![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is metabolism? |
Is the sum of all the chemical processes carried out by living organisms. |
|
|
|
What is anabolism? |
Reactions that require energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler one. |
It is needed for growth, reproduction, and repair of cellular structures |
|
|
What is catabolism? |
Reactions that release energy by breaking complex molecules into simpler ones that can then be reused as building blocks |
It provides an organism with energy for its life processes, including movement, transport, and the synthesis of complex molecules that is anabolism |
|
|
What is Autotrophs? |
Making of own food by reducing CO² |
|
|
|
What is photoautotrophs? |
Falls under autotrophs. Uses light energy to make own food. |
|
|
|
What is chemoautotroph? |
Uses inorganic compounds make larger organic compounds for themselves . Make energy for themselves. Not relaying on the others. Make their own food. |
|
|
|
What is Heterotrophs? |
They feed on the others. Use ready made organic molecules for their food. |
|
|
|
What is photoheterotrophs? |
Use the light energy. Depends on ready made organic molecules for food. |
|
|
|
What is Chemoheterotrophs? |
Feeding on others. We humans are chemoheterotrophs. Our energy source is organic compounds for energy. We relay on getting our energy through chemicals. Ex. Carbs |
|
|
|
What are Enzymes? |
Special category of proteins found in all living organisms |
|
|
|
True or False? Most cells contain hundreds of enzymes, and cells are constantly synthesizing proteins, many of which are enzymes |
True |
|
|
|
Enzymes are ________________. All enzymes are ________________. |
1. Protein catalyst 2. Biological catalysts |
|
|
|
What are catalysts? |
Substances that can speed up a chemical reaction without being permanently altered themselves. |
|
|
|
True or False? Catalysts speed up reactions. |
True |
|
|
|
Whats the only other way to speed up the reaction rate? |
Increase temperature |
|
|
|
What happens when a 10-degree increase in temperature occurs? |
It doubles the reaction rate |
|
|
|
True of false? Most cells would not die when exposed to such rise in temperature |
False |
|
|
|
An enzyme is a large ______ A. Carbohydrate B. Nucleic acid C. Protein D. Lipid |
C. PROTEIN |
|
|
|
True or False An organism can live without enzymes? |
False |
|
|
|
Enzymes are necessary for _______ A. Life at temperatures that cells can withstand B. To act as a catalyst in chemical reactions C. make materials that cells need D. All of the above |
D. All of the Above |
|
|
|
Catalysts A. All enzymes are organic catalysts or biological catalysts. B. Not all cataylsts are enzymes. Enzymes are complex proteins. (Fast reaction) C. Other catalysts and simple inorganic molecules. (Slow reaction). D. A and C E. All of the above |
E. All of the above |
|
|
|
True or false? Enzymes lower the activation of energy |
True |
|
|
|
What us active site? |
It is a certain area in the enzymes surface. A binding site. It forms a loose association with its substrate. |
|
|
|
What is a substrate? |
A substance on which the enzyme act. Can be broken down or come together. - enzyme binds to the active site of the substrate Has kinetic energy. Collides with various molecules within a cell |
|
|
|
What happens when a substrate collides with active site of its enzyme, an ____________________________ is formed. |
Enzyme-substrate complex |
|
|
|
True or False: As a result of binding to the enzyme, all of the chemical bonds in the substrate are weakened. |
False. Only some of the chemicals bonds in the substrate are weakened. |
|
|
|
What happens when the substrate are weakened? |
The substrate then undergoes chemical changes, the product or products are formed and the enzyme detaches. 1. Undergoes chemical changes 2. Formed 3. Enzymes detaches |
|
|
|
Enzymes generally have a ____________ of specificity |
High degree |
|
|
|
Substrate catalyze only _____ type of reaction |
One |
|
|
|
True or false: most substrate act on only one particular substrate. |
True |
|
|
|
What shape is the enzymes? |
Tertiary structure |
|
|
|
Which one does belong as a specificity for substrate? A. Substrate electrical charges at its active site , accounts for its specificity B. When ensyme acts one more than one substrate, it usually acts on substrate with the same functional group or the same kind of chemical bond C. Prototypical or protein splitting enzymes act on different proteins by always act on the peptide bonds in those proteins D. All of the above |
D. All of the above |
|
|
|
What is a tertiary structure? |
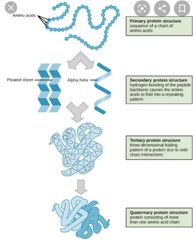
Further bending and folding of the protein molecule into globular (irregular spherical) shapes or fibrous threadlike strands. |
|
|
|
How are enzymes usually named? |

