![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
157 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Bacterial shapes |
cocci bacilli vibrio spirilla spirochete |
spheres rods curved rods twisted rods flexible twisted rods |
|
|
Treponema pallidum |
gram negative |
causes syphilis |
|
|
Cyanobacteria |
gram negative |
photosynthetic |
|
|
Heterocyst |
found in photosynthetic bacteria fix N2 |
|
|
|
Streptomyces |
gram positive |
found in soil grows as branching filaments |
|
|
S |
Svedberg unit sedimentation coefficient |
|
|
|
50 S |
23S rRNA + 5S rRNA + >30 proteins |
large ribosomal subunit |
|
|
30 S |
16S rRNA + >20 proteins |
small ribosomal subunit |
|
|
70 S |
total prokaryote ribosome |
|
|
|
Intracytoplasmic membranes |
increase area for photosynthesis stacked flattened vesicles/tubules derived from p.m. |
photosynthetic bacteria |
|
|
Inclusions |
discrete granules |
|
|
|
Storage granules |
glycogen PHB polyphosphate |
used as a source of energy/phosphates and a source of atoms for biosynthesis |
|
|
PHB |
synthesized from acetyl groups |
poly(B)hydroxybuterate |
|
|
Polyphosphate |
nucleotide triphosphate
phospholipids |
polymer of phosphate |
|
|
Carboxysomes |
multiple copies of the same protein and contains sequentially acting enzymes 1) Carbonic anhydrase 2) RuBisCo |
selectively permeable polyhedral shell: O2 cannot enter, CO2 cannot exit, HCO3- can enter |
|
|
In Carboxysomes: ____ is converted into _____ by enzyme one, which is then converted into ______ by enzyme two |
HCO3- CO2 G3P |
1) Carbonic anhydrase 2) RuBisCo |
|
|
G3P |
glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate |
|
|
|
Carbonic anhydrase |
converts bicarbonate into CO2 |
|
|
|
RuBisCo |
converts CO2 into G3P |
has a higher affinity for O2, the selectively permeable membrane (of carboxysome) prevents O2 from inhibiting CO2 fixation |
|
|
Gas Vacuoles |
hollow capped cylinders |
regulates buoyancy
|
|
|
Magnetosomes |
crystals of magnetite (fe3O4) magnetosomes for a chain
|
direct away from O2 and down toward nutrients |
|
|
Phospholipids |
fatty acids linked to glycerol by ester bonds |
amphipathic |
|
|
Two classes of proteins |
Integral proteins
peripheral proteins |
hydrophobic force
ionic bonds |
|
|
80 S |
40S rRNA + 60S rRNA |
Eukaryotic ribosomes
|
|
|
Primary transport systems |
ATP |
ABC transport system |
|
|
Secondary transport systems |
Ion gradient (H+) |
MFS
|
|
|
Group Traslocation |
solute is modified |
PTS |
|
|
ABC |
ATP Binding Cassette |
|
|
|
ABC transporter system |
uses ATP to transport solutes across plasma membrane cellular (capsule) components and antibiotics are exported |
SBP + pore + NBD |
|
|
ABC transport protein |
permease and nucleotide binding domain |
integral membrane domain cytoplasmic peripheral domain |
|
|
SBP |
periplasmic space of gram-and peripheral protein in gram+ Specific solute binding causes shape conformation and can bind to a specific ABC transport protein |
solute binding protein |
|
|
NBD |
hydrolyzes ATP to provide energy for the uptake of solutes |
nucleotide binding domain |
|
|
MFS transporter |
secondary transport system use H+ ions to transport solutes across plasma membrane |
major facilitator super family |
|
|
Lac Y uptake in E. coli |
MFS symporter |
|
|
|
Lactose |
glucose + galactose disaccharide |
|
|
|
MFS symporter |
H+ and solute transported in the same direction |
Lac Y protein transports lactose and H+ |
|
|
MFS antiporter |
H+ is transported in the cell and solute transported out |
efflux of antibodies |
|
|
Ionophores |
increases the permeability of the plasma membrane to ions |
destroys the proton gradient
|
|
|
Gramicidin |
antibiotics that forms pores in plasma membrane |
|
|
|
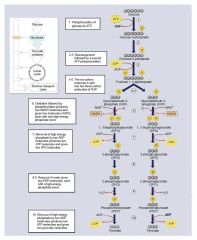
Glycolysis |
