![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 6 functions of the skin? |
*Blood reservoir *Excretion *Metabolism *Protection *Thermoregulation *Sensory reception |
|
|
What are the 4 types of epithelial cells found in the skin? |
*Keratinocytes *Melanocytes *Langerhans cells *Merkel cells/discs |
|
|
________ are dispersed only throughout the deepest layer of the epidermis. They produce _____ which is a product taken up by keratinocytes to provide them protection from UV rays. |
Melanocytes, Melanin |
|
|
_______ cells arise from bone marrow & migrate to the epidermis, dispersing throughout the second deepest layer. They ingest foreign material & activate the immune system as necessary. |
Langerhans cells |
|
|
_______ cells or discs are only found occasionally in the epidermis. They are specialized cells associated with sensory nerve endings in the dermis that respond to touch. |
Merkel cells or discs |
|
|
Most superficial layer, 20-30 layers of dead cells, flat membranous sacs filled with keratin. Glycolipids in extracellular space. Stratum Corneum or Stratum Basale? |
Stratum Corneum |
|
|
Five layers of flattened cells, organelles deteriorating, cytoplasm full of lamellar granules (release lipids) & keratohyaline granules. Stratum Spinosum or Stratum Granulosum? |
Stratum Granulosum |
|
|
Several layers of keratinocytes unified by desmosomes. Cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin. Stratum Spinosum or Stratum Granulosum? |
Stratum Spinosum |
|
|
Deepest epidermal layer; one row of actively mitotic stem cells; some newly formed cells become part of the more superficial layers. See occasional melanocytes & dendritic cells. Stratum Corneum or Stratum Basale? |
Stratum Basale |
|
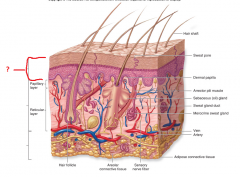
Epidermis, Dermis or Subcutaneous? |
Epidermis |
|
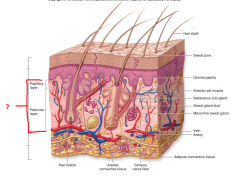
Epidermis, Dermis or Subcutaneous? |
Dermis |
|
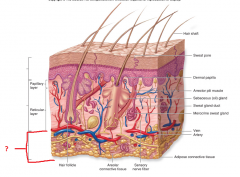
Epidermis, Dermis or Subcutaneous? |
Subcutaneous |
|
|
The dermis is made up of 2 layers? |
Papillary layer & Reticular layer |
|
|
The dermis is divided into 2 layers, the Papillary layer & the Reticular layer. Which do these descriptions belong to? *20% of the dermis *Contain dermal ridges *Contain dermal papillae *Superficial layer *Composed of Areolar CT |
Papillary layer |
|
|
The dermis is divided into 2 layers, the Papillary layer & the Reticular layer. Which do these descriptions belong to? *80% of the dermis *Contains some adipose tissue *Deep layer *Composed of dense irregular CT |
Riticular layer |
|
|
_____ are a protective covering found on the distal end of the digits. |
Nails |
|
|
_____ are formed from the stratum corneum of the epidermis and are composed of hardened keratinized cells. |
Nails |
|
|
_____follicles produce _____ (pili), which are flexible strands of hardened, dead keratinocytes. |
Hair |
|
|
Hair is important for? |
*Detecting insects on the skin before they bite or sting. *Guarding against heat loss & UV radiation. *Shielding eyes (eyelashes) *Filtering the air we breathe (nose) *Acting as sensitive touch receptor in coordination with nerve plexus. |
|
|
Each _____ follicle is associated with an arrector pili muscle which pulls it 'straight up' upon contraction (e.g. when cold or scared) creating dimples in the skin surface, known more commonly as goosebumps. |
Hair |
|
|
______ glands, the body's only type of holocrine gland, are distributed throughout the body (except in the thickest skin) as outgrowths from hair follicles. |
Sebaceous (oil) glands |
|
|
_______ glands produce and secrete sebum which: *Softens & lubricates hair and skin *Prevents hair becoming brittle *Slows water loss from the skin *Kills some bacteria |
Sebaceous (oil) glands |
|
|
______ glands are dispersed throughout the entire skin (except the nipples and parts of the external genitalia). There are two types of ______ glands. |
Sweat glands |
|
|
What are the 2 types of sweat glands? |
Eccrine & Apocrine sweat glands |
|
|
_____ sweat glands are the most abundant type of sweat gland. Particularly plentiful on the palms of the hands, soles of feet & forehead. Eccrine sweat gland or Apocrine sweat gland? |
Eccrine sweat gland |
|
|
The limited number of _____ sweat glands are found in the axillary (armpit) & anogenital (anus & gentitals) regions. These glands lie deeper in the dermis & empty into hair follicles. Eccrine sweat gland or Apocrine sweat gland? |
Apocrine sweat gland |
|
|
______glands play a major role in thermoregulation via their ability to disperse heat from the body. The water in _____ contains heat from the body and when it is secreted onto the surface of the skin it evaporates, dissipating the heat into the air and thereby removing it from the body. |
Sweat glands |