By adding the suffix-ase to the name of the substrate on which they act |
|
|
|
What are the categories of Enzymes? |
Endoenzymes Exoenzymes |
|
|
|
What is endoenzymes? |
Endoenzymes: or intracellular enzymes, act within the cell that produced them. |
|
|
|
What is exoenzymes? |
Exoenzymes: including extracelluar enzymes, are synthesized in a cell but cross the cell membrane to act in the periplasmic space or in the cells immediate environment. |
|
|
|
What is Coenzyme? |
A nonprotein organic molecule bound to or loosely associated with an enzyme. Many are synthesized from vitmains, which are essential nutrients precisely because they are required to make coenzyme. |
|
|
|
What is cofactor? |
Usually an inorganic ion, such as magnesium, zinc or manganese. They often improve the fit of an enzyme with its substrate and their presence can be essential in allowing the reaction to proceed. |
|
|
|
What is apoenzyme? |
a protein that forms an active enzyme system by combination with a coenzyme and determines the specificity of this system for a substrate. |
|
|
|
What is holoenzyme? |
an enzyme complete with its apoenzyme and cofactors |
|
|
|
What are inhibitors? |

|
|
|
|
A substance that reduces or stops a reaction. Reduces the activity of an enzyme molecule.
What Am I? |
Inhibitors
|
|
|
|
prevention of the reaction even if the substrate can still bind
|
non-competitive inhibition
|
|
|
|
What are the Two Types of Reversible Inhibition
|
Competitive
Non-Competitve |
|
|
|
Competitive inhibition
|
where inhibitor has similar shape to substrate molecule and competes with substrate for the enzyme's active site. Blocks active site and prevents enzyme-substrate complexes.
|
|
|
|
What drugs are competitive inhibitors? |
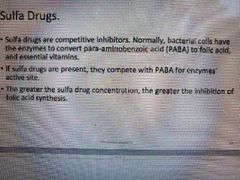
SULFA DRUGS |
|
|
|
Enzymes are affected by _____ and by extremes of ____. |
1. Heat 2. pH. |
|
|
|
What is Optimum temperature? |
Means where it works the best. 37c is normal body temperature. |
|
|
|
Human enzymes have optimum pH near netural |
True |
|
|
|
What is pH? |

The measure of a solutions potential to attract hydrogen ions.
Is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution |
|
|
|
How is Enzymes affected by temperature and pH? |
Temperature: raising the temperature generally speeds the reaction, and lowering the temperature slows down the reaction. However, extreme high temperatures can cause an enzyme to lose its shape (denature) and stop working pH: each enzyme has an optimum pH range. Changing the pH outside of this range will slow enzyme activity. Extreme pH values can cause enzymes to denature. |
*Professor want you to know what optimum temperature and optimum pH means |
|
|
Glycolysis is |
Splitting of sugar. It is anaerobic process. |
|
|
|
Glycolic glucose is |
Oxidized to pyruvic acid. Energy is needed to start the process. |
|
|
|
What are the 4 important events that occur in glycolytic pathway? |
1. Substrate level phosphorylation( the transfer of phosphate groups from ATPs to glucose 2.breaking of a six carbon molecule (glucose) into two 3- carbon molecules 3. The transfer of two electrons to the coenzyne NAD 4. The capture of energy in ATP |
|
|
|
What is the summary of glycolysis? |
1. You start with one glucose molecule 2. You use two ATP for energy. Phosphorylation occurs. 3. You gain two NADH molecules 4. You gain four ATP molecules (-2(used at the start) +4=2(net gain)) 4. You gain two pyruvic acids |
*What you need to know for the test Glucose +2ADP +2Pi +2 NAD ------> 2Pyruvate+2ATP+2NADH |
|
|
Homolactic acid fermentation pyruvic acid is directly converted to |
Lactic acid |
|
|
|
Alcoholic fermentation makes |

Alcohol |
|
|
|
Sugar Mannitol fermentation test is |

Test that uses the sugar Mannitol and the pH indicator phenol red.
|
|
|
|
What is considered noncompetitive inhibitors? |
Lead mercury and other heavy metals. They can bind to other sites on the enzyme molecules and permanently change its shape and inactivate it. |
|
|
|
___________ is a kind of reversible noncompetitive inhibition, regulates the rate of many metabolic pathways |
Feedback inhibition |
|
|
|
Protein structures chapter 2 |
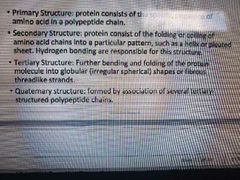
|
|
|
|
Enzyme inhibition |

|
|
|
|
Noncompetitive inhibitor |

|
|
|
|
Abbreviations |

|
|
|
|
Phosphorylation |

|
|
|
|
Summary of Glycolysis |

|
|
|
|
Alternative to Glycolysis |

|
|
|
|
Involuntary drunkness |
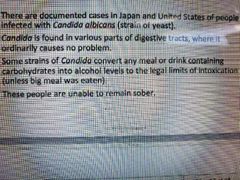
|
|
|
|
Other fermentation and their uses in diagnosis |

|
|

