![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
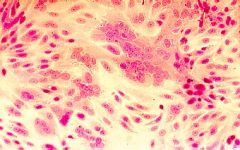
Cell culture of what virus?
|
RSV
(note the syncytia) (Lack of inclusions) |
|
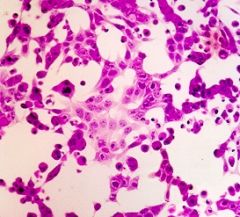
Cell culture of what virus?
|
Adenovirus
(grape-like clusters of rounded cells) (dark basophilic nuclear inclusions) |
|
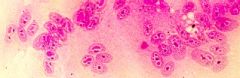
Cell culture of what virus?
|
Measles
(Syncytia) (Large intranuclear eosinophilic inclusions) |
|
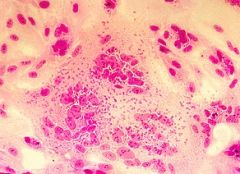
Cell culture of what virus?
|
Mumps
(Syncytia. Indistinguishable from RSV based on CPE - cytopathic effect - but has a hemagglutin protein = RBCs adhere to cell surfae. aka hemadsorption & allows differentiation between mumps & RSV) |
|
|
Which viruses form syncytia?
|
RSV
Measles Mumps HSV |
|
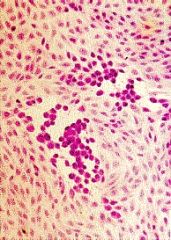
Cell culture of which virus?
|
HSV
-Grows fast in culture (3d) -Plaques of rounded cells -Nuclear inclusions -Formation of giant cells and multi-nucleate syncytia -COWDRY BODIES |
|
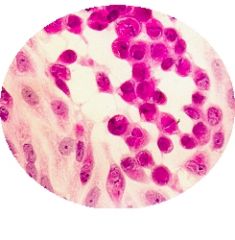
Virus?
|
CMV
Grows only in fibroblasts Slow OWLS EYE NUCLEI Nuclear & cytoplasmic inclusions |
|
|
DNA viruses that are nonenveloped?
enveloped? |
Non: Parvo, Adeno, Papova, Polyoma
Env: Herpes, Pox, Hepadna |
|
|
RNA viruses that are nonenveloped?
enveloped? |
Non: Calici (HEV), Picorna (enterov, HAV, rhino), Reo (Rota)
Env: all the rest |
|
|
Nuclear & cytoplasmic inclusions are seen in what viruses?
|
CMV
Measles |
|
|
Nuclear inclusions only?
|
HSV
Adeno |
|
|
Cytoplasmic inclusions only?
|
Rabies
|
|
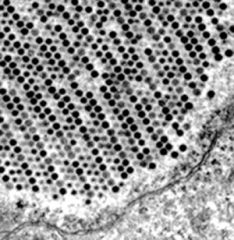
EM of what virus?
|
Adenovirus
|
|
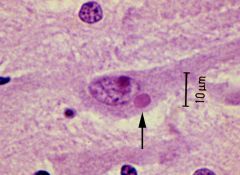
Virus?
|
Rabies
NEGRI BODY (cytoplasmic inclusion) |
|
|
Name the 7 DNA viruses
|
Parvo-viridae
Hepadna- Polyoma- Papilloma- Adeno- Herpes- Pox- |
|
|
Which DNA viruses are enveloped?
|
Hepadna
Herpes Pox |
|
|
there are 14+ RNA viruses.. which are NOT enveloped?
|
Rio / Rota
Bonya / Hanta Picorna (HAV, entero, rhino) Calici (Novo, HEV) Astro |
|
|
Which virus is ssDNA?
|
Parvo
|
|
|
Which virus is dsRNA?
|
Rota
|
|
|
What families are the hepatitis viruses in?
|
HAV: Picorna (RNA)
HBV: Hepadna (dsDNA, enveloped) HCV: Flavi (RNA, enveloped) HDV: not included - a funny type HEV: Calici (RNA) |
|
|
Which hepatitis virus is a DNA virus?
|
HBV
|
|
|
2 viruses that have both nuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions
|
CMV
Measles |
|
|
– Pneumonia in immunocompromised patients & military recruits
– Acute gastroenteritis children (40,41) – Pharyngitis, pharyngoconjunctival fever – Keratoconjunctivitis – HEMORRHAGIC CYSTITIS – Cervicitis, urethritis – Disseminated disease |
Adenovirus
|
|
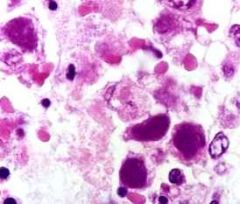
|
Adenovirus
NUCLEAR inclusion only, large basophilic Smudgy and coarse No cytomegaly or multinucleation |
|

|
EM of adenovirus virions
|
|
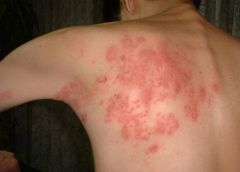
|
Shingles (zoster)
Affects one dermatome |
|
|
CMV establishes latency in?
