![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
the two types of specific immunity acquired during an individuals life: ____________ acquired- response against antigens encountered in daily life ___________ acquired- response to antigens introduced via vaccine |
artificially |
|
|
|
naturally or artificially acquired immunity can be distinghished as either: ___________- passively receive antibodies from another individual. ___________- |
|
|
|
|
five attributes of adaptive immunity -___________: only one shape -___________: cells activate only in response to specific pathogens -___________: once induced, proliferate to clones -____________ __ ______: self tolerant -_________: responds faster in subsequent encounters |
-specificity -inducibility -clonality -unresponsiveness to self -memory |
|
|
|
_________________: mature in bone marrow. ________________: mature in thymus |
T lymphocytes |
|
|
|
two types of adaptive immune rsponses: ___________ immune responses ______-_________ immune responses |
cell-mediated immune responses |
|
|
|
primary lymphoid organs: -____ ________ __________ -__________ |
thymus |
|
|
|
Secondary lymphoid organs: - lymph ________ - ________ -________ -__________ ________ ___________ ______ (MALT) |
spleen tonsils mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) |
|
|
|
-____________: -molecules the body recognizes as foreign and worthy of attack |
antigens |
|
|
|
-_____________: -recognized by three dimensional regions called epitopes |
antigens |
|
|
|
-____________: -Include various bacterial components as well as proteins of viruses, fungi, and protozoa. |
antigens |
|
|
|
-_____________: food and dust can also contain antigenic particles. |
antigens |
|
|
|
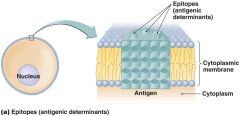
-shape: three dimensional shapes called __________. -______- 5000 Da to 100,000 Da -complexity: ______proteins, ______lipids |
size- glycoproteins, phospholipids |
|
|
|
___________ (antigenic determinants)
|
epitopes (antigenic determinants) |
|
|
|
____________ __________: orginate from microbes located outside the body cells ___________ __________: produced by intracellular microbes and incorporated in host's membrane ____________: components of normal body cells |
exogenous antigens endogenous antigens autoantigens |

|
|
|
-major function is the secretion of antibodies -small percentage of this cell circulate in blood -found primarily in the spleen, lymph nodes, and MALT -arise and mature in the red bone marrow __ ____________ (__ _____) and _______________? |
B lymphocytes (B cells) and antibodies |
|
|
|
Each ___ _____ generates a single BCR Each BCR regonizes only one __________ |
epitope |
-Two variable regions of the BCR for the antigen-binding sites -Each B lymphocytes has multiples copies of the B cell receptor (BCR) -the entire repertoire of an individual's BCRs is capable of recognizing millinons of different epitopes |
|
|
-Two variable regions of the BCR for the antigen-binding sites -Each B lymphocytes has multiples copies of the B cell receptor (BCR) -the entire repertoire of an individual's BCRs is capable of recognizing millinons of different epitopes Each ___ _____ generates a single BCR Each BCR regonizes only one __________ |
B cell epitope |

|
|
|
-___________ are immunoblobulins similar to BCRs. -Antibodies are secreted by activated B cells called ________ cells -Antibodies have identical _________-_________ sites and antigen _________ as the BCR of the activated B cell. |
antibodies are immunoglobulins similar to BCRs antibodies are secred by activated B cells called Plasma cells antibodies have identical antigen-binding sites and antigen specificity as the BCR of the activated B cell |
|
|
|
Antibody Functions: -activation of _________ and inflammation -Neutralization -___________: changing the surface of an antigen so as to enhace phagocytosis -_________ ___ ________: catalyze - ___________: soluble --> precipitates -________-dependent _______ cytotoxicity (ADCC) |
-Neutralization -opsonization: changing the surface of an antigen so as to enhance phagocytosis -killing by oxidation: catalyze; -agglutination: soluble --> precipitates -Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC |

