![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Killing Microorganisms: Fomites |
Objectsthat is capable of carrying organisms |
Tables, computers, doorknobes and US |
|
|
Killing Microorganisms: Sterilization |
Processthat destroys all organisms and infective agents on a fomite |
Kills everything |
|
|
Killing Microorganisms: Disinfection |
Processof using antimicrobial agents on non-living objects to kill microorganisms on afomite |
Doesn't kill everything |
|
|
Killing Microorganisms:Pasteurization |
Process of using heat to decrease the amount of pathogenic microorganismstml>dc8 |
Beer & Wine |
|
|
Killing Microorganisms: Antiseptics |
Antimicrobial agents that are applied to the skin |
chemicals safe enough to be used on skin |
|
|
Killing Microorganisms: Bacteriostatic |
Solutions that are over-diluted may be ineffective |
Limiting bacteria from growing |
|
|
Killing Microorganisms:Bactericidal |
Solutions are under-diluted may leave toxic residues that are harmful to humans whom come in contact with them |
Homicidal |
|
|
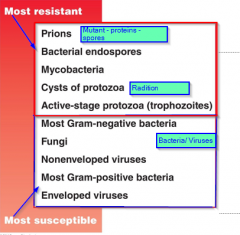
Mechanismsof Action of Anti-Microbial Agents |
•Cellwalls & cell membrane •Protein = Enzymes, Channels •Nucleicacid = DNA, RNA Protein Denature |
|
|
|
Physical Methods of ControllingMicroorganisms |
•Heat denatures proteins & destroys cellmembranes •Moist heat •Boiling - vapor pressure •Autoclave |
Heat is the common used method |
|
|
Moist heat |
Disinfection, pasteurization,sterilization |
Proteins denatures faster in solution |
|
|
Pasteurization |
•Process of using heat to decrease the amount of pathogenic microorganism •Different temperatures & duration fordifferent foods |
|
|
|
Pasteurization: High Temperature, Short Time |
Heat liquid to 72℃ for 15 seconds |
|
|
|
Pasteurization: Ultra-Heat Treating |
Heat to 140℃ for 4 seconds |
|
|
|
Filtration: HEPA |
•High Efficiency Particulate Arrestance •Filter bacteria and viruses •Meshwork of randomly arrangedfibers |
Hospital uses them a lot |
|
|
Filtration |
Mechanical separation of solid from afluid |
|
|
|
Ionizing radiation |
•Sufficient energy to eject electrons from atoms when the radiation hits amolecule •Causes direct damage to cell membranes, DNA |
Short wavelength electromagneticradiation (e.g. x rays, gamma, cancer) |
|
|
Non-ionizing radiation |
•Not enough energy to cause ionization butthe atoms are excited •usually non mutagenic •causes heating |
Long wavelength electromagnetic radiation (e.g. less energy) |
|
|
Chemical Methods of ControllingMicroorganisms |
• Phenols • Alcohols • Reducing agents • Halogens •Oxidizing agents • Surfactants • Heavy metals |
|
|
|
Phenols |
• aromaticorganic compounds • denatures protein & disrupt cell walls • toxic |
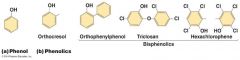
Smell sweet |
|
|
Alcohol |
· Organic compounds with a hydroxyl group(-OH) attached to an alkane (CH4) · Activity decreases with chain length · Denature proteins ·No Sporicidal action |
Requires water (don't kill spores) |
|
|
Halogen |
·Elements in Group VII of the periodictable ·Oxidize proteins, damage nucleic (Hydrofluoric) acidstructure & synthesis |
fluorine (F) chlorine (Cl) bromine (Br) iodine (I) astatine (At) |
|
|
Oxidizing Agents |
·releases free radicals ·denatures proteins ·little to no action on bacterial spores |
Alcohol and hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
Reducing Agents |
·Aldehydes ·Effective on bacteria, fungi includingspores ·Mechanism of action is through alkylationof proteins and purines (adenine and guanine) |
Kills everything we use in Cadavers |
|
|
Surfactants |
Lower the surface tension of aqueoussolutions |
Lungs from collapases |
|
|
Anionic Surfactant |
soaps,detergents |
Decrease surface area of waer lipids dissolves |
|
|
Cationic Surfactant |
•Quaternary Ammonium Compounds •Denature proteins •Disrupt cell membranes & changepermeability |
Causes cell membrane to be leaky |
|
|
Heavy Metal Surfactant |
Precipitate proteins and interferes withmetabolic reactions |
Silver, Gold and Nitrate |

