![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are proteins?
|
Proteins are large, complex molecules found in cells and all living things
|
|
|
What parts of the body do they make up?
|
Muscle mass, bones, blood and skin
|
|
|
List five functions that proteins play within the body
|
Metabolism Immunity Fluid balance Nutrient transport Provide energy In some circumstances Glyconeogenesis |
|
|
Where do we get proteins?
|
Proteins are found in a variety of food The body can synthesize its own proteins |
|
|
Proteins are made of what elements?
|
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen |
|
|
The building blocks of proteins are?
|
Amino Acids |
|
|
How many Amino acids are most of our proteins in our body made up of?
|
20
|
|
|
How many unique proteins can be made by combining amino acids?
|
10,000 to 50,000 |
|
|
Glycine, Leucine and Aspartic acid make what unique?
|
Amino Acids
|
|
|
What are essential amino acids, and where do we get it from?
|
Essential amino acids are amino acids not produced by the body, but must be obtained from food. 9 out 20 necessary amino acids are essential |
|
|
What are non-essential amino acids?
|
Non-essential amino acids can be made by our bodies, opposite of essential amino acids 11 out of 20 necessary amino acids are non-essential |
|
|
What are complete proteins?
|
Complete proteins contain sufficient amounts of all 9 amino acids; this is considered a "high-protein" protein While Incomplete proteins do not contain sufficient amounts of all 9 essential amino acids; this is considered a "low-protein" protein |
|
|
List 6 foods that are considered complete proteins
|
Egg Whites Meat Poultry Fish Milk Soybeans Quinoa (may not provide sufficient amount) |
|
|
What is a limiting amino acid?
|
Limiting amino acids are amino acids that is missing or in least supply |
|
|
What happens without the proper combination and quantity of essential amino acids?
|
Protein synthesis slows down to a point where proteins cannot be made Ex: Less histidine= less hemoglobin protein= less oxygen transport |
|
|
Inadequate energy consumption (calories) also limits protein synthesis. If this happens are body will....
|
Use any accessible proteins for energy, thus preventing it from being used to build new proteins |
|
|
What is primary structure?
|
Primary structure is the sequential order of amino acids
|
|
|
What is secondary structure?
|
Secondary structure is spiral shape due to twists and turns of the amino acid train Hydrogen bonding along the twisted spiral adds to its ability |
|
|
What is tertiary structure?
|
Tertiary structure is the further folding into a unique 3-dimensional shape Critically important because the shape determines the protein's function |
|
|
Explain the shape and relate the shape's function of muscle fibers
|
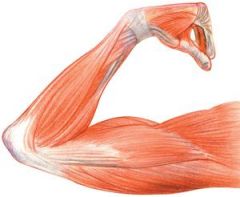
Muscles fibers are much longer than they are wide The shape of the muscle fibers enables the muscle to contract and relax |
|
|
Explain the shape and relate the shape's function of red blood cells
|
Red blood cells are shaped like flattened discs with depressed centers The shape of the red blood cells enables them to change shape and flow freely through even the tinniest openings to deliver oxygen and still return to their original shape |
|
|
What is Denaturation?
|
Denaturation is the proteins losing shape when subjected to Heat, acids and bases, heavy metals, alcohol, other damaging substances Ex: cooked egg whites and curdled milk |
|
|
What happens to the function of a protein when it's different?
|
Denaturation results in an irreversible loss in protein function
|
|
|
List 6 reasons as to why we need proteins
|
Cell growth, repair and maitenance+ Proteins act as enzymes and hormones; (Enzymes are speed up chemical reactions and Hormones are chemical messengers to the body) Help maintain fluid Help maintain acid base balance Help maintain strong immune system Proteins serve as an energy source |
|
|
Where are proteins stored?
|
Nowhere; doesn't have to be stored |
|
|
When proteins are needed for energy, where are they taken from?
|
Muscle and body tissue
|
|
|
How do we avoid protein in our body tissues from being "eaten up" as fuel?
|
Eat enough carbohydrates
|
|
|
What happens to any excess protein we eat?
|
Converted and stored as body fat
|
|
|
The RDA for a sedentary person in how many kilograms bodyweight or how many of their total energy intake?
|
0.8 kilograms bodyweight per day or 10 to 35% of their total energy intake
|
|
|
RDA for a non vergetarian strength athlete is
|
1.2 to 1.7 g/kg of bodyweight
|
|
|
RDA for a non vegetarian endurance athlete is
|
1.2 to 1.4 g/kg of bdyweight
|
|
|
Most Americans...
|
Meet or exceed the RDA for protein
|
|
|
List other sources of protein other than meat
|
Dairy products Legumes Eggs Nuts Whole grains |
|
|
Too much protein is harmful, list three reasons why
|
High cholesterol and heart disease Possible bone loss Kidney disease |

