![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
152 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
most bacteria range from what in regards to diameter and length
|
0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter
2 to 8 um in length |
|
|
basic shapes of bacteria
|
spherical coccus, rod-shaped bacillus and spiral
|
|
|
when cocci divide to reproduce the cells can remain
|
attached to one another
|
|
|
diplococci
|
are cocci that remain in pairs after dividing
|
|
|
streptococci
|
cocci that remain attached in chain like structures
|
|
|
tetrads
|
cocci that divide in two planes and remain in groups of four
|
|
|
sarcinae
|
divide in three planes and remain attached in cubelike groups of 8
|
|
|
staphylococci
|
divide in multiple planes and from grapelike clusters
|
|
|
Most bacilli appear as single rods called
|
single bacilli
|
|
|
Diplobacilli appear
|
in pairs after division
|
|
|
what type of bacilli occur in chains
|
streptobacilli
|
|
|
coccobacilli
|
are oval and look so much like cocci
|
|
|
vibrio
|
bacteria that look like curved rods
|
|
|
spirilla
|
a helical shape like a corkscrew
|
|
|
spirochetes
|
group of spirals that are helical and flexible
|
|
|
monomorphic
|
bacteria that maintains a single shape
|
|
|
pleomorphic
|
can have many shapes not just one
|
|
|
how would you be able to identify streptocci thru a microscope?
|
because of it's chain like structure
|
|
|
Does a prokaryotic cell contain a nucleus?
|
No
|
|
|
does prokaryotic cells have membrane-enclosed organelles
|
no
|
|
|
what does the flagella of a prokaryotic cell consist of
|
two protein building blocks
|
|
|
glycocalyx in prokaryotes?
|
is secreted on the surface and is present as a capsule or slim layer. (Sugar coat)
|
|
|
does a prokaryote contain a cell wall?
|
It's usually present and is chemically complex (includes peptidoglycan)
|
|
|
plasma membrane in prokaryotes
|
no carbohydrates and generally lacks sterols
|
|
|
does a prokaryote contain a cytoplasm or streaming
|
no cytoplasmic streaming or cytoskeleton
|
|
|
size of the ribosomes in a prokaryotic cell
|
70S
|
|
|
the chromosomes (DNA) of prokaryotic cells
|
are usually single circular chromosome
|
|
|
what do prokaryotic cells lack in their chromosomes
|
histones
|
|
|
how does cell division occur in prokaryotic cells
|
binary fission
|
|
|
sexual recombination in prokaryotic cells
|
does not occur only transfer of DNA
|
|
|
size of a Eukaryotic cell
|
10-100um in diameter
|
|
|
does a eukaryotic cell contain a nucleus?
|
yes, a true nucleus (nuclear membrane and nucleoli)
|
|
|
Are membrane-Enclosed organelles present in eukaryotic cells?
|
Yes, they include (lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and chloroplasts)
|
|
|
The Flagella in eukaryotes is
|
complex, consist of multiple microtubules
|
|
|
is Glcocalyx present in Eukaryotic cells?
|
yes, but it is only present in cells that lack a cell wall
|
|
|
the cell wall of eukaryotic cells is
|
chemically simple includes; cellulose and chitin
|
|
|
the plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells is
|
sterols and carbohydrates that serve as receptors
|
|
|
the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells have
|
cytoskeleton and cytoplasmic streaming
|
|
|
what size are the ribosomes of a eukaryotic cell and in organelles?
|
80S and (70S in organelles
|
|
|
the chromosomes (DNA) of eukaryotic cells are
|
multiple linear chromosomes with histones
|
|
|
cell division of eukaryotic cells involves
|
mitosis
|
|
|
sexual recombination in eukaryotic cells involves
|
meiosis
|
|
|
motility
|
the ability of an organism to move by itself
|
|
|
what is found in prokaryotic cells but not eukaryotic cells
|
peptidoglycan
|
|
|
how does most bacteria multiply
|
by binary fission
|
|
|
what type of bacteria can assume several shapes
|
pleomorphic
|
|
|
capsules may protect pathogens from what
|
phagocytosis
|
|
|
what does a flagella consist of
|
filament, hook and basal body
|
|
|
why would a prokaryotic flagella rotate
|
to push the cell
|
|
|
what type of protein is an antigen
|
Flagellar H protein
|
|
|
spiral cells that move by means of an axial filament are called
|
spirochetes
|
|
|
what is the main difference between axial filaments and flagella
|
axial filaments wrap round the cell
|
|
|
what helps the cells adhere to surfaces
|
fimbriae
|
|
|
what is simple diffusion
|
movement of molecules or ions from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
|
|
|
what is facilitated diffusion
|
proteins function as channels or carriers that facilitate the movement of ions or large molecules across the plasma membrane
|
|
|
osmosis
|
movement of solvent molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area with a high concentration of solvent molecules to an area of low concentration solvent molecules
|
|
|
osmotic pressure
|
the pressure required to prevent the movement of pure water into a solution containing some solutes
|
|
|
isotonic solution
|
a medium in which the overall concentration of solutes equals that found inside the cell
|
|
|
hypotonic sol
|
concentration of solutes is lower than that inside the cell
|
|
|
what can happen if the cell wall is weak and it takes in water?
