![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Multiple choice. ○ active ○ inactive ○ inattentive ○ abiotic |
|
|
|
Multiple choice. ○ binary ○ log ○ doubling ○ exponential |
|
|
|
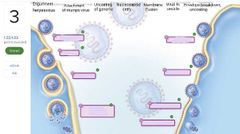
|
|
|
|
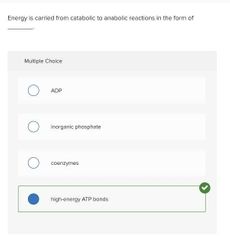
Multiple choice. ○ ADP ○ inorganic phosphate ○ coenzymes ○ high-energy ATP bonds |
|
|
|
Multiple choice. ○ The role of the electron transport system is to dispose of electrons that were moving during glycolysis and Krebs cycle and use these electrons to make water. ○ The electron transport system is instrumental in the creation of an electron cell membrane (bacteria) to inner mitochondrial membrane (eukaryotes) phosphorylation of ADP by the ATP synthase enzyme. ○ The electron transport system transforms the energy of electrons into the potential energy of an electrochemical gradient (portion gradient) across the cell membrane (bacteria) or inner mitochondrial membrane (eukaryotes). This portion gradient provides the energy used by ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP; producing ATP. |
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ Transforming ○ Lytic ○ Lysogenic ○ Hemorrhagic ○ Oncogenic |
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ transformation ○ colony ○ suncytium ○ plaque |
|
|
|
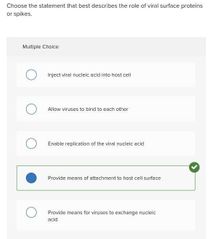
Multiple choice. ○ Inject viral nucleic acid into host cell
○ Allow viruses to bind to each other
○ Enable replication of the viral nucleic acid
○ Provide means of attachment to host cell surface
○ Provide means for viruses to exchange nucleic acid |
|
|
|

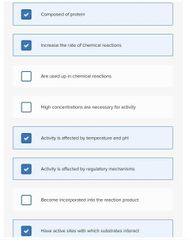
Select all that apply. □ Composed of protein
□ Increase the rate of chemical reactions
□ Are used up in chemical reactions
□ High concentrations are necessary for activity
□ Activity is affected by temperature and pH
□ Activity is affected by regulatory mechanisms
□ Become incorporated into the reaction product
□ Have active sites with which substrates interact
□ Increase the activation energy of a reaction |
|
|
|
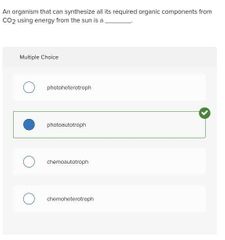
Multiple choice. ○ photoheterotroph ○ photoautotroph ○ chemoautotroph ○ chemoheterotroph |
|
|
|

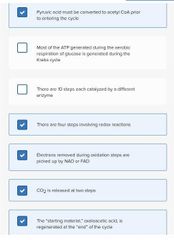
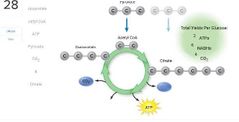
Select all that apply. □ Pyruvic acid must be converted to acetyl CoA prior to entering the cycle
□ Most of the ATP generated during the aerobic respiration of glucose is generated during the Krebs cycle
□ There are 10 steps each catalyzed by a different enzyme
□ There are four steps involving redox reactions
□ Electrons removed during oxidation steps are picked up by NAD or FAD
□ CO2 is released at two steps
□ The "starting material," oxaloacetic acid, is regenerated at the "end" of the cycle |
|
|
|
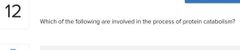
Select all that apply. □ Lipases □ Deamination □ Proteases □ Beta oxidation □ Glycolysis |
|
|
|

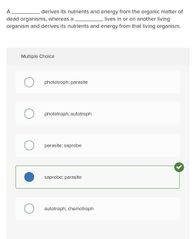
Multiple choice. ○ phototroph; parasite ○ phototroph; autotroph ○ parasite; saprobe ○ saprobe; parasite ○ autotroph; chemotroph |
|
|
|
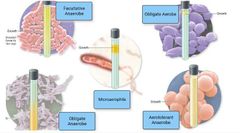
Word bank: Obligate Aerobe Facultative Anaerobe Aerotolerant Anaerobe Obligate Anaerobe Microaerophile |
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ cytopathic ○ persistent ○ acute ○ syncytial |
|
|
|

