![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the half life of bacterial mRNA? |
About 2 minutes |
|
|
What is the half life of eukaryotes mrna? |
4-24 hours |
|
|
When are bacterial genes usually translated? |
Usually translated as mrna is being synthesised |
|
|
What is the general structure of bacterial gene? |
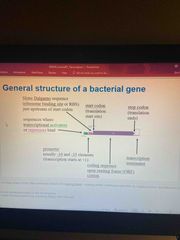
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What strand of DNA are genes on? |
Both but bias towards leading as it has continuous replication |
|
|
How are genes distributed on the chromosome? |
Generally evenly distributed |
|
|
Are introns rare in bacteria |
Yes |
|
|
What is an operon |
Cluster of protein coding open reading frames transcribed as a single mRNA |
|
|
How many bases are there usually between coding regions |
4-50 bp |
|
|
What does the control of a operon control? |
Expression of the entire function eg. Pathway |
|
|
What is transcription catalysed by? |
RNA polymerase |
|
|
What is transcription |
The copying of genetic information from its DNA repository (genome) in the functional RNA molecules, is catalysed by RNA polymerase (RNAP) |
|
|
What does bacterial RNAP do? |
Unwinds DNA tk for a transcription bubble containing ss non template DNA and the 8-9 No template DNA/ RNA hybrids |
|
|
What does RNAP do after forming transcription bubble |
Moves along the DNA while maintaining the transcription bubble until the end of RNA synthesis |
|
|
What replaces thymine in RNA |
Uracil |
|
|
Why is uracil not used in DNA |
It is easily degraded to cytosine |
|
|
What forms the main catalytic centre |
Beta and beta’ crab craw structure |
|
|
What do alpha^2 have a primary role in |
RNAP assembly |
|
|
What is the role of the sigma factor |
Determines promoter specificity Housekeeping/ group 1 contain 2 domains one recognising -10 region and second -35 region |
|
|
What is -10 region |
Interact with an alpha helix in the protein |
|
|
What is -35 region |
Interacts with DNA via HTH motif, forming H bonds with DNA bases |
|
|
What does the housekeeping sigma factor help do |
Helps catalyse the opening of the DNA strands near the transcription start point initiation |
|
|
What are the three major phases of transcription |
Intimation Elongation Termination |
|
|
How does imitation occur |
Sigma factor interact with RNAP core forming holoenzyme RNAP holoenzyme binds promoter and opens DNA duplex Often synthesises short abortive transcription before correct promoter escape Sigmas factor usually released and core RNAP continues to elongation |
|
|
What is RNAP role in elongation |
It moves akin the DNA maintaining transcription bubble until end of RNA synthesis |
|
|
What do elongation factors control |
Control the speed of RNAP by modulating pausing |
|
|
What is the error rate of elongation |
~10^-4 - 10^-6 error rate |
|
|
Where does mRNA synthesis terminate |
At the specific sequence at the end of genes |
|
|
What are anti terminator factors and what do they allow |
Allow RNAP to read through terminators |
|
|
What are the two types of anti termination factors |
Intrinsic terminators and Rho-dependent terminators |
|
|
What are intrinsic terminators |
Palindrome followed by poly u tract Stem loop causes pause leading to dissociation of RNAP |
|
|
What are Rho-dependent terminators |
Require Rho protein |
|
|
What does Rho-dependent terminator do |
Rho binds specific sequences in the mRNA, moves down transcript until it contact the eloping RNAP RNAL pauses at rho dependent terminator= termination |
|
|
How is gene expression is regulated at post translation |
Protein stability |
|
|
How is gene expression is regulated at translation regulation |
Translation initiation |
|
|
How is gene expression is regulated at post transcription |
mRNA stability |
|
|
How is gene expression is regulated at transcription regulation |
Transcription initiation |
|
|
What is a regulon |
The set of all genes regulated by a particular factor sigma or tf |
|
|
What is global regulation |
Genes in a regulon distributed throughout the genome |
|
|
What is the E.Coli Maria’s regulon |
A. Umber if operon involved in transport and utilisation of malting |
|
|
What is local regulation |
Bacteria often need to regulate just a few specific genes |
|
|
What do sigma factors do to RNA polymerase wh |
Give it its specificity |
|
|
What are the two major groups of sigma factor |
70 and 54 |
|
|
What do transcription factors do |
Bind specific DNA sequences usually close to the promoter and modulate transcription |
|
|
What can tf allow for |
Positive control and negative control |
|
|
General principle for making gene deletions |
Remove or replace most or all of the coding sequence of a gene Delete putative regulatory proteins and determine the effect in the phenotypes or gene expression |
|
|
How do you directly measure gene expression in bacteria |
Northern blots Reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR Microassays RNA- seq |
|
|
What is the general principle for reporter gene fusion |
Expression of a protein with an easy to assay activity is used as a proxy for the expression kf a gene of interest |
|
|
Can you use lacZ as a selectable marker |
Yes |
|
|
General principle of reporter fusions lacZ |
Transcriptional or translation reports LacZ can cleave chromogenic substrates |
|
|
How do you measure protein DNA interactions |
Vitro assay Kinetics Structure function studies |