|
|
|
Class of antibody involved in the immune response depends on the type of _________, ______ of _________, and antibody ___________ needed.
|
class of antibody involved in the immune response depends on the type of antigen, portal of entry, and antibody function needed.
|
|
|
|
five different classes of antibodies: -Ig__- first antibody produced, pentamer -Ig__- most common and longest lasting antibody, 80% -Ig__-associated with body secretions, 12% -Ig__- involved in response to parasitic infection and allergies -Ig__- membrane bound receptor of B cells; exact function is not known |
-IgM- first antibody produced, pentamer -IgG- most common and longest lasting antibody, 80% -IgA-associated with body secretions, 12% -IgE- involved in response to parasitic infection and allergies -IgD- membrane bound receptor of B cells; exact function is not known |
|
|
|
__ ___________: -Circulate in the lyph and blood and migrate to the lyph nodes, spleen, and Peyer's patches. -produced in the red bone marrow and mature in the thymus |
T Lymphocytes
|
-Have TCRs on their cytoplasmic membrane |
|
|
T Lymphocytes: -TCRs do not recognize _______ directly. - TCRs only bind epitopes associated with a ______ protein. |
TCRs do not recognize epitopes directly TCRs only bind epitopes associated with a MHC protein |
-Cell mediated immune responses: interact directly with antigens |
|
|
Describe the structure and visualize the T cell receptor (TCR) using: -Antigen-binding site (groove) -variable region -constant region -carbohydrate -disulfide bond -cytoplasmic membrane of T cell -cytoplasm : T Cell Receptor -c |

|
|
|
|
Three types of T lymphocytes: 1. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) 2.Helper T lymphocyte- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. 3. Regulatory T lymphocyte- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases, Cluster of deferentiation- CD |
|
|
|
|
Three types of T lymphocytes: 1._________ __ ___________- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) 2._______ __ __________- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. 3. __________ ___ __________- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases, ________ ___ __________- CD |
Three types of T lymphocytes:
1. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) 2.Helper T lymphocyte- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. 3. Regulatory T lymphocyte- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases, Cluster of deferentiation- CD |
|
|
|
3. __________ ___ __________- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases,
|
Three types of T lymphocytes: 1. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) 2.Helper T lymphocyte- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. 3. Regulatory T lymphocyte- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases, Cluster of deferentiation- |
|
|
|
2._______ __ __________- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. |
Three types of T lymphocytes: 1. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) 2.Helper T lymphocyte- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. 3. Regulatory T lymphocyte- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases, Cluster of deferentiation- |
|
|
|
1._________ __ ___________- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) |
Three types of T lymphocytes: 1. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte- CD8 or Tc cell, Directly kills other cells (infected or caner) 2.Helper T lymphocyte- CD4 or Th cells, Helps regulate the activities of B cells and cytotoxic T cells; secrety cytokines. 3. Regulatory T lymphocyte- Tr cells (CD4 & CD25), Represses adaptive immune responses, prevent autoimmune diseases, Cluster of deferentiation- |
|
|
|
Elements of Adaptive immunity _________ ________: -Body eleiminates self-reative lymphocytes. -Lymphocytes that react to autoantigens undergo apoptosis. -Surviving lymphocytes respond to foreign antigens |
Clonal Deletion |

|
|
|
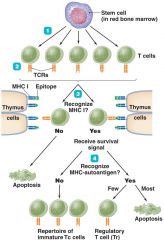
clonal deletion of T cells 1. bone marrow produces __ ____. 2. Each lymphocyte generates TCR with a particular shape. 3. T cells pass through a series of decision questions in _______. 4. Surgiving cells(?) recognize _____ _ protein bound to autoantigen. 5. ___- they survives ____- apoptosis/few Tr cells |
clonal deletion of T cells 1. bone marrow produces T Cells. 2. Each lymphocyte generates TCR with a particular shape. 3. T cells pass through a series of decision questions in thymus. 4. Surgiving cells(?) recognize MHC I protein bound to autoantigen. 5. NO- they survives YES- apoptosis/few Tr cells |
|
|
|
4 steps of Clonal deletion of B cells? (hint): similar to T cell clonal deletion. |

