![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Simple Microscope |
Early Microscope that consisted of biconvex lenses that were magnifying glasses |
|
|
Brightfield Compound Microscope |
Shows dark object in a bright field, used most often, used to observe unstained microorganisms |
|
|
Base of Microscope |

The bottom part of the microscope |
|
|
Stage |

Part of the microscope that holds the slide that is being viewed |
|
|
Arm |

The part on the side of the microscope is used to support it when it is carried |
|
|
Condensor |

Above the light source, has several lenses that concentrate light on the slide by focusing it into a cone |
|
|
Iris Diaphragm |

Controls the angle and size of the cone of light |
|
|
Objective Lenses
|

Lenses on the nosepiece |
|
|
Ocular/Eyepiece Lenses |

On the upper end of the tube |
|
|
Coarse Adjustment |
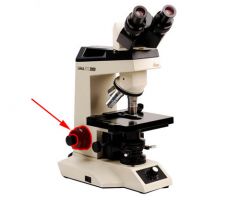
Larger knob used for focusing low power objectives (4x and 10x) |
|
|
Fine Adjustment |

Smaller knob, used for focusing high power and oil immersion lenses |
|
|
Field of Vision
|
The area seen through the microscope |
|
|
4x Magnification |

Scanning |
|
|
10x Magnification |

Low Power |
|
|
40-45x Magnification |

High Dry |
|
|
100x Magnification |

Oil Immersion Lens; Most important, must be used with immersion oil |
|
|
Total Magnification |
Magnifying power of the objective lens times the magnifying power of the eyepiece lens (usually 10) |
|
|
Resolution/Resolving Power |
Ability of a lens to reveal fine detail or two points distinctly separated |
|
|
Refractive Index |
The amount the light bends |
|
|
Focal Point
|
Light rays pass through a lens and converge here, where an image is formed |
|
|
Spherical Aberration
|
When you bring the center of a microscope field into focus, the periphery may be fuzzy because of the curvature of the lens, resulting in multiple focal points |
|
|
Chromatic Aberration |
Multitude of colors are seen in the field, caused by the prism like effect of the lens as various wavelengths of white light pass through a different focal point for each wavelength |
|
|
Monochromatic Light |
Light source of one wavelength, eliminates chromatic aberration, most logical, most expensive
|
|
|
Achromatic Lenses |
Lens system corrected for red and blue light
|
|
|
Apochromatic Lenses |
Lenses corrected for red, blue and other wavelengths
|
|
|
Parfocal |
When a subject is in focus with one lenses, it is in focus with all lenses
|
|
|
Working Distance |
The distance between the objective lens and the specimen
|
|
|
Bacillus/Bacilli/Rod |
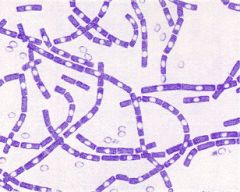
|
|
|
Coccus/Cocci |
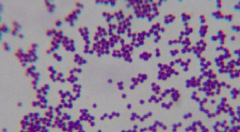
|
|
|
Spiral Bacteria |
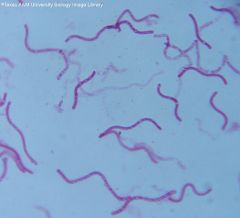
|
|
|
Phase Contrast Microscopy |
Small differences in the refractive properties of the objects and the aqueous environment are transformed into corresponding variations of brightness. |
|
|
Diffracted/Retarded |
Light rays that do not hit the object |
|
|
Brownian Movement |
Not true motility, but movement caused by molecules in the liquid striking an object and causing it to shake/bounce, not directed movement |
|
|
Aseptic Technique |
Procedures used to avoid introducing unwanted microbes and to prevent spreading of microbes where they are not wanted. |
|
|
Zacharias Janssen |
Invented the microscope shortly before 1600's |
|
|
Chemically Defined Medium |
A medium whose exact chemical composition is known |
|
|
Complex Media |
Media for which the exact chemical composition varies slightly from batch to batch |
|
|
Nutrient Broth |
Commonly used liquid complex medium |
|
|
Nutrient Agar |
Agar is added to a nutrient broth |
|
|
Agar |
Extract from marine red algae, liquefies at 100C/Solid at 40C
|
|
|
Autoclaving/Steam Sterilization |
Steam under pressure heated to 121*C at 15 psi for 15 minutes |
|
|
Petri Plates |
Contain solid media that provides a large surface for examination of colonies
|
|
|
Inoculation |
Intentionally introduced
|
|
|
Colony |
Population of cells that arises from a single bacterial cell
|
|
|
Colony Forming Unit |
Group of the same microbes attached to one another
|
|
|
Colony Elevation |
Flat, raised, convex, umbonate |
|
|
Whole Colony appearance |
circular, irregular, biconvex, filamentous, rhizoid |
|
|
Colony margin |
Entire, Undulate, Lobate, Filamentous, Curled |
|
|
Flocculent |
clumps of microbial cells |
|
|
Sediment |
Microbial cells that have settled at the bottom of the tube |
|
|
Bacterial growth in broth |
