![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Def: Decontamination |
The treatment of an object to make it safe to handle |
|
|
Def: Disinfection |
Directly targets the removal of all pathogens, not necessarily all microorganisms |
|
|
Def: Heat Sterilization |
The most widely used method of controlling microbial growth. |
|
|
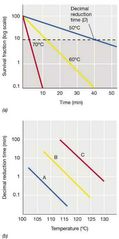
Decimal Reduction Time (D) |
Amount of time required to reduce viability tenfold.
exponential relationship. Heat kills faster as temperature rises. Moist heat works better than dry heat.
Endospores can survive heat that would rapidly kill vegetative cells. |
|
|
Def: Thermal Death Time |
Time to kill all cells at a given temperature; affected by population size. |
|
|
Decimal Reduction Time Visual |
|
|
|
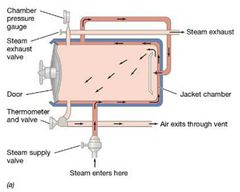
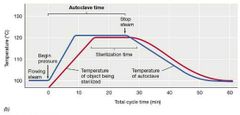
Def: Autoclave |
The autoclave is a sealed device that uses steam under pressure. - Allows temperature of water to get above 100°C. - Kills endospores. - Not the pressure but the high temperature that kills the microbes. |
|
|
Def: Pasteurization |
The process of using precisely controlled heat to reduce the microbial load in heat-sensitive liquids.
- Does not kill all organisms, so it is different from sterilization. |
|
|
Autoclave Structure Visual |
|
|
|
Autoclave Cycle Visual |
|
|
|
Control Method: UV |
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation (between 220 and 300 nm) has sufficient energy to cause modifications and breaks in DNA.
- UV useful for decontaminating surfaces. - Cannot penetrate solid, opaque, or light-absorbing surfaces. |
|
|
Control Methods: Ionizing Radiation (Part 1) |
Electromagnetic radiation that produces ions and other reactive molecules upon collision.
Amount of energy required to reduce viability tenfold (D10) is analogous to D value. |
|
|
Control Methods: Ionizing Radiation (Part 2) |
Some microorganisms more resistant to radiation than others (e.g., endospores vs. vegetative cells, viruses vs. bacteria).
Used for diverse items including surgical supplies, plastic labware, drugs, fresh produce, meat. |
|

|
|
|
|
UV Survival Rate Visual |
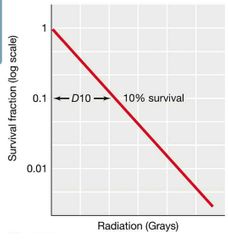
|
|
|
Control Methods: Ionizing Radiation (Part 3) |
Sources of radiation include cathode ray tubes, X-rays, and radioactive nuclides.
Radiation is used for sterilization in the medical field and food industry. |
|
|
Control Methods: Ionizing Radiation (Part 4) |
Radiation is approved by the WHO and is used in the United States for decontaminating foods particularly susceptible to microbial contamination. - Hamburger, chicken, and spices may all be irradiated. |
|
|
Control Methods: Filtration (Part 1) |
Filtration avoids the use of heat on sensitive liquids and gases. - Pores of filter (0.45 and 0.2 μm) are too small for living organisms to pass through but do not trap most viruses. - pores allow liquid or gas to pass through. |
|
|
Control Methods: Filtration (Part 2) |
Depth filters made of overlapping paper or glass fibers. - HEPA filters Membrane filters function more like a sieve. Nucleopore filters for scanning electron microscopy. |
|
|
Antimicrobial Agents |
Chemicals that kill or inhibit growth. |
|
|
-cidal vs. -static |
-cidal kills microorganisms (e.g., bactericidal, fungicidal, viricidal). -static inhibits growth (e.g., bacteriostatic, fungistatic, viristatic). |
|
|
The Three Classification of Antibacterial Agents |
Classified as Bacteriostatic, Bacteriocidal, and Bacteriolytic. |
|
|
Bacteriostatic Agents w/ Visual |
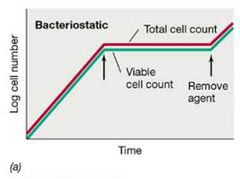
Inhibit biochemical processes such as protein synthesis and bind weakly. |
|
|
Bactericidal Agents w/ Visual |
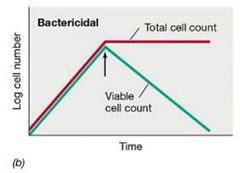
Bind tightly and kill the cell. |
|
|
Bacteriolytic Agents w/ Visual |
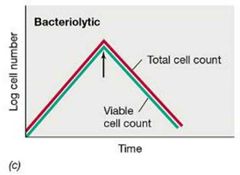
Kill by lysis (e.g., detergents). |
|
|
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) |
The smallest amount of an agent needed to inhibit growth of a microorganism. |
|
|
Disc Diffusion Assay |
Uses solid media. Antimicrobial agent added to filter paper disc, diffuses into agar. MIC is reached at some distance. - Zone of inhibition: area of no growth around disc. |
|
|
The Control of Growth on Various Surfaces |
Sterilants, disinfectants, sanitizers, and antiseptics are used to prevent growth on inanimate surfaces and external body surfaces. |
|
|
Def: Sterilants |
Destroy all microorganisms, including endospores. |
|
|
Def: Disinfectants |
Used on surfaces to kill microorganisms but not necessarily endospores. |
|
|
Def: Sanitizers |
Reduce microbial numbers but do not sterilize. |
|
|
Def: Antiseptics (germicides) |
Kill or inhibit microbial growth but are nontoxic enough to be applied to living tissues. |
|

Antiseptic Visual |
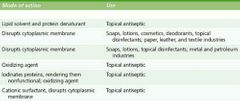
|
|

Sterilants, Disinfectants, and Sanitizers Visual |
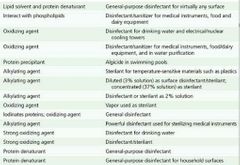
|