Arrange the following in the correct order. |
|
|
|

Remember the ORDER!! |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

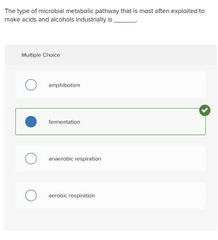
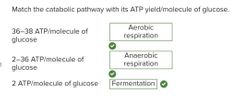
Multiple choice. ○ amphibolism ○ fermentation ○ anaerobic respiration ○ aerobic respiration |
|
|
|

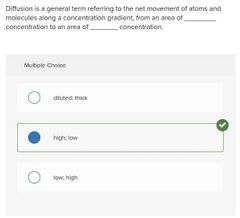
Multiple choice. ○ diluted; thick ○ high; low ○ low; high |
|
|
|
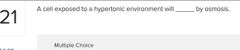
○ neither gain nor lose water ○ lose water ○ gain water ○ burst |
|
|
|

Hint: Look for these key words! Turbidometry- (Transmitted) the T's! Flow cytometry- (Fluorescent) the F's! Coulter counter- (Cell-counting/cultures) the C's! |

|
|
|

Determine whether they are catabolic (energy releasing) or anabolic (energy requiring) process.
Hint: Catabolic breaks down or removes. Everything else is anabolic. |

|
|
|

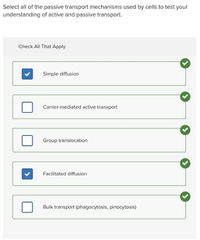
Select all that apply. □ Simple diffusion □ Carrier-mediated active transport □ Group translocation □ Facilitated diffusion □ Bulk transport (phagocytosis, pinocytosis) |
|
|
|

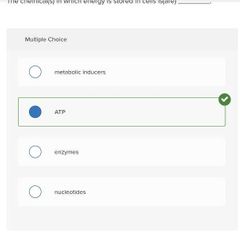
Multiple choice. ○ metabolic inducers ○ ATP ○ enzymes ○ nucleotides |
|
|
|
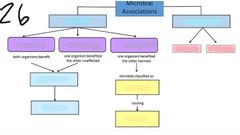
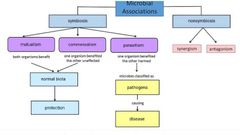
Word bank: Parasitism Antagonism Disease Normal biota Symbiosis Synergism Commensalism Protection Pathogens Nonsymbiosis Mutualism |
|
|
|

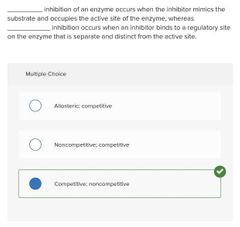
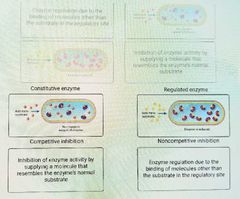
Multiple choice. ○ Allosteric; competitive ○ Noncompetitive; competitive ○ Competitive; noncompetitive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ receptors on the host cells ○ DNA in host cells ○ proximity of host cells ○ concentration of host cells in vicinity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
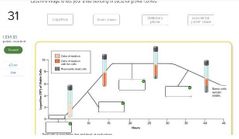
|
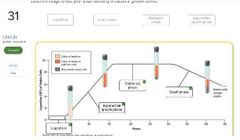
|
|
|
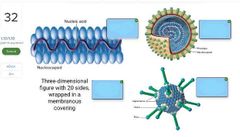
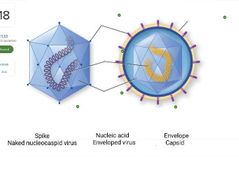
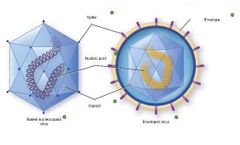
Word bank: Naked Icosahedral Virus Naked Helical Virus Enveloped Helical Virus Enveloped Icosahedral Virus |
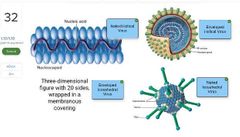
|
|
|