glucose -> (ATP->ADP) -> glucose 6 P -> 2 G3P -> 2 PEP -> (2 ADP -> 2 ATP) -> 2 pyruvate |
|
|
|
PEP |
phosphoenolpyruvate |
|
|
|
PTS |
used for uptake of sugars energy provided by PEP |
phosphotranspherase system |
|
|
non-specific proteins for sugar uptake |
E-I HPs |
in the cytoplasm
|
|
|
HP |
histodine protein |
|
|
|
E-II A |
cytoplasm |
|
|
|
E-II B |
peripheral cytoplasmic side phosphorylation of E-II B causes conformation change in E-II C |
|
|
|
E-II C |
permease integral plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Iron |
required for function of enzymes O2 transoprt electron transport chain insoluble in soil |
|
|
|
Transferrin |
transports Fe3+ in blood |
|
|
|
Lactoferrin |
binds to Fe3+ in tears |
|
|
|
Chelator |
an agent that has a high affinity for a metal ion |
|
|
|
Siderophore |
iron carrier |
|
|
|
Fep A |
integral outer membrane receptor |
Iron protein A |
|
|
Ton B |
integral plasma membrane with periplasmic domain |
energy transducer and interacts with Fep A
|
|
|
Fe3+ siderophore complex |
binds to Fep A, transported through the pore and binds to a specific SBP. After going through the ABC an enzyme releases the iron |
|
|
|
Translocation |
transportation into the periplasm |
|
|
|
Secretion |
released outside the cell |
|
|
|
Exoenzymes |
hydrolyse large nutrients outside the cell |
|
|
|
Protease |
proteins -> amino acids |
|
|
|
Lipase |
triglyceride -> glycerol + fatty acids |
|
|
|
Cellulase |
cellulose -> glucose |
|
|
|
Amylase |
starch -> glucose |
|
|
|
Sec system |
insert proteins into plasma membrane or remove unfolded proteins into the periplasm |
|
|
|
Signal peptide |
hydrophobic slows the folding of preprotein |
25 amino acid peptide
|
|
|
Preprotein |
signal peptide + protein |
|
|
|
Sec B |
cytoplasmic chaperone protein inhibits folding delivers it to Sec A |
|
|
|
Sec YEG |
integral pm translocator uses PMF |
|
|
|
Sec A |
inner surface of Sec YEG ATPase |
|
|
|
Signal peptidase |
outer surface of plasma membrane removes the signal peptide from preprotein |
|
|
|
T3SS |
hollow syringe in gram-negative bacteria |
type 3 secretion system |
|
|
T4SS |
used in conjugation in gram-negative it secretes proteins into the cytoplasm |
type 4 secretion system |
|
|
Sex pilus |
tubular structure attached to the outer surface T4SS |
gram-negative |
|
|
Helicobacter pyloria |
gram negative helical shaped rod injects Cag A in stomach epithelial cells |
T4SS stomach ulcers and cancers |
|
|
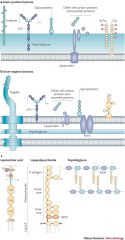
Gram-positive cell wall |
peptidoglycan teichoic acids (plasma membrane) lipo |
30 layers thick |
|
|
Gram-negative cell wall |
thin peptidoglycan lipoproteins |
|
|
|
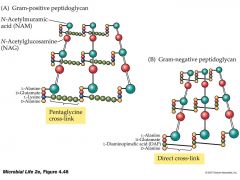
Glycan chain |
long chain of two alternating sugars: NAG NAM |
|
|
|
NAG |
glucose + amine group + acetyl group |
N-acetylglucosamine |
|
|
NAM |
NAG + lactic acid |
N-acetylmuramic acid |
|
|
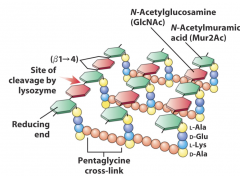
Pentapeptides |
N-terminus - L-ala - D-glu - L-lys - D-ala - D-ala - C-terminus |
attached to NAMs |
|
|
Peptide interbridge |
C terminus attached to N terminus of L-lys. N terminus attached to C terminus of D-ala |
Gram-positive |
|
|
L-lys |
3rd peptide in gram+ diamino acid amino group on the R group covalently links to C terminus of interbridge |
|
|
|
Tetrapeptide |
2nd peptide after interbridge crosslinks are formed |
|
|
|
Teichoic acid |
extends through peptidoglycan attached to sugar alcohols attached to NAM negative surface charge (PO43-) in gram-positive |
teichoic + lipoteichoic polyanionic polymer of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphates |
|
|
Mycobacterium |
mycolic acids on outersurface makes it hydrophobic |
gram-positive rods that dont gram stain well |
|
|
Tuburculosis |
Mycobacterium tuburculosis |
|
|
|
Leprocy |