|
it can burst or indergo osmoticlysis
|
|
|
what is a hypertonic sol
|
when its higher concentration outside the cell than inside
|
|
|
what do the terms isotonic, hyper and hypotonic describe
|
the concentration of solutions outside the cell relative to the concentration inside the cell
|
|
|
active transport
|
the uses of energy in the form of ATP to move substances across the plasma membrane
|
|
|
once a substance is altered and inside the cell what happens to the plasma membrane
|
it becomes impermeable to it
|
|
|
what is the cytoplasm
|
substance in side the plasma membrane of prokaryotic cel
|
|
|
nucleoid
|
contains a single long, continuous and frequently circularly arranged thread of double stranded DNA
|
|
|
plasmids are
|
circular extrachromosomal double-stranded DNA molecules
|
|
|
plasmids may be gained or lost without
|
hurting the cell
|
|
|
what does the cytoplasm consist of
|
mostly water, organic and inorganic molecules, DNA ribosomes and inclusion
|
|
|
the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells contain numerous
|
70s ribosomes (rRNA and protein)
|
|
|
where does protein synthesis occur
|
at ribosomes
|
|
|
how can ribosomes be inhibited
|
by certain antibiotics
|
|
|
what are inclusions
|
reserve deposits in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
what are endospores
|
resting places for some bacteria
|
|
|
what is the shape of flagella and where are they found
|
they are few and long found in eukaryotic celsl
|
|
|
describe cilia
|
they are numerous and short
|
|
|
flagella and cilia are used for
|
motility
|
|
|
cilia move
|
substances along the surface of cells
|
|
|
what is the arrangement of flagella and cilia
|
nine pairs and two single microtubules
|
|
|
what does the cell walls of many algae and fungi contain
|
cellulose
|
|
|
what is the main material of fungal cell walls
|
chitin
|
|
|
what are animal cells surrounded by
|
glycocalyx
|
|
|
what does glcocalyx do
|
strengthen the cell and provide means of attachment to other cells
|
|
|
the eukaryotic plasma membrane is a
|
phospholipid bilayer containing proteins
|
|
|
how can eukaryotic cells move materials across the plasma membrane
|
by the passive processes used by prokaryotes and by active transport and endocytosis
|
|
|
the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells includes
|
everything inside the plasma membrane external to the nucleus
|
|
|
the 80s ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells are attached to
|
rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
what is the most characteristic eukaryotic organelle
|
the nucleus which contains DNA in the form of chromosomes
|
|
|
what is the endoplasmic reticulum
|
what the nuclear envelope is connected to in the cytoplasm
|
|
|
the ER provides
|
surface of chemical reactions and serves as a transport network
|
|
|
what occurs on the rough ER
|
protein synthesis and transport
|
|
|
what is the function of the Golgi complex
|
to help with membrane formation and protein secretion
|
|
|
how are lysosomes formed
|
from Golgi complexes
|
|
|
what do lysosomes store
|
digestive enzymes
|
|
|
what is the primary site of ATP production
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
what does the mitrochondria contain
|
70S ribosomes and DNA
|
|
|
what do chloroplast contain
|
chlorophyll and enzymes for photosynthesis
|
|
|
what is the endosymbotic therory
|
the belief that eukaryotic cells evolved from symbiotic prokaryotes living inside other prokaryotic cells
|
|
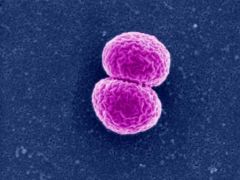
this is an example of
|
Diplococci
|
|
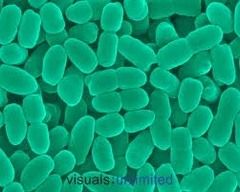
this is an example of
|
coccobacillus bacteria
|
|
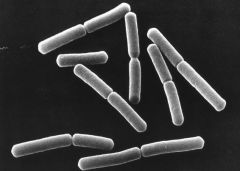
this is an example of
|
diplobacilli bacteria
|
|

this is an example of
|
sarcinae bacteria
|
|
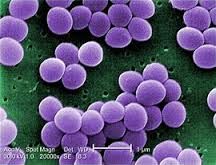
This is an example of
|
staphylococci bacteria
|
|
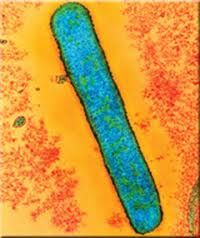
This is an example of
|
single bacillus bacteria
|
|
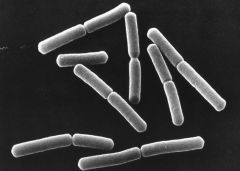
This is an example of
|
diplobacilli bacteria
|
|
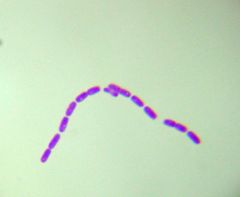
This is an example of
|
streptobacilli bacteria
|
|
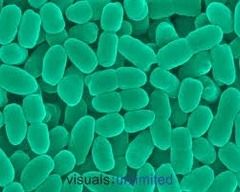
This is an example of
|
coccibacillus bacteria
|
|
|
cytoplasm refers to
|
the substance inside the cell
|
|
|
what are the major structures in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes
|