33 |

|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ aerobic; fermentive ○ aerobic; anaerobic ○ fermentative; anaerobic ○ anaerobic; aerobic |
|
|
|
Multiple choice. ○ weak ○ active ○ attenuated ○ abiotic |
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ aerobic; anaerobic; fermentation ○ aerobic; fermentative; anaerobic metabolism ○ anaerobic; aerobic; fermentation |
|
|
|
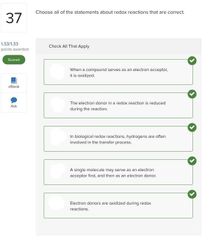
|
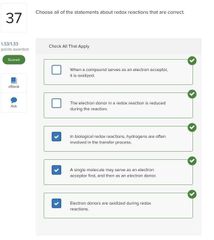
|
|
|

38 |

|

|
|
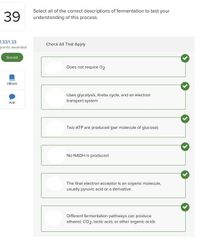
|
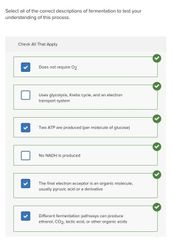
|
|
|
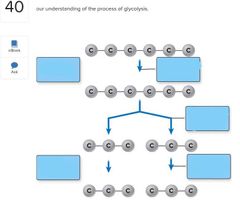
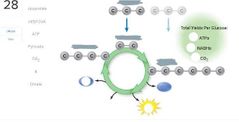
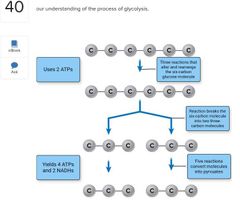
Word bank: Five reactions convert molecules into pyruvates Yields 4 ATPs and 2 NADHs Three reactions that alter and rearrange the six-carbon glucose molecule Uses 2 ATPs Reaction breaks the six-carbon molecule into two three-carbon molecules |
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
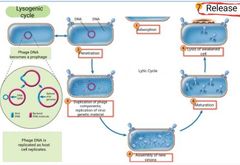
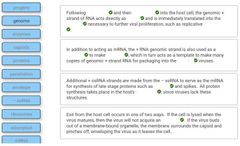
Word bank:
Lytic cycle Lysogenic cycle Release Maturation Penetration Adsorption Phage DNA becomes a prophage Lysis of weakened cell Duplication of phage components; replication of virus genetic material Phage DNA is replicated as host cell replicates Assembly of new virions |
|
|
|
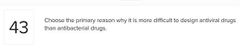
Multiple choice.
○ Viral cell structure is different than bacterial cell structure.
○ Anti viral drugs often must target host cell functions which results in side effects in the host.
○ Antiviral drugs must target viral envelopes and capsids.
○ Antiviral drugs can't readily penetrate host cells. |
|
|
|

Hints: HYPOtonic- hippopotamus' are big and look SWOLLEN. HYPERtonic- when hyper, you workout and LOSE WATER weight. |

|
|
|

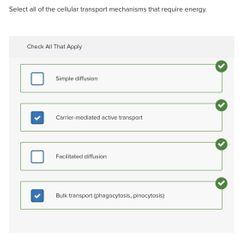
Select all that apply. □ Simple diffusion □ Carrier-mediated active transport □ Facilitated diffusion □ Bulk transport (phagocytosis, pinocytosis) |
|
|
|
|
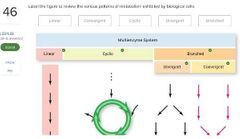
|
|
|

47 |

|
|
|
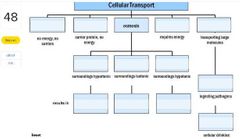
Word bank: phagocytosis facilitated diffusion cell in saline net flow of water out of cell cell in 20% NaCl cell in pure H2O active transport simple diffusion pinocytosis net flow of water into cell bulk transport net flow of water in or out |
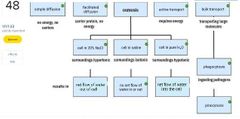
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ Obligate anaerobe ○ Obligate aerobe ○ Capnophile ○ Facultative anaerobe ○ Microaerophile |
|
|
|
|
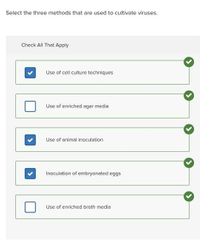
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

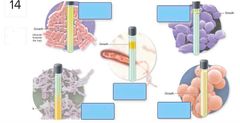
53 Word bank: Saprobe Chemoautotroph Photoautotroph Parasite Chemoheterotroph Photoheterotroph |

