![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Basidio life cycle |

|
|
|
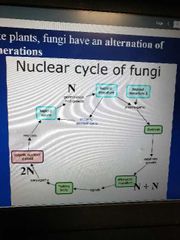
Nuclear cycle |
|
|
|
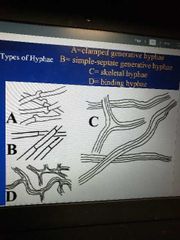
Hyphal types |
|
|
|
Monomitic |
Only septate generated hyphae |
|
|
Dimitic skeletal |
Septate generated hyphse and thick walled non septate hyphse |
|
|
Dimitic binding |
Septate generative hyphae and thin binding hyphae |
|
|
Trimitic |
Septate generative hyphae and thick walled skeletal and thin binding |
|
|
Mycosis |
Growing on human tissue |
|
|
Mycetismus |
Ingested toxic fungi |
|
|
Mycotoxicosis |
Ingested fungal toxins in food |
|
|
Mycoallergies |
Allergic to fungi |
|
|
Cyclopeptides |
Attacks rna in the liver |
|
|
Monomethyl hydrazine |
Destroys red blood cells |
|
|
Coprine |
Blocks alcohol dehydrogenase |
|
|
Muscarine |
Induces fluid loss |
|
|
Ibotenic acid |
Powerful halucigen |
|
|
Basidiocarp |
In gasteromycetes a sac where basidia form |
|
|
Peridium |
Outer enclosed layer of gasteromycetes |
|
|
Gleba |
Spore bearing inner mass of gasteromycetes |
|
|
Perdiole |
Spore filled thing in Nidulariales |
|
|
Hapteron |
Sticky end of funicular cord that hangs peridole from a leaf or something |
|
|
Morphological species concept |
Visible characters on the specimen |
|
|
Biological species concept |
Populations of fungi that can mate |
|
|
Ecological species concept |
Determined by substrate and host |
|
|
Evolutionary species concept |
Common ancestral lineage |
|
|
Composite species concept |
Combination of all factors |
|
|
Artificial system approach to systematics |
Based on large scale features, not used in science |
|
|
Gestalt system approach to systematics |
Id by overall characters all together |
|
|
Phenetic system approach to systematics |
Numbers based approached that excludes evolutionary factors |
|
|
Cladistic system approach to systematics |
Based on shared derived characters |
|
|
Synapomorphy |
Shared form evolved separately |
|
|
Isozymes |
Slightly different forms of the same protein used in molecular ID |
|
|
Rust life cycle |

|
|
|
Macrocyclic |
Long cycled, rusts |
|
|
5 spore stages of rusts |
Pycina, aeciospores, urediniospores, teliopores, basidiospores |
|
|
Heteroecious |
Need more than one host specues |
|
|
Autoecious |
Single host species |
|
|
Obligate parasite |
Cannot complete life cycle without host |
|
|
Facultative parasite |
Can complete life cycle without host |
|
|
Demicyclic |
Rust life cycle thats missing aeciospores (2) |
|
|
Microcyclis |
Rust life cycle that only has teliospores and basidiospores |
|
|
Smut life cycle |

|
|
|
Differences between rusts and smuts |

|

