![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nervous system |
Communication network within the body. |
|
|
|
Central nervous system (CNS) |
Brain & spinal cord; coordinates activity of the body. Controls & interprets information. |
They never let me do anything. Tell me what they’re saying. |
|
|
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
Nerves connecting the CNS to the rest of the body & environment. |
|
|
|
2 peripheral nervous system subdivisions : |
Somatic Autonomic |
2-ic |
|
|
Somatic |
Serves outer areas of the body & skeletal muscle; voluntary. |
S.O. You’re all bones |
|
|
Autonomic |
Involuntary systems (heart, digestion). |
|
|
|
2 Autonomic subdivisions : |
Parasympathetic Sympathetic |
2-pathetic |
|
|
Parasympathetic |
Decreases activation during rest & recovery. |
R&R |
|
|
Sympathetic |
Increases activation to prep for activity. |
Meal ... for tomorrow |
|
|
Neuron |
Functional unit of the nervous system. |
|
|
|
Motor (efferent) neurons : Transmit...; Stimulate... |
Transmit nerve impulses from CNS to effector sites. Stimulate muscle contraction & create movement. |
Taking the bus to the effector. Pain of child birth to Make life |
|
|
Sensory (afferent) neurons |
Respond to stimuli; transmit nerve impulses from effector sites to CNS. |
Answering a question. Send to C. |
|
|
3 Nervous system functions |
Sensory Integrative Motor |
There are 3 |
|
|
Sensory |
Changes in the environment. |
Metamorphosis. |
|
|
Integrative |
Analyze & interpret. |
|
|
|
Motor |
The neuromuscular response. |
Answers NM. |
|
|
Mechanoreceptors |
Sense distortion in body tissues. |
3rd eye, something is wrong. |
|
|
Joint receptors |
Responds to pressure, acceleration, & deceleration of joints. |
Answer me. speeds you’re under. |
|
|
Muscle spindles |
Sense changes in muscle length. |
How big you’ve grown! |
|
|
The cell body (soma) of a neuron contain |
A nucleus Lysosomes Mitochondria Golgi complex |
GLAM |
|
|
What are the 3 main parts that make up a neuron? |
Axon Dendrites The cell body |
|
|
|
What does the axon provide? |
Communication from the brain/spinal cord to other parts of the body. |
Communication from CNS |
|
|
Dendrites |
Gather info from other structures, transmitting it back into the neuron. |
Collect & return to sender. |
|
|
Tendons |
Connect bone to muscle; provide anchor for muscles to produce force. |
|
|
|
Fascia |
Outer layer of connective tissue surrounding a muscle. |
Covers the epimysium. Banana peel. |
|
|
Fascicles |
Bundle of individual muscle fibers. |
Pack of singular box braids. Surrounded by perimysium. |
|
|
Cross section of a muscle : 4 parts : |
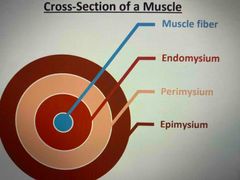
Back (Definition) |
3 -mysium |
|
|
Epimysium |
layer of connective tissue underneath the fascia, surrounding the muscle. |
1st |
|
|
Perimysium |
Connective tissue that surrounds the fascicles. |
|
|
|
Endomysium |
Deepest layer of connective tissue surrounding individual muscle fibers. |
Surrounds middle. |
|
|
Muscle fiber |
Cellular components & myofibrils encased in a plasma membrane. |
In a case |
|
|
Sarcomere pictured: |
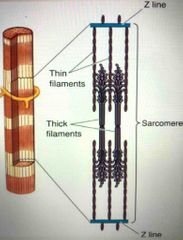
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Sliding filament theory |
Thick/thin filaments slide past one another, shortening the entire sarcomere. |
The sarcomeres length is changed. |
|
|
Type I (slow twitch) muscle tissue |
Smaller size; fatigue slowly. |
Little cross country. |
|
|
Type II (fast twitch) muscle tissue |
Larger size; quick to produce maximal tension; fatigue quickly. |
Big sprinter. |
|
|
Motor unit |
1 motor neuron & the muscle fiber it connects with. |
Connecting fiber . |
|
|
Neural activation |
Contraction of a muscle generated by neural stimulation. |
Flex by waking up. |
|
|
Neurotransmitters |
Chemical messengers that transport impulses from nerve to muscle. |
Scientist/mail man acting on instinct. N-M |
|
|
Local stabilization system |
Attach directly to vertebrae. |
Good posture. |
|
|
Local stabilization system consists of : |
Transverse abdominis Internal oblique Multifidus Pelvic floor Diaphragm
|
5 Timpd |
|
|
Global stabilization system |
Attach from pelvis to spine. |
Women bore the world |
|
|
Movement system |
Attaching spine &/or pelvis to extremities. |
global stabilization attaching to others. |
|
|
The Movement system consists of : |
Latissimus dorsi Hip flexors Hamstring complex Quadriceps |
4 muscles. L Double H, Q |
|
|
The muscle action spectrum : |
Concentric Eccentric Isometric |
There are 3. I.C.E. |
|
|
Hamstring complex |
Biceps femoris – long head Biceps femoris-short head Semimembranosus Semitendinosus |
BBSS |
|
|
Concentric |