|
Macrophages
|
|

CPE of which virus?
|
CMV
Grape like clusters of rounded cells in a clean background |
|

|
CPE of VZV
Foci of sandpaper with rounded cells |
|
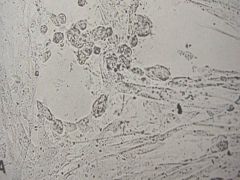
|
HSV
Rounded cells at the edge |
|
|
What virus causes roseola and what cell does it live in?
|
HHV6 (sixth disease)
T CELLS! |
|
|
What virus is the hardiest to transport and is the quickest to grow in cell culture?
Which takes the longest to grow in cell culture? |
HSV (24hrs!)
CMV (14-21d) RSV (10-14d) |
|
|
Adenovirus is latent in?
|
Lymphoid tissue
|
|
|
What strains of adenovirus cause gastroenteritis in kids?
|
40 & 41
|
|
|
HEMORRHAGIC CYSTITIS
|
adenovirus
BK virus |
|
|
Fifth disease
|
Parvovirus B19
|
|
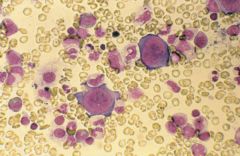
Bone marrow aspirate. Dx?
|
Parvovirus
Mature erythroid precursors are absent, and giant pronormoblasts are typical of B19 infection. |
|
|
Polyomaviruses & associations
|
JC - PML
BK - hemorrhagic cystitis |
|
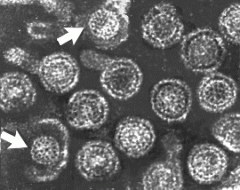
Dane particle
|
HBV virion
|
|
|
HBV belongs to what family?
|
Hepadnavirus (dsDNA enveloped)
|
|
|
HBeAg?
|
Chronic infection
|
|
|
HCV belongs to what family?
Which type of HCV is worst? HCV treatment? |
Flaviviridae
Type 1 is worst. IFN & ribavirin |
|
|
What % of HBV becomes chronic?
HCV? |
9% HBV becomes chronic
80% HCV; 25% get cirrhosis |
|
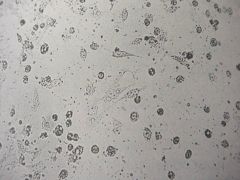
|
Enterovirus
Teardrop & Kite-like cells! |
|
|
Coxsackie A
Coxsackie B |
A: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
B: Pericarditis, myocarditis |
|
|
Picornaviridae
|
Enteroviruses (Polio, coxsackie, enterovirus)
HAV Rhinovirus non-enveloped RNA |
|
|
Orthomyxoviridae
|
Influenza
enveloped RNA Helical capsid |
|
|
Antigenic drift
|
Minor change in amino acid of H or N. cross-antibody protection
|
|
|
Antigenic shift
|
Major change. Genome rearrangement. "New" virus! No protection
|
|
|
Subtyping of influenza is based on what?
|
H (hemagglutinin) and N (neuraminidase)
|
|
|
Which influenza type is worse and why?
|
Influenza A. Can have antigenic drift or shift!
Influenza B only drifts. |
|
|
Amantidine treats?
Tamiflu treats? |
Amantidine treats Influenza A only
Tamiflu treats Influenza A & B |
|
|
Paramyxiviridae
|
Measles
Mumps RSV Parainfluenza enveloped RNA virus |
|
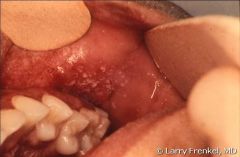
|
Koplik spots of measles
|
|
|
Atypical measles
|
Hypersensitivity reaction that occurs in patients incompletely vaccinated for measles
high fever, headache, cough, and abdominal pain. The rash may appear 1 to 2 days later, often beginning on the limbs. SUBACUTE SCLEROSING PANENCEPHALITIS |
|
|
Croup
|
Parainfluenza
Member of paramyxoviridae, enveloped RNA virus |
|
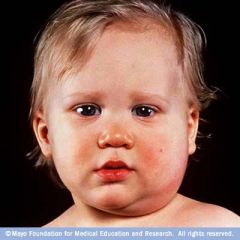
Parotitis
testes/ovary eye/ear CNS |
Mumps (paramyxoviridae)
|
|
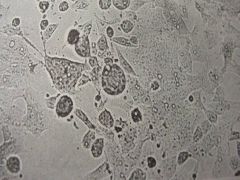
|
CPE of RSV
syncytium formation |
|
|
RSV is in what family?
