![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipid Catabolism |
•Involve Detaching fatty acids chains from glycerol •Glycerol Can be converted into a glycolysis intermediate •Fatty Acids undergo β - oxidation |
|
|
Lipid Metabolism Ex: 1 gram fat around 9 glycol |
•Beta oxidation •Carbon backbone depends/convert medium •Glycerol |
|
|
Protein Catabolism |
•Catabolized by proteases •Broken Down into amino acids •Amino Acids could then be recycled or excreted through the urea cycle |
|
|
Photosynthesis (Algae, Archaea, Bacteria,Prokaryotes organelles) |
•Carried Out in Chlorophylls Divided Into two sets of reactions •light dependent reactions •light independent reactions |
|
|
Light Dependent Reaction |
•Produce ATP •Pigment molecule in the chlorophyll is excited when it absorbs light •Passes its electrons to the electron transport chain •Specific wavelengths of light can provide the required energy |
|
|
Light Independent Reaction |
•Fixing Carbon •Uses A large amount of ATP •RuBisCO catalyzes the attachment of CO2 to RuBP to form two molecules of 3 carbon sugar |
|
|
What are the 2Carbonand Energy Sources? |
•Carbon Based organisms •CO2 •Other Organic material |
|
|
Carbon Source |
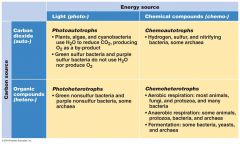
•CO2 - Autotroph •Organic Compounds - Heterotroph |
|
|
Energy Source |
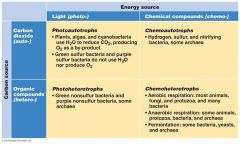
•Light- phototroph •Oxidation Of electron donors - chemotroph |
|
|
Oxygen Requirement: Obligate Aerobes (w/air) |
We are, need oxygen to survive |
|
|
Oxygen Requirement: Obligate Anaerobes (w/out) |
Can't have oxygen, gangreene, die w/oxygen Ex: yeast |
|
|
Oxygen Requirement: Facultative Anaerobes (w/air) |
Do better w/oxygen but does not need it |
|
|
Oxygen Requirement: Microaerophiles |
•Likes a lot of oxygen, need it
•High Levels death |
|
|
Oxygen Requirement: Aerotolerant |
Don't like it but will tolerate it |
|
|
Oxygen Requirement: Valence Electrons |
•Outer shell of oxygen makes it very reactive •Reduced to superoxide & hydrogen peroxide• •Organismsmust be able to neutralize these reactive molecules |
|
|
Reactive Oxygen Species |
•Superoxide(O2-) •superoxidedismutase •Peroxides(H2O2) •catalase |
|
|
Nitrogen Requirement |
•Required For several important organic molecules •Atmospheric Nitrogen can be converted into ammonium (NH4+) or nitrogen dioxide •Diazotrophs Are the only organism that can fix atmospheric nitrogen |
|
|
Optimal Range |
Organisms Have an optimal range of physical properties for growth and survival |
|
|
Temperature |
•Psychrophiles •Mesophiles •Thermophiles •Hyperthermophiles |
|
|
pH |
•Acidophiles •Neutrophiles •Alkalinophiles |
|
|
Biofilms |
•Groups Of organisms when they stick to each other on any surface •Formon organic or inorganic surfaces •Important In pathogenesis |
|
|
Biofilm involves 3 steps? |
•Attachment •Growth (maturation) •Dispersion |
|
|
Biofilm Formation |
•Free Floating organisms attach to a surface •Maintained By Van der Waal’s forces & bacterial structures such as pili •Bacterial Detach from the biofilm & disperse into the environment |
|
|
Biofilm Formation develops a thick extracellular matrix composed of? |
•Extracellular Polymeric Substance (EPS) •DNA,Proteins, Polysaccharides •Scaffolding & protection |
|
|
Cultures |
•Method Of growing microbial organism in specific media •Specific Nutrients for the growth of the organism is known as the medium •Broth Are liquid medium |
|
|
Cultures: Sample of an organism? |
Inoculum |
|
|
Cultures: Microbial colonies visible clusters of? |
•Microorganisms growing on the surface of media
|
|
|
Cultures: Colony Forming Unit |
Colonies descended from a single cell/ group of cells |
|
|
Defined Medium |
All chemicals used are known, no yeast, animal or plant tissues |
|
|
Complex Medium |
Yeastor animal extracts as a source of amino acids and nitrogen |
|
|
Minimal Medium |
Minimum Nutrients for colony growth |
|
|
Selective Medium |
Only Support the growth of selected organisms•antibiotics •amino acids gment |
|
|
Differential Medium |
Visible Indicator in the presence of specific organisms |

