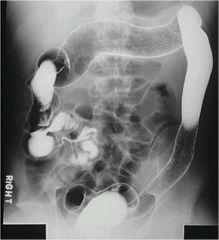
|
‘lead pipe’ appearance
Shortening of the colon Ulcerative colitis |
|
|
what is 90% sensitive for finding ulcerative colitis?
|
A/C barium enema 90% sensitive
(A/C=air contrast) |
|
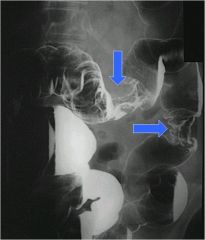
|
Apple core lesions- starting adenomas
|
|
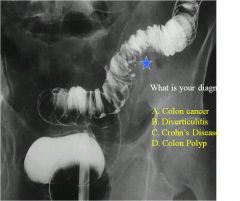
|
a/c barium enema
See diverticuli with star B. |
|
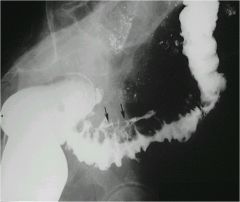
|
accordion like appearance, spiculated appearance, classic for acute diverticulitis
|
|
|
pt presents with left lower quadrant pain and fever, you are guessing they have diverticulitis. What area of the GI would most likely be affected?
|
Sigmoid colon
has the smallest diameter of any portion of the colon, and therefore the portion which would be expected to have the highest intraluminal pressure |
|
|
Points to Remember: just read
|
Air contrast BE is complementary to endoscopy
Request air contrast unless contraindicated (suspected obstruction or perforation) Use barium unless suspected perforation (signs or symptoms of peritonitis) |
|
|
most common cause of ulcers?
|
h. pylori
|
|
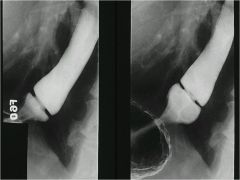
|
Hiatal hernia- portion of the stomach comes above the diaphragm
‘shatzki’s ring’ Seperation of epithelium If you don’t see a nice outline of distal esophagus, it could be barretts --> cancer |
|
|
what is a sliding hiatal hernia?
|
Very common
Stomach migrates through the esophageal hiatus Schatzki’s ring: believed to represent stricture a squamo-columnar junction Reflux esophagitis (GERD) |
|
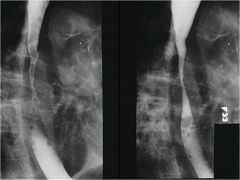
|
stricture of esophagus
|
|
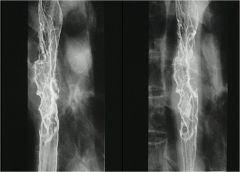
|
Varices can appear this way also (secondary to portal hypertension)
This is cancer, varicoid cancer |
|
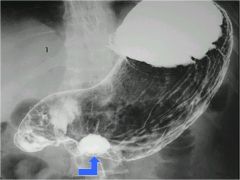
what does the arrow show? when you see this what must you also do?
|
gastric ulcer
have to have an endoscopy or biopsy bc increased risk of cancer |
|
|
will a gastric or duodenal ulceration be more likely to be associated with malignancy?
|
Gastric
|
|
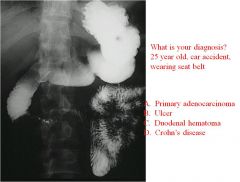
|
Cut off not completely obstructed
Duodenal hematoma- injury and tear of the duodenum |
|
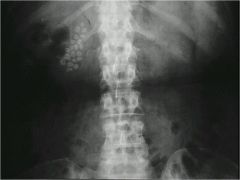
|
GB- cholelithiasis
|
|
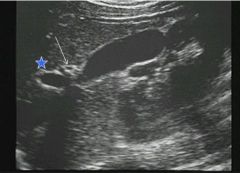
name the structures
|
GB with normal wall
Star is the portal vein, right above it is the common bile duct |
|
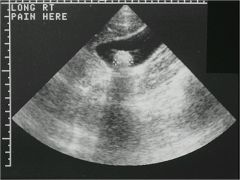
*********TEST
|
gallbladder with mobile stone in it
|
|
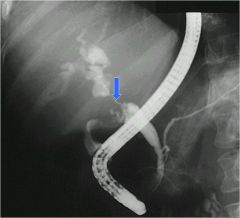
|
ERCP of colangiocarcinoma
Pancreatic duct looks normal Severly strictured area of common duct (arrow) |
|
|
best study for pancreatitis?
|
CT
(get it right after xray) |
|
|
colon cut off sign?
Sentinel loop? what are they associated with? |
Colon cut off sign- dilated colon going around splenic flexure, and then it cuts off and you see no gas past that point
Sentinel loop- dilated intestine in area of inflammation (focal loop) Both of these signs are associated with inflammation |
|
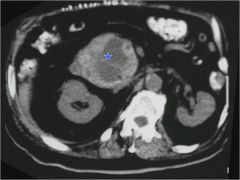
|
cancer mass on head of pancreas
|
|
|
FACTS TO TAKE HOME:
1. Barium studies are complementary to? 2. What modality is best for imaging the gallbladder? This modality is equal to what for assessment of biliary obstruction? 3. What is the best imaging modality for the pancreas? 4. If you suspect a perforated bowel, use what to see it? 5. For bowel obstruction, use ___ **** |
1. Endoscopy
2.Ultrasound is best for the GB and equal to CT for assessment of biliary obstruction 3. CT 4. Water soluble contrast 5. Barium |
|
|
what is the most sensitive place on an xray?
** |
see air underneath hemidiaphragm on both sides, remember the right side of hemidiaphragm is the most sensitive place on the x ray (higher, air migrates to the highest area)
|
|
|
if pt can't physically do an upright film, what should you do?
*** |
lateral decubitis
|
|
|
if you see colon cut off sign,what is it and what does this show?
** |
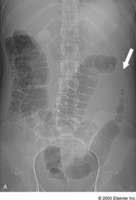
The colon cutoff sign describes the abrupt termination of gas within the proximal colon at the level of the radiographic splenic flexure, usually with decompression of the distal colon --> this represents inflammation, most likely pancreatitis
|
|
|
Appendix in a normal pt should never be more than how big?
** |
7mm
|
|
|
in a hiatal hernia, what will you start seeing before you get past the diaphragm?
** |
rugal folds
|
|
|
aorta greater than what size with symptomatology is an emergency because of risk of rupture
** |
5cm
|
|
|
Best place to look for free air??
**TEST |
3 way abdomen (esp upright) and look for free air on right side between hemidiaphragm
|
|
|
in a barium study, how can you see colon cancer?
**TEST |
apple core appearance
|
|
|
Why is bowel obstruction becoming so common?
**TEST |
due to people getting surgery and getting sections stuck together
|
|
|
what is Adynamic ileus?
**TEST |
there is not a physical obstruction, more of a functional obstruction, the fluid levels are all the same; obstruction fluid levels are all different; Paralysis of peristalsis
acts like an obstruction, but just a small intestinal dilitation, just quits working, won’t hear anything on auscultation Obstruction auscultation gives a high pitched sounds |

