![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lichen concept |
Algae and fungus must form a new morphological entity |
|
|
Controvery around lichens |
Ended when grown apart and the put together |
|
|
How lichen interact within |
Hyphae attached to surface of alage sometimes penetrate forming hyphae, division of algal cells leads to hyphal branching |
|
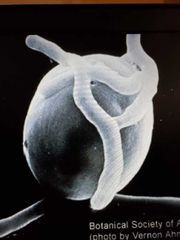
|
Lichen cell combo |
|
|
Resynthesize of lichens |
Is very difficult and only seems to work when conditions are unfavorable for individual growth, sometimes requires bacterial signalling |
|
|
Lichen uses |
Breaks down rock, reindeer food, tweed, litmus paper, usnic acid |
|

Specific lichen to know |
Letharia vulpina: vulpinic acid, wolf poison |
|
|
Lichen cortex |
Outer thick layer of hyphae |
|
|
Lichen Medulla |
Fluffy middle |
|
|
Lichen thallus |
Sterile tissue |
|
|
Three types of lichen |
Crustose, foliose, fruticose |
|

|
Foliose lichen |
|

|
Lichen |
|
|
Soredia |
Spore like lichen cells spread in asexual reproduction through fragmentation |
|
|
Lichen sexual reproduction |
Spores released from pycnidia then reach trichogyne and ascogonium. Algae does not go with |
|
|
2 major lichen photobionts |
Trebouxia, nostoc |
|
|
Lichens last few slides |
Read over |
|
|
Mantle |
Hyphae around root tip in ectomycorrhizae species |
|
|
Hartig net |
Hyphae between cortical cells in roots of mycorrhizal species |
|
|
Endomycorrhizal fungi |
Fungi penetrates cortical cells but not the cell membrane |
|

|
Endomycorrhizae |
|

|
Arbuscules of endomycorrhizae |
|

|
Vesicles of endomycorrhizae |
|
|
Fungi involved in endomycorrhizae |
Glomeromycota, obligate mutualists, fruiting bodies form underground |
|
|
Orchid mycorrhizae |
Specific to orchids, basidomycota, Rhizoctonia, parasitic on fungi for period |
|
|
Ericaceous mycorrhizae |
Heathers, rhododendrons, cranberry. Found in nutrient poor soils, hyphae fill 80% of root tissue. Nitrogen fixing |
|
|
Non-photosynthetic plants |
All vascular flowering plants, parasitic on other plants or fungi, all heterotrophic, 3000 species |
|

|
Monotropa uniflora |
|
|
3 Orders of zygomycetes |
Mucorales: sprophytic, extensive mycelium Entomopthorales: few mycelium formed, mostly insect parasites Zoopagles: predacious fungi of amoebae, paramecia, and nematodes |
|
|
Steps of mucorales sexual reproduction |
Progametangia form, gametangia walled off at tips, gametangia fuse, nuclear fusion, wall form around nuclei forming zygospore. Zygospore undergoes meiosis and creates sporangiophore. |
|

|
Zygospore |
|
|
Evolution of asexual zygomycota state |
Mortierella: simple sporagium Mucor, Rhizopus: sporagium with many spores Thamnidium: reduction is spore number, formation of sporangiola Cunninghammela: no sporangia, sporangiola only contain one spore Mycotypha: many sporangiola, densely covered |
|

|
Entomophthora muscae |
|
|
Zoosporic |
Flagellated cells at some point, somatic phase walled |
|
|
Two types of flagellum |
Whiplash: simple strand, pushes Tinsel: string like appendages, pulls |
|
|
Phyla with flagellated cells |
Chytridiomycota, hypochytridiomycota, oomycota, Myxomycota, plasmodiophoromycota |
|
|
Chytridiomycota flagella |
Posterior whiplash flagellum |
|
|
Hypochytridiomycota flagella |
Single anterior tinsel flagella |
|
|
Oomycota flagella |
One whiplash one tinsel |
|
|
Myxomycota flagella |
Two equal posterior whiplash |
|
|
Plasmodiophomycota |
Two unequal whiplash flagella |
|
|
3 orders of Chytridiomycetes |
Chytridales Blastocladiales Monoblepharidales |
|
|
Holocarpic |
Entire thallus is a reproductive structure |
|
|
Eucarpic |
Reproductive structures are formed on certain portions of the thallus |
|
|
Chytridales |
Order of Chytridiomycetes Largest order, most simple Black wort of potato |
|
|
Black wort of potato species |
Synchytrium endobioticum |
|