Mycobacterium leprae |
|
|
|
Mycolic acids |
protects against dehydration and slows nutrient uptake |
lipids covalently linked to peptidoglycan in gram-p |
|
|
Acid fast stain |
1) red primary stain - phenol + heat 2) acid alcohol decolorized 3) blue counterstain |
acid fast bacteria = red, non-acid fast bacteria = blue |
|
|
DAP |
replaces L-lys in gram- links to R group of peptides directly |
diaminopimedic acid |
|
|
Outer membrane |
inner leaflet = phospholipids outer leaflet = lipopolysaccharides |
|
|
|
LPS |
lipid A core polysaccharide O antigen negative charge of cell from PO43- on core polysaccharides |
lipopolysaccharides |
|
|
Lipid A |
endotoxin 2 glucose amines with phosphates attached to each 6 fatty acids |
causes fevers, shock, death |
|
|
Core Polysaccharides |
several sugars, some phosphorylated |
|
|
|
O antigen |
polysaccharide of repeating sugars |
negative charge on gram- |
|
|
Mg2+ |
divalent cation that neutralize phosphate charges on Lipid A and excludes hydrophobic molecules |
|
|
|
EDTA |
divalent cation chelator to gram- destroys outer membrane and releases periplasmic contents |
|
|
|
Bile salts |
hydrophilic group + cholesterol = amphipathic molecule can emulsify phospholipid membrane |
inhibits growth of gram+ |
|
|
Porins |
trimers B barrel hydrophilic R group in pore outer membrane functions as sieve |
periplasmic proteins cant get out, exogenous proteins cant get in |
|
|
Non-specific porins |
any small -philic molecules pass freely |
|
|
|
Specific porins |
constricted channel with several amino acids with charged R group |
charged + for phosphate porin in E. coli |
|
|
Lipoproteins |
phospholipid leaflet of outer membrane C-terminus is covalently linked to DAP anchors to peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
Mycoplasm |
no cell wall smallest autonomously growing species polymorphic |
|
|
|
Walking Pneumonia |
Mycoplasm pneumoniae |
|
|
|
UDP |
nucleotide diphosphate cytoplasmic assembly of peptidoglycan subunits |
uridine diphosphate |
|
|
Bactoprenol phosphate |
55C lipid + PO43- hydrophobic hydrocarbon in plasma membrane moves NAG NAM pentapeptide into periplasm |
|
|
|
Autolysins |
periplasmic enzyme breaks covalent bond btw NAG + NAM in glycol chain breaks peptide crosslinks in peptidoglycan |
enables insertion of new subunits so peptidoglycan can grow |
|
|
Transglycosylase |
covalently links NAG NAM to glycan chain |
|
|
|
Transpeptidase |
breaks terminal D-ala - D-ala bond, uses energy to form new peptide bond btw terminal D-ala tetrapeptide and amino group of DAP |
covalently links peptides(transpeptidation) |
|
|
Bactoprenol diphosphate |
flipped across plasma membrane with NAG NAM pentapeptide. loses phosphate when flipped back |
|
|
|
Bacitracin |
prevents dephosphorilation of bactoprenol diphosphate |
stops peptidoglycan synthesis |
|
|
Penicillin |
size of 2 amino acids blocks active site of transpeptidase |
autolysins continue and cell lyses |
|
|
Ampicillin |
penicillin + amino group = ionized and positive charge can cross outer membrane of gram- |
|
|
|
Vancomycin |
large stops transpeptidation by binding to pentapeptide |
autolysins continue |
|
|
Lysozyme |
120 amino acid enzyme hydrolyses bonds of NAG NAM |
found in tears, saliva, lysosomes |
|
|
isotonic solution |
15% sucrose |
|
|
|
Protoplast |
cell w/o cell wall cell rounds up can still grow |
|
|
|
Spheroplasts |
fragmented peptidoglycan cell rounds up can still grow |
gram-negative |
|
|
Hypertonic solution |
protoplast or spheroplast will lyse |
|
|
|
Capsule / Slim layer |
sticky polysaccharides seen with negative stain attachments to surfaces (biofilms) hydrophobic, prevents desication inhibits phagocytosis |
|
|
|
Biofilms |
group of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other on a surface |