a nucleoid (containing DNA), ribosomes, and reserve deposits called inclusions
|
|
|
what does the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells lack
|
cytoskeleton and cytoplasmic streaming
|
|
|
the nucleoid of a bacterial cell is attached to what
|
the plasma membrane
|
|
|
what is a plasmid and where is it located
|
plasmid is small circular double stranded DNA molecules. Located in the nucleoid
|
|
|
why are plasmids important
|
because they may carry genes for such activities as antibiotic resistance, tolerance to toxic metals, the production of toxins and the synthesis of enzymes
|
|
|
ribosomes are found in
|
both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
|
|
|
ribosomes function as
|
the site of protein synthesis
|
|
|
the letter S in ribosomes refers to
|
Svedberg units, which indicate the relative rate of sedimentation during ultra high speed centrifugation
|
|
|
what is an organelle
|
structures with specific shapes and specialized functions and are characteristic of eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
what does a organelle include
|
nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria, chloroplasts, peroxisomes and centrosomes
|
|
|
what contains almost all of the cells hereditary info
|
nucleus
|
|
|
what is the nucleus surround by
|
a double membrane called the nuclear envelope
|
|
|
what do nuclear pores allow
|
the nucleus to communicate with the cytoplasm
|
|
|
what controls the movement of substances between the nucleus and cytoplasm
|
nuclear pores
|
|
|
what is nucleoli aka nucleolus
|
nucleoli are condensed regions of chromosomes where ribosomal RNA is being synthesized
|
|
|
what is an essential component of ribosomes
|
ribosomal RNA
|
|
|
the nucleus of eukaryotic cells contains what main protein
|
histones
|
|
|
chromatin is
|
threadlike mass of DNA
|
|
|
when do chromatin turn into chromosomes
|
during nuclear division
|
|
|
to segregate chromosomes prior to cell division what elaborate mechanisms are required in eukaryotic cells
|
mitosis and meiosis
|
|
|
what is in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
|
endoplasmic reticulum or ER
|
|
|
what is the function of smooth ER
|
to sythesisize phosopholipids, fats and steroids
|
|
|
where is the first place that proteins go after they are synthesized?
|
Golgi complex
|
|
|
what does the Golgi complex consist of
|
3 to 20 cisternae. give Golgi cuplike shape
|
|
|
what is a transport vesicle
|
ribosomes of the rough ER that fuse with a portion of the ER membrane
|
|
|
how do the proteins move from one cistern to another
|
by transfer vesicles
|
|
|
when enzymes in the cisternae modify proteins, what do they form
|
glycoproteins, glycolipids and lipoproteins
|
|
|
how do proteins leave the cistern
|
by secretory vesicles or storage vesicles like (lysosomes)
|
|
|
what are lysosomes formed from
|
Golgi complexes
|
|
|
what do lysosomes contain
|
40 different kinds of powerful digestive enzymes
|
|
|
what is a vacuole
|
a space or cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell
|
|
|
what doe some vacuoles serve as
|
a temporary storage organelle for substances such as proteins, sugars, organic acids and inorganic ions
|
|
|
other vacuoles from endocytosis
|
help bring food into the cell
|
|
|
mitochondria
|
spherical or rod shaped organelle that appear throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
the mitochondria consist of
|
a double membrane, cristae (inner, series of folds), matrix (center of mitochondria
|
|
|
chloroplasts
|
membrane enclosed structure that contains both the pigment chlorophyll and enzymes required for light-gathering phases of photosynthesis
|
|
|
where is the chlorophyll in chloroplasts contained
|
in thylakoids(flattened membrane sacs)
|
|
|
what do chloroplasts contain
|
70S ribosomes, DNA and enzymes
|
|
|
perioxisomes
|
similar to the structure of lysosomes, but smaller
|
|
|
what happens in peroxisome
|
AA and fatty acids are oxidized
|
|
|
what do the enzymes in peroxisomes do such as the enzyme catalase
|
oxidize toxic substance such as alcohol. Or decompose toxic compounds like carbon dioxide
|
|
|
what is the centrosome
|
located in the nucleus contains: pericentriolar area and centrioles
|
|
|
within the pericentriolar material is a pair of cylindrical structure called
|
centriole
|
|
|
what is the endosymbiotic theory
|
explains the origin of eukaryotes from prokaryotes. That larger bacterial cells lost their cells walls and engulfed smaller bacterial cells
|

