![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nausea/Vomiting
What is the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ)? |
A cerebral center that lies near the medulla. The CTZ receives most of the impulses from drugs, toxins, and the vestibular center in the ear & transmits them to the vomiting center.
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting
What is the vomiting center? |
A cerebral center in the medulla. Dopamine, acetylcholine, sensory impulses (odor, smell, taste, & gastric mucosal irritation) stimulate the vomiting center.
When the VC is stimulated, the motor neuron responds by causing contraction of the diaphragm, the anterior abdominal muscles, and the stomach. The glottis closes, the abdominal wall moves upward, and vomiting occurs. |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting
Pathophysiology |
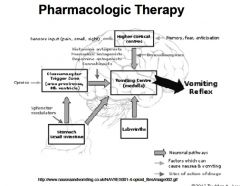
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting
Drug Classes/Types (10)? |
Antihistamine-Anticholinergic Agents
Phenothiazines Butyrophenones Corticosteroids Metoclopramide (Reglan) Selective Serotonin Antagonists Cannibinoids Benzodiazepines Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) Receptor Antagonist Trimethobenzamide (Tigan) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Antihistamine-Anticholinergic Agents
Agents (6)? |
dimenhydrinate (Dramamin)
diphenhydramine (Benadryl) hydroxyzine (Atarax) promethazine (Phenergan) meclizine (Bonine) scopolamine (Transderm Scop) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Antihistamine-Anticholinergic Agents
Indications? |
simple N/V, N/V due to motion sickness, in combination for more complex N/V
Inpatient - adjunct Outpatient - 1st line |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Antihistamine-Anticholinergic Agents
MOA? |
interrupts various visceral afferent pathways that stimulate nausea and vomiting
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Antihistamine-Anticholinergic Agents
Adverse Effects? |
Drowsiness, confusion, blurred vision, dry mouth, urinary retention, and possibly tachycardia
Higher doses / more frequent administration increases the risk of anticholinergic adverse effects. |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Phenothiazines
Agents (3)? |
chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
perphenazine (Trilafon) prochlorperazine (Compazine) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Phenothiazines
Indications |
simple N/V, mildly emetogenic doses of chemotherapy; in combination for more complex N/V
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Phenothiazines
MOA? |
blocks dopamine receptors, most likely in the CTZ
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Phenothiazines
Adverse Effects? |
extrapyramidal reactions, marrow aplasia, excessive sedation, cardiac arrhythmias
QTC prolongations, dysrhythmias Excess sedation (especially in elderly) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Butyrophenones
Agents (1)? |
droperidol (Inapsine)
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Butyrophenones
Indications? |
Post-operative N/V (PONV); adjunct for chemotherapy induced N/V (CINV)
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Butyrophenones
MOA? |
blocks dopaminergic stimulation of the CTZ
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Butyrophenones
Adverse Effects? |
sedation, dystonic reactions, cardiac arrhythmias
Higher doses (>2.5 mg) may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Corticosteroids
Agents (2)? |
dexamethasone (Decadron)
methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Corticosteroids
Indications? |
PONV, CINV
NOT indicated for simple nausea & vomiting |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Corticosteroids
MOA? |
unknown; inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may play a role
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Corticosteroids
Adverse Effects? |
mood changes (anxiety to euphoria), HA, metallic taste, abdominal discomfort, hyperglycemia, itchy throat
Monitor blood glucose in DM patients |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Metoclopramide (Reglan)
Indications? |
PONV, CINV, delayed CINV
Adjust dose in renal dysfunction |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Metoclopramide (Reglan)
MOA? |
blocks dopaminergic receptors in the CTZ; stimulates cholinergic activity in the gut increasing gut motility; blocks serotonin receptors in the intestines
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Metoclopramide (Reglan)
Adverse Effects? |
extrapyramidal effects, dystonic reactions, restlessness, drowsiness, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, urinary retention, tachycardia, arrhythmia
Give with IV diphenhydramine to avoid EPS (delayed CINV) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Selective Serotonin Antagonists
Agents (4)? |
ondansetron (Zofran)
dolasetron (Anzemet) granisetron (Kytril) palonosetron (Aloxi) - slightly longer duration ALL agents have similar efficacy |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Selective Serotonin Antagonists
Indications? |
PONV, CINV, delayed CINV
May not be effective for controlling delayed emesis as monotherapy |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Selective Serotonin Antagonists
MOA? |
blocks serotonin receptors in the medulla, as well as those located along the vagal afferent nerves in the GI tract
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Selective Serotonin Antagonists
Adverse Effects? |
generally well tolerated, diarrhea, HA, fever, constipation, dizziness, drowsiness, arrhythmias
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Cannabinoids
Agents (2)? |
dronabinol (Marinol)
nabilone (Cesamet) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Cannabinoids
Indications? |
N/V associated with cancer chemotherapy
Reserved for patients who fail to respond adequately to other antiemetic agents. |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Cannabinoids
MOA? |
inhibition of prostaglandins or blocking adrenergic activity
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Cannabinoids
Adverse Effects? |
Mood changes, anxiety, hallucinations, memory loss, fear, confusion, euphoria, hunger, time distortion, vertigo, sedation
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Benzodiazepines
Agents (2)? |
lorazepam (Ativan)
diazepam (Valium) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Benzodiazepines
Indications? |
anticipatory N/V, rescue N/V
short-term use, huge role in CINV |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Benzodiazepines
MOA? |
causes antegrade amnesia, and decreases associated anxiety that may contribute to vomiting.
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Benzodiazepines
Adverse Effects? |
sedation, hypnosis, anxiolytic, muscle relaxation, disorientation, hallucinations, urinary incontinence
Increased fall risk d/t oversedation (esp in elderly) |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist
Agent (1)? |
aprepitant (Emend)
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist
Indications? |
delayed N/V secondary to chemotherapy (2-3 days after)
NOT recommended for long-term use in N/V |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist
MOA? |
antagonizes neurokinin (which mediates emesis)
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist
Adverse Effects? |
asthenia, dizziness, hiccups, fatigue, elevated LFT's & BUN
Drug interactions: warfarin, oral contraceptives |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Trimethobenzamide (Tigan)
Indications? |
simple N/V; PONV
alternative for patients with allergies or intolerances to other agents |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Trimethobenzamide (Tigan)
MOA? |
anticholinergic agent; inhibits stimulation of the CTZ
Offers no advantage over others, should be reserved for pts unresponsive to primary agents |
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting: Trimethobenzamide (Tigan)
Adverse effects? |
well tolerated; hypotension, somnolence, anticholinergic effects; EPS
|