|
Synchytrium endobioticum |
|
|
Frog chytrid species |
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis |
|

|
Sporagia of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis |
|
|
Joyce Longcore |
Chytrid researcher |
|
|
Blastocladiales |
True mycelium, sexual reproduction by fusion, alternation of generations, form zoospores |
|
|
Anisogamous |
Two gametes within separate gametangia on same thallus |
|
|
Allomyces |
Family within blastocladiales that is anisogamous. Sirenin |
|
|
Monoblepharidales |
Most advanced chytridiomycetes No economic importance Motile male gamete fusion with non-motile female Forms oospore |
|
|
Hyphochytridiomycoya |
Within kingdom Stramenopila, chitin or cellulose cell wall. Single anterior tinsel flagellum |
|
|
Oogamous |
Reproduction by mobile male and immobile female gametes |
|
|
Oomycota clade |
Stramenopila due to: Glucans and cellulose cell wall Diploid nuclei Metabolic differences |
|
|
Orders of Oomycetes |
Saprolegniales Peronosporales |
|
|
Saprolegniales |
Order of oomycetes Water molds Poor mycelium Saprophyte Multiple oospores in oogonium |
|
|
Peronosporales |
Developed mycelia Mostly parasitic Single oospore in oogonium |
|
|
Disease on perch |
Saprolegnia |
|
|
Saprolegniales reproduction |
Meiosis, atheridium makes contact with oogonium, gametangia formed, asexual zoospores released |
|
|
Zoospore vs oospore |
Zoospore is asexual motile spore with flagella Oospore is fertilized female zygote with chitinous wall |
|
|
Peronosporales reproduction |
Asexual: cool= zoospores with indirect germination, warm= direct germination by germ tube Sexual: fusion of gametes between antheridium and oogonium, forms oospore |
|
|
Families of peronosporales |
Albuginaceae: club shaped sporangiophore Peronosporaceae: sporangiophore with determinate growth Pythiaceae: sporangiophore with indeterminate growth |
|

|
Downy mildew of crucifer caused by peronosporaceae |
|

|
Peronospora parasitica |
|

|
Phytophora infestans, late blight of potato |
|
|
Sudden oak death |
Phytophthora ramorum |
|
|
Slime mold types |
Myxomycota: acellular true slime molds Plasmodiophomycota: parasitic slime molds Dictyosteliomycota: dictyostelid cellular |
|
|
Myxomycota |
No cell well in vegetative stage Feed by phagocytosis Reproduce by spores |
|
|
Life cycle of myxomycota |
Spore, germination, plasmogamy, karyogamy, maturation, sporulation, sporagium, meiosis |
|
|
Plasmogamy |
Sexual fusion of cytoplasm bringing two haploid nuclei together |
|
|
Karyogamy |
Fusion of haploid nuclei |
|
|
Three fruiting body types in myxomycota |
Sporangium: stalk with peridium Aethallium: clump formed sporangia Plasmodiocarp: veins of plasmodium |
|

|
Diachea in myxomycota |
|

|
Fuligo septica in myxomycota |
|

|
Myxomycota |
|
|
Cellular slime molds |
Dictyosteliomycota, vegetative state is free-living amoeba, aggregate to form sorocarp |
|
|
How aggregation occurs in cellular dictyosteliostelium |
Break down ATP into cAMP which attracts other cells |
|
|
Pseudoplasmodium |
Slug, dictyosteliomycota |
|
|
Plasmodiophoromycota |
Endoparasitic slime molds Rhizaria not amoebozoa Obligate parasites Cruciform division of nuclei |
|
|
Club root of cabbage |
Plasmodophora brassicae of plasmodiophomycota |
|
|
Powdery scab of potato |
Spongospora subterranea |
|

|
Spongospora of plasmodiophomycota |
|
|
What makes kingdom fungi |
Spores, chitinous cell wall, ergosterol, exoenzymes, small nucleus |
|
|
Question for exam How does reproduction within Allomyces and Dictyostelium relate in terms of attractants? |
Allomyces female gametes release sirenin to attract male gametes while amoebas in dictyosteliomycota break down ATP and release cAMP which attracts nearby cells. |
|
|
Coln of dmckpcofgs |
Domain: Eukarya Clade: Stramenopila Kingdom: Oomycota Class: Oomycetes Order: Peronosporales Family: Pythiaceae Genus: Phytophthora Species: Phytophthora infestans |
|
|
Sporangium vs sporangiolum |
Sporangium: Globose structure around a sterile columella with an outer spore region Sporangiolum: spore bering structure with few spores. More advanced |

