![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some issues that can predispose someone to serious bacterial infections?
|
viral infections, broad-spectrum antibiotic use, more…..
|
|
|
What are some key characteristics that define BACTERIA?
|
-Prokaryotic
-Not cytoplasmic organelle other than ribosomes -Genetic info stored in CIRCULAR chromosome -Genetic info can also be extra-chromosomal (Plasmids) |
|
|
What is the general picture of a Prokaryotic cell?
|
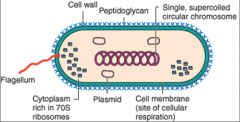
|
|
|
What is the general picture of a Eukaryotic cell?
|
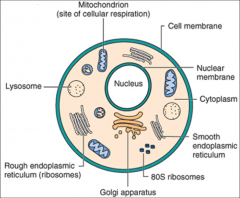
|
|
|
What are the GENERAL characteristics of a bacterial cell wall?
|
-Excellent target for antibacterial agents and immune cells
-Gram (-) or gram (+) based on features of cell wall: (+) -thick (20-80 nm) & ext. to cell memb; (-) -thin (5-10 nm) and b/w inner & outer memb **Purple is Positive, Red is negative** (never get in the habit of saying "pink" instead of red because that screws up everything! :-)) |
|
|
What are the defining differences between a gram (-) cell and a gram (+) cell?
|
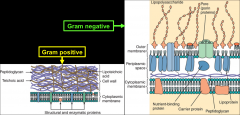
(+) - cell walls contain LOTS of peptidoglycan plus techoic acid (which retains the purple stain) and NO LPS
(-) cell walls contain LPS, only a small amount of peptidoglycan (b/w memb layers), NO techoic acid |
|
|
How do you perform a gram stain? (steps)
What do the results mean? |
Stain with CV, rinse, apply IODINE, rinse, add decolorizer (70% etoh), rinse then add SAFRANIN (counterstain).
(+) cells will remain purple because the CV will form a complex with the techoic acid in the cell wall so it will not release the stain when decolorized. The red stain will not be able to overcome the purple color. (-) cell walls do NOT contain techoic acid, so the CV will decolorize and the red will stain all of the cells. |
|
|
What are the different shapes that used to classify bacteria?
|
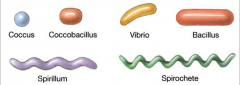
|
|
|
What are the growth requirements that are used to classify bacteria?
|
Aerobic: grows in the presence of oxygen
Facultative: Can grow with or without oxygen Anaerobic: grows in the absence of oxygen Fastidious: special growth requirement (Divas!) Non-fastidious: simple growth requirement Capnophilic: Requires CO2 Halophilic: Salt loving |
|
|
What is an organism called that can grow in the presence or absence of oxygen?
|
Facultative
|
|
|
What is an organism called that has:
Special growth requirements? Simple growth requirements? |
Fastidious
Non-Fastidious |
|
|
What is an organism called that requires CO2 to survive?
|
Capnophillic
|
|
|
What is an organism called that LOVES high salt concentrations?
|
Halophllic
|
|
|
What are the characteristics and significance of a gram (+) cell wall?
|
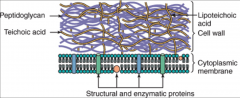
Thick PG layer with teichoic (TA) & lipoteichoic acids (LTA).
TA & LTA: Important for viability, virulence and serotyping. Promote attachment to mammalian cells, low endotoxin activity. |
|
|
What is more effective at fighting toxigenic diseases than cell wall inhibitors?
|
Protein synthesis inhibitors that target bacterial ribosomes (30s & 50s) subunits that make up the 70s ribosome)
|