Muscle force greater than resistive force; muscle shortens. |

Jumping upward “Lifting” phase of resistance “dumbbells” ___ Force vs ___ force |
|
|
Eccentric |

Muscle develops tension while lengthening; decelerates force. |

Landing from a jump “Lowering” phase (weight) of resistance ___ gets into a fight & grows, ____ force. |
|
|
Length tension relationship |
Resting length of a muscle & the tension it can produce at that length. |
Resting and fighting |
|
|
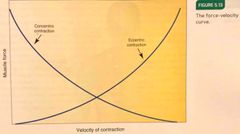
Force velocity curve |
As the velocity of a contraction increases, concentric force decreases & eccentric force increases. |
Contract up ➡️ C in I.C.E. down ➡️ E In I.C.E. up |
|
|
The force-velocity curve pictured : |
Projection protruding from a bone; muscles, tendons, & ligaments can attach. |
There are 12 3 rhomboids 3 trapezius 2 pectoralis 3 deltoid |
|
|
Neuromuscular efficiency |
Ability to produce/reduce force, & stabilize the kinetic chain in all 3 planes. |
Produce force & stabilize chain. |
|
|
Structural efficiency |
Alignment of the musculoskeletal system that allows center of gravity to be maintained over base of support. |
Lining up MSS for COG to be kept. |
|
|
Important joint types to know : (plane) |
Hinge : elbows, ankles; sagittal plane movement Ball & socket : shoulders, hips; most mobile ROM, all 3 planes of motion |
Door  |
|
|
Weight bearing exercise : |
The best method to strengthen bones. |
|
|
|
Autogenic inhibition |
When neural impulses sensing tension are greater than impulses causing muscles to contract; inhibits the muscle spindles. |
More Senses |
|
|
Reciprocal inhibition |
Simultaneous contraction of one muscle, and relaxation of its antagonist to allow movement. |
Contract+relax |
|
|
Relative flexibility |
Tendency of the body to seek the path of least resistance. |
Less tightness. Going down the easiest trail. |
|
|
Axial skeleton |
Skull, rib cage, vertebral column. |
RSV |
|
|
Appendicular skeleton |
Upper/lower extremities, shoulder & pelvic girdle’s. |
ULSP |
|
|
What are the Skeletal system functions? |
Supports, protects, allows bodily movement. |
|
|
|
Depressions |
Flattened indented portions of a bone; can be muscle attachment sites. |
|
|
|
Process |
Projection protruding from a bone; muscles, tendons, & ligaments can attach. |
|
|
|
Ligaments |
Connect bone to bone; little blood supply; slow to heal. |
3 things they do. |
|
|
Arthrokinematics |
Joint motion. |
|
|
|
Non-synovial joints |
No joint cavity, connective tissue, or cartilage; little to no movement. Skull, pubic bones, distal joint of tibia & fibula. |
JCC |
|
|
Synovial joints are |
Held together by joint capsules & ligaments; greatest capacity for motion. 80% of all joints in the body |
JL |
|
|
What are the 6 types of synovial joint? |
Gliding (plane). Saddle. Condyloid (condylar/ellipsoidal). Hinge. Pivot. Ball-&-socket |
6. |
|
|
Types of long bones : |
Epiphysis-end of the bone. Diaphysis-this shaft portion. Epiphyseal plate-connects the 2 (epi & dia). |
|
|
|
Isometric |
Muscular force equal to resistive force; no change in muscle length. |
|