|
|
|
Capsules |
adhears to cell tightly |
|
|
|
Slim layer |
not as organized or tightly attached to cell |
|
|
|
Leuconostoc |
gram-positive cocci LAB capsule composed of dextran capsule is used as plasma volume expands |
|
|
|
LAB |
lactic acid bacteria |
|
|
|
Dextran |
branched polymer of glucose |
|
|
|
Xanthomonas |
gram-negative rod capsule is heteropolysaccharide xanthan gum |
|
|
|
Xanthan gum |
food stabilizer and thickener |
|
|
|
S layer |
sheet of tetragon/hexagonal proteins adhears to outer membrane (gram-) and peptidoglycan (gram+) under capsule/slim layer |
excludes large molecules, allows teichoic acid and O antigen to poke through |
|
|
Bdello vibrio |
aquatic gram-negative polar flagellum |
|
|
|
The attack of the of the Bdello vibrio |
1) prey is gram- w/o S layer
2) flagella bores through outer membrane with enzymes 3) damages plasma membrane and leaks cytoplasmic contents 4) grows into long filaments and divide into individual cells |
cytoplasmic contents provide energy and nutrients unusual method of replication the prey is lysed and Bdellovibrio are released |
|
|
Fimbriae / Pili |
multiple subunits of proteins arranged in a helix fiber by hydrophobic force and noncovelent bonds with an adhesive protein at the tip |
thin filaments located all over the cell adheres to cell or surfaces |
|
|
Chaperone / Usher system |
chaperone prevents assembly in the periplasm usher complex assemble fimbriae |
helps build fimbriae from the proximal end |
|
|
Sex Pilus |
filament composed of multiple protein subunit larger in diameter and longer than finbriae |
used in conjugation to overcome electrostatic barrier btw cells copy of plasmid is transferred from donor to recipient using T4SS |
|
|
F plasmid |
genes for the synthesis of sex pilus and T4SS |
in E. coli |
|
|
Conjugation |
two bacterial cells come together in a temporary fusion to transfer genetic material |
|
|
|
Monotrichous |
one polar flagella |
|
|
|
Peritrichous |
multiple flagella all over |
|
|
|
Flagella components |
Basal body + hook + filament |
|
|
|
Basal body |
hollow central rod + 4 protein rings |
|
|
|
L ring |
associated with the LPS |
|
|
|
P ring |
associated with the peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
MS ring |
inserted in the plasma membrane (M=membrane, S=surface) |
|
|
|
C ring |
on the cytoplasmic side of MS ring, indirectly attached to rod made of multiple copies of fli proteins |
|
|
|
Fli proteins |
fli G, M, N |
C ring |
|
|
Mot proteins |
motor proteins surrounds the MS ring Mot A and Mot B form proton channel |
|
|
|
Mot A |
anchors the Mot A/Mot B complex to the peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
Mot B |
forms proton channel w Mot A |
|
|
|
Hook |
short curved sleeve that connects to the rod of the basal body and filament |
|
|
|
Flagella filament |
semirigid hollow helical filament made of multiple copies of flagellin |
|
|
|
Flagellin |
synthesized in the cytoplasm transported through hollow core of rod and attaches to distal end |
|
|
|
Stater |
stationary use PMF to turn router produces a conformation change in Mot proteins |
Mot proteins |
|
|
Router |
rotation of C ring turns MS ring, attached rod, hook, and filament
|
C ring |
|
|
Bushings |
a structure that constrains moving mechanical parts protects peptidoglycan and outer membrane |
P ring, L ring |
|
|
Counterclockwise |
default setting hook bends, filaments form rotating bundle |
run |
|
|
Clockwise |
undoes the bundle of filament cell stays in the same area random direction |
tumble |
|
|
Influences movement |
frequency of run/tumble # of tumbles random changes in direction length of run |
|
|
|
Lipoteichoic acids |
Attached to the phospholipid of the plasma membrane |
Glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate |

