![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

What is this and how does it work? |
Kirby-Bauer sensitivity test and is a technique used to determine antibiotic resistance and susceptibility using discs. Clear zones will appear around the discs to show effectiveness of the antibiotic.
|
|
|
A strain of gonorrhea that has a gene for producing the enzyme pencillinase |
Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae (PPNG) |
|
|
The lowest dose of a drug that will stop the growth of an organism |
Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) |
|
|
What color is a positive result for the Gram test? |
Purple |
|
|
What substance is present in a positive acid-fast test? |
Mycolic Acid |
|
|
What color is a positive result for the Acid Fast test? |
Red |
|
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is fast-growing
T/F? |
False: Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a slow growing organism and takes weeks to incubate because of the complexity of the cell wall |
|
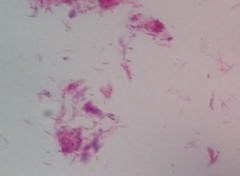
Identify this acid-fast |
Mycobacterium leprae |
|
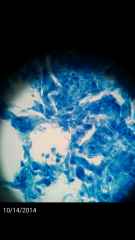
Identify this acid-fast |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis from nodules (section) |
|
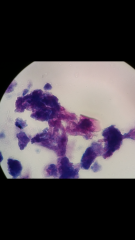
Identify this acid-fast |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis from culture |
|
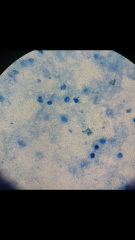
Identify this acid-fast |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis from positive sputum |
|
|
A positive EMB will result in? |
Metallic green colonies |
|
|
EMB is both selective and differential
T/F? |
True: EMB isolates gram-negative enteric, therefore it tests for both selective and differential |
|
|
MacKonkey Agar will form ______ colonies if positive for fermentation |
Pink |
|
|
What is a durham tube and what does it test? |
A tube that is used to test if a bacteria is capable of fermenting the sugar, to produce acid and/or gas. |
|
|
What three things does the SIM deep test? |
Sulfide- H2S Indole Motility |
|
|
After incubation, Indole is tested by adding Kovak's reagent which will turn _______ for a positive result. |
Pink/Red |
|
|
What color is a positive test for Citrate? What does it test for? |
Blue It determines whether the bacterium can survive on citrate as its only carbon source |
|
|
What does Urease test for and what color will result in a positive? |
It will determine whether the bacterium can produce the enzyme urease, the urea will be broken down into ammonia and a positive result will be indicated by a bright pink-red color |
|
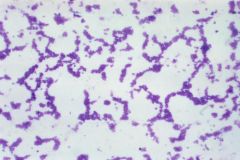
Is this a positive or negative gram stain? |
Positive; (Staphylococcus aureus) |
|
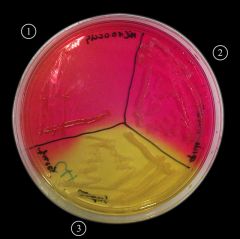
Identify this |
Mannitol Salt Agar |
|

Identify this and which bacterium did we grow on it? |
Chocolate (Blood) Agar and we grew Neisseria subflava |
|
|
What did we use to detect catalase in the pathogenic cocci lab? |
Hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
What is hemolysis? |
Breakdown of red blood cells |
|

True or False
Test tube labeled #2 is a positive for coagulase test |
False: Test tube #1 is positive for the enzyme coagulase because it is showing turbidity
|
|
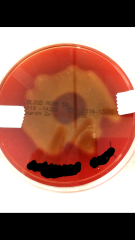
Identify Is this alpha, beta or gamma hemolysis? |
S. pyrogenes w/ Bacitracin Beta-hemolysis |
|
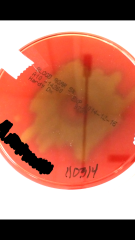
Identify Is this alpha, beta or gamma hemolysis? |
S. pneumoniae w/ Optochin Alpha-hemolysis |
|
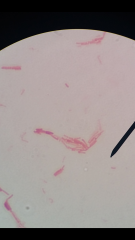
Identify this spore stain and determine if it is gram-positive or negative |
Bacillus megaterium and is gram-positive |
|
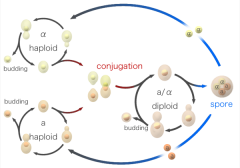
What is this a depiction of? |
Budding Yeasts Life Cycle |
|
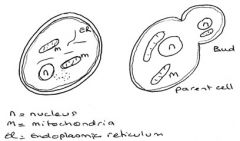
These are... |
Vegetative and Budding Yeasts Cells (Simplified picture)
|
|
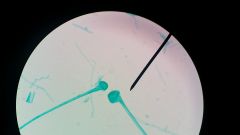
Identify this by name and is it a Yeast or Mold |
Rhizopus (Mold) |
|
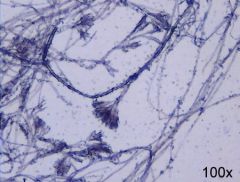
Identify this by name and is it a Yeast or Mold |
Penicillum (Mold) |
|