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
55 |

|
|
|

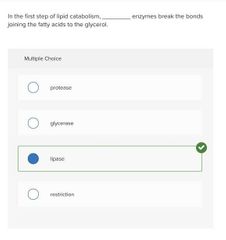
Multiple choice. ○ protease ○ glycerase ○ lipase ○ restriction |
|
|
|

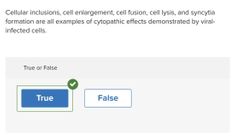
True or False. |
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
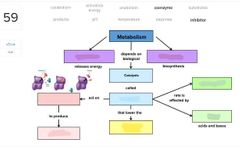
|
|
|
|
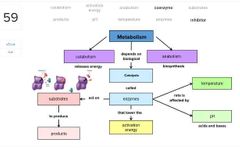
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
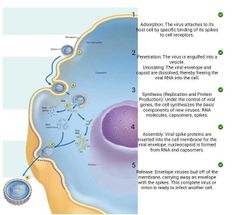
Multiple choice. ○ the inside of the host cell membrane becomes coated with viral matrix protein
○ the viral capsid becomes enclosed by the cell membrane
○ the inside of the host cell membrane becomes coated with capsid
○ viral spike proteins are inserted into the host cell membrane |
|
|
|

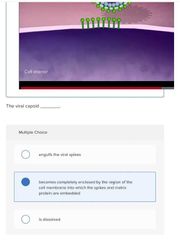
Multiple choice. ○ engulfs the viral spikes
○ becomes completely enclosed by the region of the cell membrane into which the spikes and matrix protein are embedded
○ is dissolved |
|
|
|

Multiple choice. ○ lysis of the host cell
○ endocytosis
○ budding
○ phagocytosis |
|
|
|
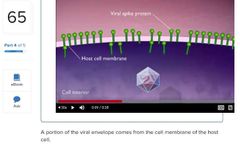
True or False. |
|
|
|
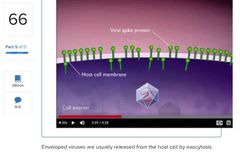
True or False. |
|
|
|
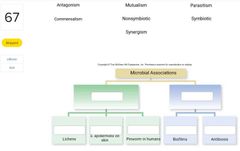
|
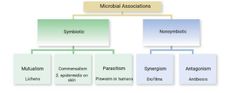
|
|
|

Check all that apply.
□ The suffix "-ase" indicates an enzyme
□ Often enzymes are named for the substrates they act upon
□ Enzymes are larger than their substrates
□ Enzymes have to be constantly produced because they are used up in reactions |
|
|
|

Select all that apply. □ Microorganisms live singly, independently.
□ Microorganisms participate in quorum sensing.
□ Microorganisms secrete extracellular material, usually polysaccharide, that forms a matrix.
□ Microorganisms are readily eradicated using antibiotics.
□ Microorganisms exist as part of a diverse interdependent community. |
|
|
|

Multiple choice.
○ oncogenic ○ subclinical ○ latent ○ syncytial |
|
|
|
|
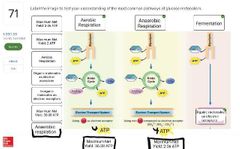
|
|
|
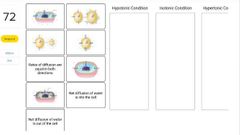
|
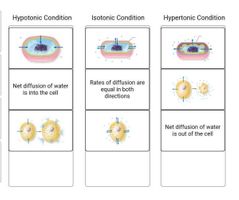
|
|
|
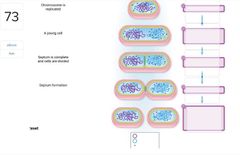
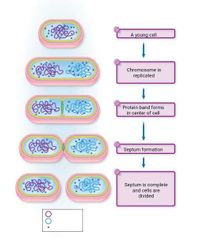
Chromosome is replicated A young cell Septum is complete and cells are divided Septum formation Protein band forms in center of cell |
|
|
|
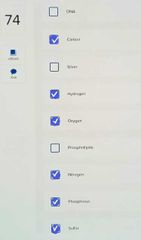
Select all of the nutrients that are essential for growth, reproduction, and maintenance of a bacterial cell. HINT: CHONPS |
|
|
|
|
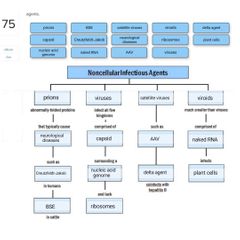
|
|