|
paramyxoviridae
|
|
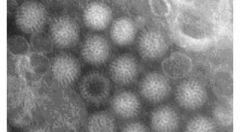
Gastroenteritis in a child
fecal specimen |
ROTAVIRUS! (wheels)
|
|
|
Adult T cell lymphoma
Tropical spastic paraperesis |
HTLV (of the retrovirsuses)
|
|
|
What type of vaccine is MMR?
|
live attenuated
|
|
|
What family are the arboviruses?
|
Trick question!
term used to refer to a group of viruses that are transmitted by arthropod vectors. The word arbovirus is an acronym (ARthropod-BOrne viruses) RNA viruses |
|
|
What mosquitoes transmit WNV, dengue and yellow fever?
|
Aedes (A. aegypti)
|
|
|
maculopapular and progresses to vessicular - all lesions
in same stage on a body area - central body outward |
Smallpox
ALL LESIONS SAME STAGE |
|
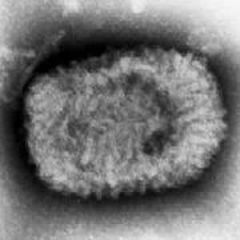
|
smallpox
|
|
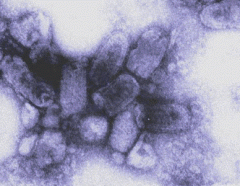
|
Rabies
bullet-shaped |
|
|
What family is rabies?
|
rhabdoviridae
|
|
|
For HIV, which proteins encode the envelope? core? reverse transcriptase?
|
envelope - gp160/gp120
core - p24 reverse transcriptase - p41 |
|
|
what is the viral transport media? What temperature is short term transport storage? What temperature is long term (>72) transport storage?
|
Hank's balanced salt solution with antibiotics
short term is 4C long term is -70C viral specimens are filtered prior to being placed on cell monolayer to eliminate bacterial contamination |
|
|
what are primary cell lines?
|
direct from animals (rhesus monkey kidney - RMK)
|
|
|
what are diploid cell lines?
|
viable for 20-50 passes, MRC-5- (microbiology research council 5) human diploid fibroblasts
|
|
|
what are continuous cell lines?
|
tumor lineage, HEp-2 and HeLa
|
|
|
Parvovirus B19 is a (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
Parvovirus B19 is a single stranded DNA virus.
|
|
|
Hepatitis B virus is a (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
Hepatitis B is a double stranded DNA virus.
NOTE: enveloped |
|
|
Polyomaviruses (JC and BK) are (single or double) stranded (linear or circular) (DNA or RNA) viruses.
|
Polyomaviruses (JC and BK) are double stranded circular DNA viruses.
|
|
|
HPV is a (single or double) stranded (linear or circular) (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
HPV is a double stranded circular DNA virus.
|
|
|
Adenovirus is (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
Adenovirus is double stranded DNA virus.
|
|
|
Name 5 members of the Herpesviridae family.
|
EBV, CMV, VZV, HSV, HHV8
|
|
|
Members of Herpesviridae are (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) viruses.
|
Members of Herpesviridae are double stranded DNA viruses.
|
|
|
Members of Poxviridae are (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) viruses.
|
Members of Poxviridae are double stranded DNA viruses.
NOTE: members include smallpox, vaccinia, molluscum contagiosum |
|
|
Rotavirus is a (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
Rotavirus is a double stranded RNA virus.
|
|
|
Hepatitis C is a (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
Hepatitis C is a single stranded RNA virus.
NOTE: Plus–stranded single–stranded RNA |
|
|
Influenza is a (single or double) stranded (DNA or RNA) virus.
|
Influenza is a single stranded RNA virus.
NOTE: is a minus–stranded single–stranded RNA virus and enveloped |
|
|
Name 2 retroviruses.
|
HIV, HTLV
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Rounding and aggregation in grape–like clusters usually in 2–10 days. Best seen in the HEP–2 line. |
Adenovirus
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Small foci of rounded cells usually in 5–21 days. Best seen in the HDF line. |
CMV
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Refractile, angular or tear–shaped in 2–8 days. Best seen in the PMK line. |
Enterovirus
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Rounded, swollen, refractile, syncytia in 1–5 days. Best seen in the HEP–2 and HDF lines. |
HSV
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Degeneration in 2–10 days. Best seen in the PMK line. |
Influenza
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
CPE usually absent in 5–10 days. (2) |
Mumps and parainfluenza
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Syncytia in 3–10 days. Best seen in HEP–2 line. |
RSV
|
|
|
Name that cytopathic effect:
Foci of rounded swollen refractile cells in 5–28 days. Best seen in HDF. |
VZV
|
|
|
Are rapid antigen tests sensitive or not?
|
Not sensitive.