clear, turbid, pellicle, flocculent, sediment |
|
|
Broth cultures |
provide large numbers of bacteria in a small space and are easily transported |
|
|
contaminants |
unwanted microbes |
|
|
Agar slant |
test tubes containing solid culture media that were left at an angle while agar solidified. They provide a solid growth surface |
|
|
Agar Deep |
Deeps are used to grow bacteria that require less oxygen than is present on the surface of the medium |
|
|
Semi Solid Agar Deeps |
Can be used to determine if a bacterium is motile |
|
|
Patterns of Growth on Agar Slants |
Arborescent, Beaded, Echinulate, Filiform, Rhizoid, Spreading |
|
|
Simple Stain |
Only one reagent is used and all bacteria are stained similarly |
|
|
Differential Stains |
Multiple reagents are used and bacteria react to the reagents differently |
|
|
Smear |
Thin film of bacterial cells |
|
|
chromophore |
ion that is colored (simple stain) |
|
|
Direct Stain |
A simple stain that stains the bacteria |
|
|
Negative Stain |
A simple stain that stains the background but leaves the bacteria unstained e.g. India Ink |
|
|
Gram Stain |
Useful in identifying and classifying bacteria. It is a differential stain that enables you to tell if bacteria is gram + or gram - |
|
|
Primary Stain |
Crystal Violet |
|
|
Mordant |
Gram's Iodine |
|
|
Decolorizing Agent |
Ethanol or Ethanol-Acetone |
|
|
Secondary Counter Stain |
The basic dye stains the decolonized bacteria red e.g. safranin |
|
|
Gram - |
Decolorize more easily, thin layer of peptidoglycan surround by an outer layer of lipoproteins, phospholipids, lipopolysaccharides |
|
|
Gram + |
Decolorize more slowly and retain primary stain, multiple layers of peptidoglycan |
|
|
Gram Positive Cocci |
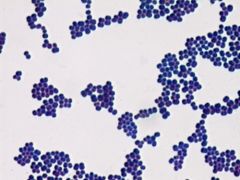
|
|
|
Gram Negative Bacilli |
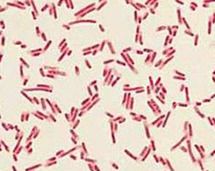
|
|
|
Pure Culture |
Consists of only one species of microorganism |
|
|
Contamination |
The presence of unwanted microorganisms |
|
|
Streak Plate |
A loop is used to streak the mixed sample many times over the surface of a solid culture medium in a Petri Plate, the most common isolation technique used today |
|
|
Spread Plate |
Quantitative, A small amount of previously diluted specimen is spread over the surface of a solid medium using a spreading rod |
|
|
Pour Plate |
Quantitative, A small amount of diluted sample is mixed with melted agar and poured into empty, sterile, petri dishes |
|
|
Selective Media |
Contains chemicals that prevent the growth of unwanted bacteria without inhibiting the growth of the desired bacteria |
|
|
Enrichment Media |
Contains chemicals that enhance the growth of the desired bacteria |
|
|
Differential Media |
Contains various nutrients that allow the investigator to distinguish one bacterium from another by how they metabolize or change the media with a waste product |
|
|
EMB Agar with Escherichia |
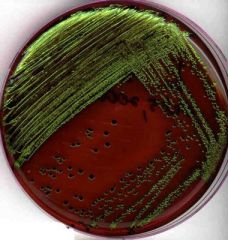
|
|
|
Mannitol Salt Agar |
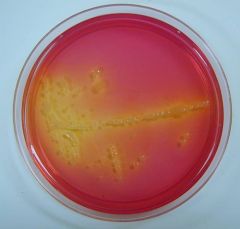
Bacteria that produce acid from mannitol will cause the phenol red to turn yellow (Staph) |
|
|
Catabolism |
Chemical reactions that release energy from the decomposition of the complex organic molecules |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen |
|
|
Monosaccharides (Carb) |
Simple Sugars containing 3-7 carbon atoms |
|
|
Oligosaccharides (carb) |
Composed of 2 to 20 monosaccharide molecules |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Consist of 20 or more monosaccharide molecules |
|
|
Hydrolytic Enzymes |
Leave the cell and break down with the addition of water |
|
|
OF Medium |
A nutrient semisolid agar deep containing a high concentration of carbohydrate and a low concentration of peptone, contains the indicator bromthymol blue that turns yellow in the presence of acids indicating the catabolism of the carb |
|
|
OF Glucose Medium |
af- does not use glucose pf-oxidizer ea-fermenter |
|
|
Starch Hydrolysis Test |
After incubation, add iodine to detect starch, the clearing around the bacteria indicates that the starch was hydrolyzed |
|
|
Fermentation Tube |
Used to detect acid and gas production from carbs, it contains peptone, an acid base indicator (phenol red) and an introverted (Durham) tube to trap gas |
|
|
MRVP Broth |
Glucose supplemented nutrient broth used for MR (methyl red res) and (V-P Voges-Proskauer test) Distinguishes organisms that produce large amounts of acid from glucose and ones that produce the neutral acetoin |
|
|
Carbohydrate Fermentation Tube |

