![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Classical Perspective |
(The oldest formal viewpoints of management) Scientific (Frederick Taylor/Frank and Lillian Gilbreth): Focuses on the productivity to the individual worker Administrative (Henri Fayol): Focuses on managers and the functions they perform. Bureaucratic Management ( Max Weber): Focuses on the overall organizational system.
|
|
|
Behavioral Perspective |
Mary Parker Follett: Coordination requires interaction with each other, must address everything, and is a never ending process. Elton Mayo: Human element significant in worker output & behavior. Hawthorne study: Individual & group performance affected by behavior. Douglas McGregor: Theory X & Theory Y Managers Chester Bernard: Employees will accept supervisory orders if the understand what's required, the orders are consistent with organization's goals and they perceive a positive personal benefit.
|
|
|
Quantitative Perspective |
Characterized by it's use of math, statistics and other quantitative techniques for management decision-making and problem solving. This approach has 4 basic characteristics: 1.) Decision making focus - problems that require direct action 2.) Measurable criteria - compare alternatives via physical numbers 3.) Quantitative Model - use formulas and equations to create a model 4.) Computers - quick method for mass scale or extremely complex things. |
|
|
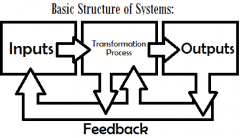
Systems Perspective |
3 main building blocks: Inputs, Outputs and Transformation Processes. Feedback: Information about the performance and status of the system. Synergy: "The sum of the whole is greater than the sum of it's parts" because each individual department organizes itself then relays information to each other part, thus creating a strong unit working together. |
|
|
Contingency Perspective |
A new managerial approach that recognized there is no one best approach to management. Any of the other 4 ways could work alone or in combination for different situations.
|
|
|
Theory X & Theory Y |
( Douglas McGregor)
Theory X: Advocates that a manager perceives that subordinates have an inherent dislike of work and will avoid it if possible.
Theory Y: Advocates that a manager perceives that subordinates enjoy work and will gain satisfaction from their jobs.
|
|
|
Basic Structure of Systems Perspective Management |
|

