![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what type of lymphadenitis is a culture indicated? |
1. Acute |
|
|
What are the ssx of acute lymphadenitis? |
1. Redness 2. Swelling 3. Tenderness 4. Rarely bx 5. CULTURE |
|
|
What are the histological patterns of lymphoid hyperplasia? |
1. Follicular pattern 2. Paracortical 3. Sinus |
|
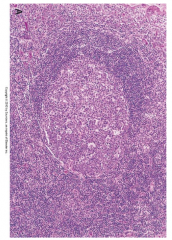
|
1. Reactive follicle--- bacterial |
|
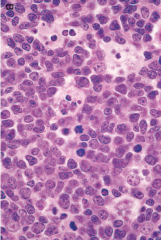
|
1. Centroblasts and macrophages in reactive follicle |
|
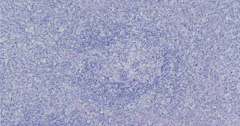
|
1. Diffuse hyperplasia-- viral |
|
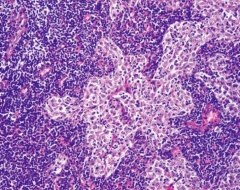
|
1. Sinus hyperplasia--- lymph nodes draining tumors |
|
|
What can cause granulomatous lymphadenopathy? |
1. Infection 2. Foreign bodies 3. Secondary response to malignancy |
|
|
What causes necrotizing granulomas? |
1. TB 2. Histoplasmosis 3. Cat scratch disease |
|
|
What causes non-necrotizing granulomas? |
1. Sarcoidosis |
|
|
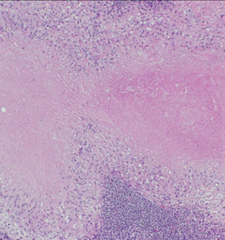
1. Necrotizing grauloma |
|
|
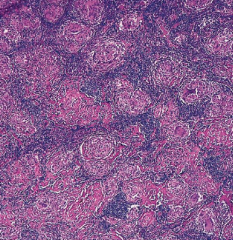
1. Non-necrotizing granuloma |
|
|
when is an accessory spleen of clinical significance? |
1. Hematological issue affecting the spleen, but you don't remove both spleens |
|
|
How does perisplenitis present? |
1. Thick white fibrous plaques coating the surface 2. Common incidental finding in autopsy |
|
|
What are the MCC of splenic insufficiency? |
1. Infarction-- sickle cell 2. Splenectomy |
|
|
What is the risk of infection in a spleen-less patient? |
1. S. pneumoniae 2. H flu 3. N. meningitidis |
|
|
What are the MCC of splenomegaly? |
1. Hematolymphoid malignancies 2. Infection 3. Congestive states 4. Autoimmune diseases |
|
|
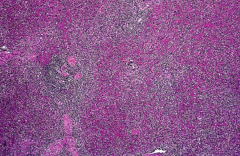
What is congestive splenomegaly? |
1. Venous outflow obstruction 2. Cirrhosis 3. Thrombosis of splenic veins 4. Occlusive thrombosis, sclerosis, or stenosis of the portal vein |
|
|
1. Congestive splenomegaly |
|
|
What are the MCC of splenic rupture? |
1. Trauma 2. Surgical intervention 3. Mono, malaria, typhoid, bacterial endocarditis |
|
|
What is a possible sequel to splenic rupture? |
1. Splenosis |
|
|
What are the ssx of hypersplenism? |
1. One or more peripheral blood cytopenias due to splenic sequestration and destruction |
|
|
What are the MCC of hypersplenism? |
1. Autoimmune 2. Congestive splenomegaly 3. Gaucher disease |
|
|
What is the MC primary tumor of the spleen? |
1. Hemangioma----> angiomatosis |
|
|
What is a lymphangioma? |
1. Subcapsular tumor of spleen 2. May involve entire organ |
|
|
What is a hamartoma? |
1. Rare, nodular lesion of splenic sinus
|
|
|
What is the most common type of malignancy in the spleen? |
1. Lymphoma 2. Usually confined to spleen----- DLBCL most common |
|
|
What are the MC sites of metastasis from the spleen? |
1. Melanoma 2. Lung 3. Breast 4. Stomach |
|
|
What is an angiosarcoma? |
1. Malignant blood vessel |
|
|
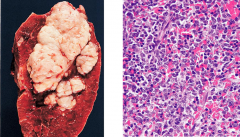
1. DLBCL |
|
|
What are the characteristics of ectopic thymus? |
1. Rare 2. Usually incidental finding |
|
|
With what syndrome is thyme hypoplasia associated? |
1. DiGeorge |
|
|
What causes thyme hyperperplasia? |
1. Reactive B-lymphoid follicles within the thymus 2. Seen in:chronic inflammatory and immunologic states 3. **Myasthenia gravis |
|
|
What is the origin of a thymoma? |
1. Thymic epithelial cells 2. MC primary anterior mediastinal neoplasm |
|
|
What diseases are associated with thymoma? |
1. Paraneoplastic syndrome 2. Myasthenia gravis |
|
|
What is the histology of a thymoma? |
1. Plump epithelioid cells 2. Spindle cells 3. Mix of both |
|
|
What are the diagnostic patterns of malignant thymomas? |
1. Invasive--- benign cytologic features 2. Thymic carcinoma-- malignant features |
|
|
To where does a thymoma most often metastasize? |
1. Esophagus 2. Lung/pleura 3. Breast 4. Thyroid 5. Melanoma |