a) Phenol red indicator is red in neutral or alkaline solutionb)Phenol red turns yellow in the presence of acidsc) Gases are trapped in the tube while the indicator shows the production of acid |
|
|
Citrate Agar |

The use of citric acid as the sole carbon sourcea) Citrate negativeb) Citrate positive (alkalized because of ammonia) |
|
|
MR (Methyl Red) Test |

|
|
|
V-P (Voges-Proskauer) Test |

Added 2-3 drops of V-P reagent |
|
|
Proteins |
Large organic molecules |
|
|
Amino Acids |
Consist of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur |
|
|
What color does litmus turn in the presence of acid? |
Pink |
|
|
Gelatin Hydrolysis |
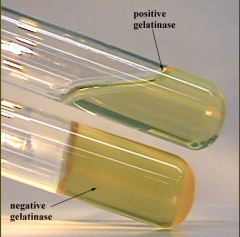
|
|
|
Urease Production |

a) Fuchsia color + Urease hydrolysis of urea produces ammonia b) Yellow - for Urease/negative control |
|
|
Litmus Milk |

|
|
|
Deamination |
The removal of an amino group |
|
|
Phenylalanine Deamination |

Phenylpyruvic acid resulting from the deamination of phenylalanine is detected by adding ferric ion |
|
|
Ornithine Decarboxylation |

Decarboxylation of the amino acid causes a change in the bromcreson (purple) |

