![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
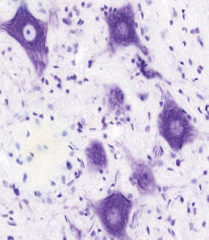
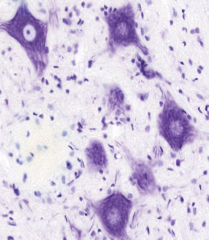
Neuron - Nissl stain
|
|
|
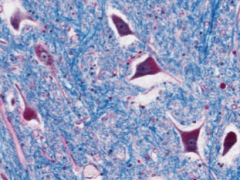
Neurons, spinal cord, grey matter.
|
|
|
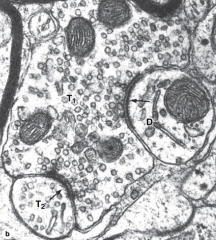
Synapse, micrograph.
|
|
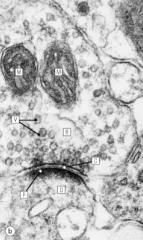
|
synapse
|
|
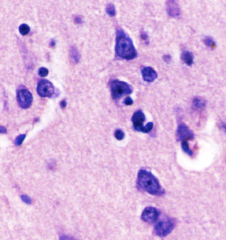
|
Grey Matter, Brain.
|
|
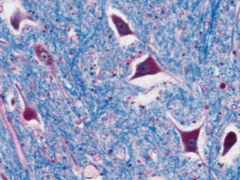
|
Grey Matter, spinal cord
|
|
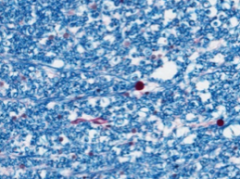
|
White matter, spinal cord
|
|
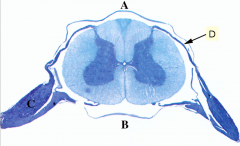
What is C?
|
Dorsal root ganglion
|
|
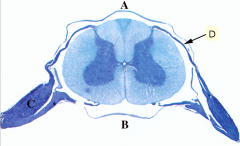
What is D
|
Dorsal root (incoming sensory fibers)
|
|
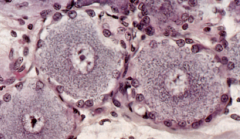
what/where?
|
Neurons with satellite cells (Peripheral nervous system)
|
|
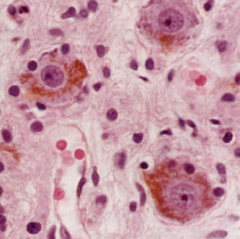
|
Neuron and lipofuscin granules
|
|
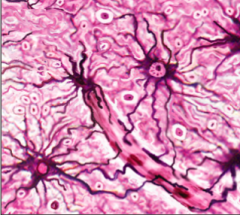
Name, function and location:
|
Astrocytes. Support, nutrition, control of environment, formation of scar tissue. CNS.
|
|
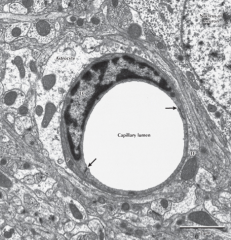
Name and location
|
Astrocyte surrounding blood vessel, CNS.
|
|
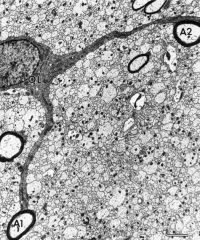
|
Oligodendrocyte
|
|
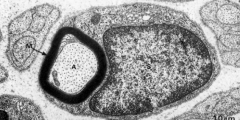
What is A
|
Axon
|
|
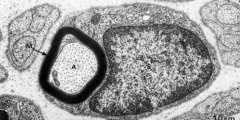
s?
|
Schwann cell nucleus
|
|
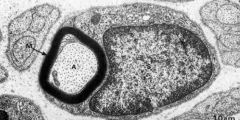
M?
|
Myelin sheath
|
|
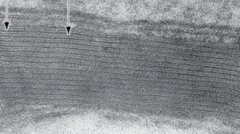
|
Myelin sheath
|
|
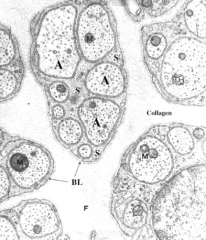
|
Schwann cell and unmyelinated axons
|
|
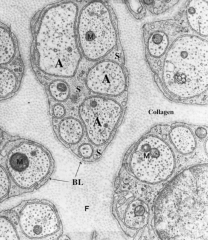
What does BL stand for?
|
Basal lamina
|
|
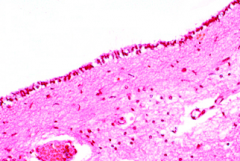
|
ependymal
|
|
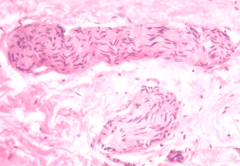
|
Peripheral nerves
|
|
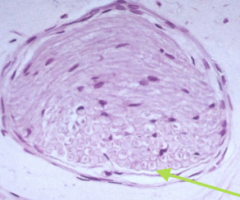
|
Peripheral nerves
|
|
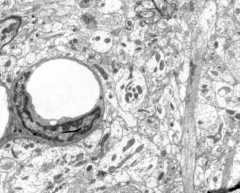
PNS or CNS
|
CNS - no connective tissue between cells
|
|
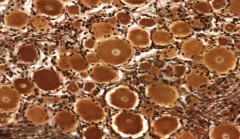
CNS or PNS
|
PNS - neuronal cell bodies surrounded by satellite cells. Cross section of ganglion
|
|
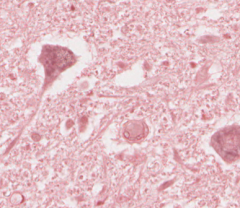
CNS or PNS?
|
CNS - neurons with surrounding glial cells. The white area around the neurons is the space where they have shrunk during processing
|
|
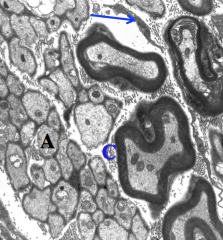
CNS or PNS?
|
PNS. Space around cells is filled with collagen, the arrow is pointing to a fibrocyte, and the structures at A are unmyelinated axons.
|
|
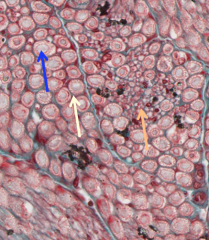
CNS or PNS?
|
PNS, as there is connective tissue - the blue tissue is endoneurium. Can see myelinated and nonmyelinated axons.
|
|
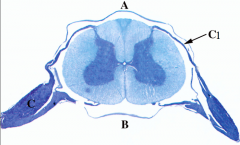
What is at C1?
|
Dorsal root, carries sensory information to the CNS, afferent.
|
|
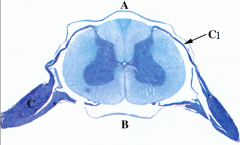
What is at C?
|
Dorsal root ganglion, carries sensory information to the CNS, afferent.
|