Identify this by name and is it a Yeast or Mold |
Aspergillus (Mold) |
|
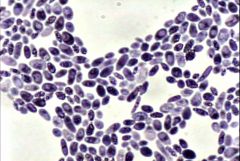
Identify this by name and is it a Yeast or Mold |
Saccharomyces (Yeast) |
|
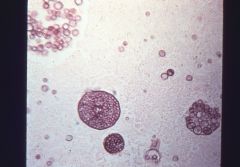
Identify this by name Yeast or Mold Name the disease it causes |
Coccidioides immitis Yeast Valley Fever
|
|
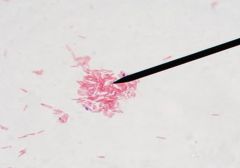
Name this Yeast and its disease |
Candida albicans Yeast infection |
|

Identify 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) |
1.) Zygosporangium 2.) Sexual conidium 3.) Asexual conidium 4.) Hypha |
|

Identify this picture |
Rhizopus |
|

Identify this picture |
Penicillum |
|

Identify this picture |
Aspergillus |
|
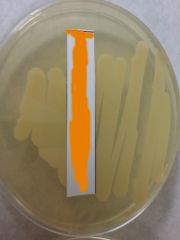
Identify by name Name the function of this Yeast |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Used in making beer, wine and bread |
|

Identify this by name Yeast or Mold |
Aspergillus Mold |
|
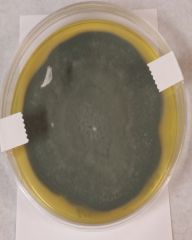
Identify this by name Yeast or Mold |
Penicillum Mold |
|

Identify this by name Yeast or Mold |
Rhizopus Mold |
|

Identify |
Enterobium vermicularis (pinworm) -roundworm -nematode |
|
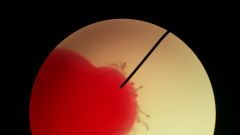
Identify What is the purpose of the hooks? |
Taenia Scolex (tapeworm) Hooks hold on to the host's tissues |
|
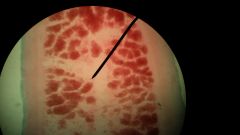
Identify what is at the pointer |
Fertilized cells in the gravid proglattids |
|

Identify this and the disease it causes |
Fasciola hepatica (flatworm) Fasciolasis- liver fluke |
|
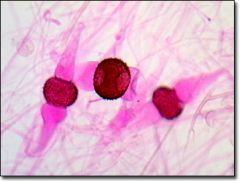
This contains spores
T/F? |
True: This is a picture of Rhizopus, which contains spores. |
|
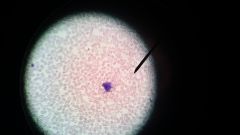
Identify this and the disease that it causes |
Plasmodium in blood smear Malaria |
|
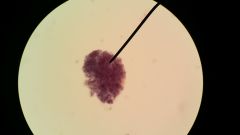
Identify this and the disease it causes |
Giardia lamblia (cysts in fecal smear) Giardiasis- Beaver fever |
|
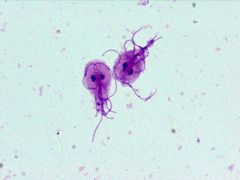
Identify this |
Giardia lamblia (Trophozoites) |
|
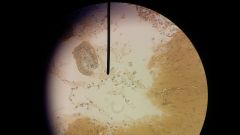
Identify and name the disease it causes |
Toxoplasm gondii Toxoplasmosis- parasitic disease, primary host is cat |
|
|
Indole test
|
This test determines the ability of the organism to convert tryptophan into the indole
|