NOTE: available for influenza, RSV, adenovirus |
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus only has intranuclear inclusions (not intracytoplasmic). Early inclusions are eosinophilic, finely granular, smaller and herpes–like; late inclusions are deeply basophilic and larger, with nucleocytoplasmic blurring (i.e. smudge cells). |
Adenovirus
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus has both intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions. Characterized by cytomegaly, the nucleolus is often retained; single, amphophilic intranuclear (Cowdry A) inclusion forms early on. Intracytoplasmic inclusions are multiple, smaller, basophilic, GMS and PAS positive tend to form late. |
CMV
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus has only intranuclear inclusions. There are no intracytoplasmic inclusions. Early inclusions are amphophilic with "ground glass" appearance; late inclusions eosinophilic, homogenous (Cowdry A) and surrounded by clear halo, with marginated chromatin; multinucleated syncytia (giant cells) and "molding". |
HSV
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus does not produce inclusions. |
Influenza
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus produces both intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions. Associated with multinucleated giant cells (a.k.a. Warthin–Findelday giant cells); intranuclear inclusions are herpes like. Intracytoplasmic inclusions are pleomorphic, deeply eosinophilic, hyalinized, and tallow–like. |
Measles
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus does not produce intranuclear inclusions and only very rarely produces intracytoplasmic inclusions. Associated with multinucleated giant cells (syncytia), when intracytoplasmic inclusions are present, tend to be pleomorphic. |
Parainfluenza
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus only produces intracytoplasmic inclusions and not intranuclear inclusions. Tends to form multinucleation and multiple discrete, smoothly contoured and deeply eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions. |
RSV
|
|
|
Viral histopathology:
This virus only has cytoplasmic inclusions called Negri Bodies (eosinophilic balls). No syncytia. |
Rabies
|
|
|
What is the HBV status?
HBsAg negative Anti–HBc negative Anti–HBs negative |
Never infected, never vaccinated/immunized
|
|
|
What is the HBV status?
HBsAg negative Anti–HBc negative Anti–HBs positive |
Vaccinated/immunized
|
|
|
What is the HBV status?
HBsAg positive Anti–HBc positive (IgM) Anti–HBs negative |
Acute infection
|
|
|
What is the HBV status?
HBsAg positive Anti–HBc positive (IgG) Anti–HBs negative |
Chronic HBV
|
|
|
What is the HBV status?
HBsAg negative Anti–HBc positive Anti–HBs positive |
Prior HBV infection, now recovered and immune
|
|
|
What percentage of people infected with HCV will develop chronic infection?
How about cirrhosis? HCC? |
Chronic infection: 55–85%
Cirrhosis: 10–15% of chronically infected people develop cirrhosis HCC: 5% of those with cirrhosis develop HCC |
|
|
What are 3 extrahepatic manifestations of HCV?
|
Mixed cyroglobulinemia, glomerulonephritis, aplastic anemia
|
|
|
What is the HCV status?
Anti–HCV negative HCV RNA negative |
No infection
|
|
|
What is the HCV status?
Anti–HCV positive HCV RNA negative |
– False positive Anti–HCV, no infection
– Recent recovery from acute HCV NOTE: recommend retesting in a few weeks. |
|
|
What is the HCV status?
Anti–HCV negative HCV RNA positive |
– Possible early HCV infection
– Possible chronic HCV in immunosuppressed person – Possible false negative anti–HCV due to hemodialysis NOTE: recommend retesting in several weeks |
|
|
What is the HCV status?
Anti–HCV positive HCV RNA positive |
Infected
|
|
|
How many HCV genotypes?
|
9
|
|
|
What is the response rate of combination peginterferon alpha with ribavirin in genotypes 1, 2, and 3?
What is the most common genotype in the USA? |
Genotype 1: 40% response
Genotype 2, 3: 70% response Most common genotype is 1 (80%). NOTE: genotype 2 = 20%; genotype 3 = 5% |
|
|
A positive HIV Western blot is defined as what by the CDC?
|
Any two of the followign bands:
– p24 – gp41 – gp120 or gp160 |