|
|
|
|
Elements of Adaptive Immunity ___________: -Soluble regulatory proteins that act as intercellular signals. -secreted by various leukocytes. - Interleukins (ILs): signal among leukocytes. -Interferons (IFNs): antiviral proteins that may act as cytokines. -tumor necrosis factor (TNF): secretey by macrophages and T cells to kill tumor cells and regulate immune responses and inflammation. -Chemokines: chemotactic cytokins that signal leukocytes to move |
Cytokines _________ are secreted by various leukocytes |
Cytokines |
|
|
______________ (ILs): Signal among leukocytes _____________ (IFNs): antiviral proteins that may act as cytokines _________ _______ ________ (TNF): secreted by macrophages and T cells to kill tumor cells and refulate immune responses and inflammation ____________: chemotactic cytokines that signal leukocytes to move. |
- Interleukins (ILs): signal among leukocytes. -Interferons (IFNs): antiviral proteins that may act as cytokines. -tumor necrosis factor (TNF): secretey by macrophages and T cells to kill tumor cells and regulate immune responses and inflammation. -Chemokines: chemotactic cytokins that signal leukocytes to move |
|
|
|
Preparation for an Adaptive Immune Response The roles of the ______ ________________ _______: -Goup of antigens first identified in graft patients. -Important in determining compatibility of tissues for tissue grafting. MHC antigens are glycoproteins found in the membranes of most cells of vertebrate animals. -Hold and position antigenic determinant for presentation to T cells. |
Major Histocompatibility Complex |
|
|
|
the two classes of MHC proteins
|
Eg. Skin, muscle cells MHC II- APCs- B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells.
|

|
|
|
visualize- antigen processing for endogenous antigens |
|

|
|
|
visualize- antigen processing for exogenous antigens |
|

|
|
|
activation of a clone of cytotoxic T cells stepos involved in activation of cytotoxic T cells -___________ presentation -_______ __ ____ differentiation -________ expansion -______ stimulation |
-Helper T cell differentiation -clonal expansion -self stimulation |

|
|
|
A cell-mediated immune response TCR is complementary to ____ __ + epitope complex CD8 complementary to _____ __ protein |
MHC I |

|
|
|
T-independent immune response ________ _______ responses mounted against exogenous pathogens, activates only in response to specific pathogens. 1. binding of a __ _____ to bacterial capsules, LPS of gram negative cells, capsid, bacterial glagella |
Humoral immune responses
|

|
|
|
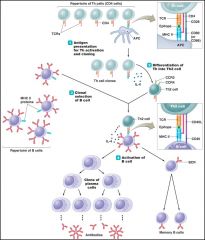
Inducement of T dependent immune response _______ ____: -majority of cells produced during B cell proliferation -Only secrete antibody molecules complementary to the specific antigen -200 antibody molecules are produced per second -short lived cells that die within a few days of activation -- their antibodies and progeny can persist |
Plasma cells |
|
|
|
_______ __ ___ and the establishment of immunological memory -produced by B cell proliferation but do not secrete antibodies -have BCRs complementary to the antigenic determinant that triggered their production -long lived cells that persist in the lymphoid tissue. -initiates antibody production if antigen is encountered again |
Memory B cells |
|
|
|
primary humoral immune responses VS Secondary humoral immune responses compare and contrast IgM and IgG at day 3 and day 6 after exposure to tetanus toxin... |

|
|
|
|
2 types of specific immunity acquired during an individual's life: -____________ acquired -____________ acquired further distinguished as: -____________ or -____________ |
naturally acquired artificially acquired active or passive |
|
|
|
________ acquired- response against antigens encountered in daily life ________ acquired- response to antigens introduced via a vaccine |
artificially |
|
|
|
________, received antibodies from another individual
|
passive immunity
|
|

