![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Several enzymatic triglycerides methods measure the production or consumption of
|
NADH
|
|
|
The most likely cause for serum/plasma to appear "milky" is the presence of:
|
Increased chilomicrons
|
|
|
In the colorimetric determination of cholesterol, using the enzyme cholesterol oxidase, which the agent that oxidizes the colorless organic compound, 4aminoantipyrine, to a pink complex?
|
hydrogen peroxide (h202)
|
|
|
Which lipoprotein is the major carrier of cholesterol to peripheral tissues?
|
VLDL
|
|
|
Are increased levels of apolipoprotein A-I are associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease?
|
False
|
|
|
A patient is admitted to the hospital with intense chest pains. The patient's primary care physician requests that the emergency room doctor order several tests, including a lipid profile with cholesterol fractionation. The patient's results are as follows:Total Cholesterol = 400 mg/dL Triglycerides = 300 mg/dLHDL Cholesterol = 100 mg/dL LP Electrophoresis - pending The LDL cholesterol for this patient would be ____ mg/dL.
|
240 |
|
|
A patient is admitted to the hospital with intense chest pains. The patient's primary care physician requests that the emergency room doctor order several tests, including a lipid profile with cholesterol fractionation. The patient's results are as follows: Total Cholesterol = 400 mg/dL Triglycerides = 300 mg/dL HDL Cholesterol = 100 mg/dL LP Electrophoresis - pending This patient's LDL cholesterol is:
|
PT's cholesterol is High > 135mg/dL
|
|
|
As part of a lipoprotein phenotyping, it is necessary to perform total cholesterol and triglyceride determinations, as well as lipoprotein electrophoresis. The test results obtained from such studies were: Triglyceride, 340 mg/dL (reference range, < 150 mg/dL) Total cholesterol, 180 mg/dL (reference range, < 200 mg/dL) Pre-beta-lipoprotein fraction increased, Beta-lipoprotein fraction normal, No chylomicrons present, Serum appearance turbid The best explanation for these results would be that the individual exhibits a phenotype indicative of:
|
hyperlipoproteinemia |
|
|
Which apolipoprotein, when present in an increased concentration, would be associated with a decreased risk of coronary artery disease?
|
Apo AI
|
|
|
Which results would be the most consistent with high risk for coronary heart disease?
|
20 mg/dL HDL cholesterol and 250 mg/dL total cholesterol
|
|
|
What is the presumed defect in most cases of familial type IIa hyperlipoproteinemia?
|
Defective receptors for LDL
|
|
|
Hyperchylomicronemia (type l) in childhood has been associated with
|
Deficiencies of apolipoprotein cII and lipoprotein lipase
|
|
|
Which cardiac marker is elevated for the longest period after myocardial infarction (Ml)?
|
tropoin T |
|
|
What occurs during a state of low blood volume and decreased extracellular sodium level (as in cardiac failure)?
|
converted to angiotension which endues the secretior of aldosteron by the agenio gland which in terns increasion in sodium and retention of water |
|
|
A hemolyzed specimen is received in the laboratory for enzyme analysis. The assay for which of the following enzyme values would be affected by hemolysis?
|
creatine kinase |
|
|
Which isoenzyme of creatine kinase (CK) is primarily found in cardiac muscle?
|
CK-MB |
|
|
Myocardial infarction can produce a CK isoenzyme profile that is similar to:
|
strenuous exercise |
|
|
Which cardiac markers is the first to increase after an acute myocardial infarction?
|
myoglobin Ck- mb |
|
|
What is true regarding the clinical use of CK-MB (CK2)?
|
mass unit assays are more sensitive than electrophratic method |
|
|
Isoforms of CK are
|
formed in the circulation by hydrlolsis of lycine from ck mm and ck-mb |
|
|
In a nonmyocardial, as opposed to a myocardial, cause of an increased serum or plasma CK-MB, what would be expected?
|
increased ck-mb that is persistent |
|
|
An LD flip, in assessing a possible myocardial infarction, refers to:
|
LD grater than LD2 |
|
|
Which Ml marker is the most specific and sensitive and remains elevated for 14 days or more?
|
troponin T |
|
|
how are proteins classified? |
on their shape and solubility
|
|
|
3 tissue sources |
skeletal muscle, heart muscle, brain tissue |
|
|
3 tropoin |
TnT, TnI, TnC |
|
|
triglycerides components
|
three fatty acids and one glycerol molecule
|
|
|
general structure of amino acid |
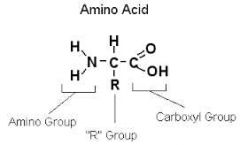
|

