![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Molecular Biology |
Investigating biological activity at a molecular level |
|
|
Metabolism |
The sum of all reactions that occur in an organism |
|
|
Anabolism |
Synthesis of polymers from monomers (requires energy) |
|
|
Catabolism |
Breakdown of polymers into monomers (releases energy) |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Compounds that have carbon atorm in the structure along with other atoms |
|
|
Why Carbon? |
Carbon atoms can form 4 covalent bonds. This allows C to form a wide variety of stable compounds. |
|
|
Properties of Carbohydrates |
Composed of C, H and O Monomers are polar Soluble in water |
|
|
Function of Carbohydrates |
It's function is to be a source of quick energy |
|
|
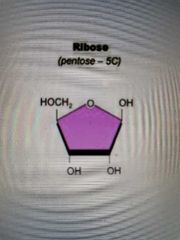
Ribose structure |
|
|
|
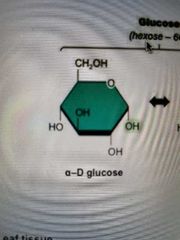
a-Glucose structure |
|
|
|
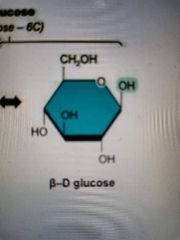
b-Glucose structure |
|
|
|
Properties of Lipids |
Involve fatty acid chains Non-polar Insoluble in water |
|
|
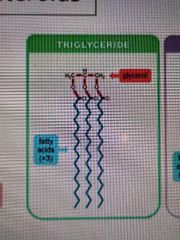
Triglyceride structure |
|
|
|
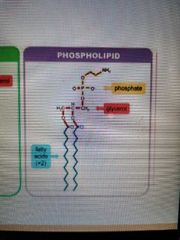
Phospholipid structure |
|
|
|
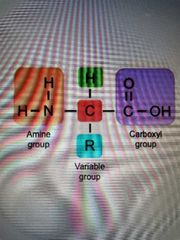
Amino acid structure |
|
|
|
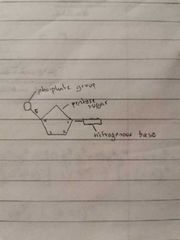
Mononucleotide structure |
|
|
|
Falsification of Vitalism |
Friedrich Wohler synthesized urea artificially in the lab. |
|
|
What gives water dipolarity? |
The polarity of water is caused by the high electronegativity of the O atom, which "pulls" the electrons toward it, creating a slightly negative charge |
|
|
Thermal property of water. Why? |
Can absorb a large amount of heat before changing state (100°C) This is because of the many hydrogen bonds between water molecules. |
|
|
Water is good for homeostasis. Why? |
Water is relatively slow to change temperature. When sweat evaporates, the body cools down because the water takes energy with it. |
|
|
Cohesive properties of water |
Cohesion is the ability of water molecules to "stick" together. This is due to hydrogen bonding. High surface tension
|
|
|
Adhesive properties of water |
Adhesion is the ability to "stick" to other molecules. This occurs through polar bonding or hydrogen bonding. Allows water to flow in opposition of gravity |
|
|
Solvent properties of water |
The polarity of water allows it to dissolve charged and polar molecules. |
|
|
Transport in plasma |
Sodium Chloride Glucose Amino acids Oxygen |
|
|
How are lipids transported in blood (non-polar) ? |
Lipids form complexes with proteins, called lipoproteins. Hydrophilic proteins face outward, hydrophobic lipids face inwards. |
|
|
Functions of saccharides |
Mono - energy source Di - transport Poly - storage |
|
|
Saturated fatty acids |
Have no double bonds, come from animals |
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acids |
Contain double bonds, come from plants |
|
|
Formation of triglycerides |
Glycerol + 3 fatty acid chains gives a triglyceride and 3 water molecules |
|
|
Storing energy in carbohydrates |
Easier to transport Readily accessible Can't store as much energy |
|
|
Storing energy as lipids |
Harder to transport Harder to access Store twice as much energy |
|
|
BMI formula |
mass kg/ height m² |

