![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ingredients in Mannitol Salt agar
|
7.5% NaCl
Mannitol Phenol Red |
|
|
Ingredients in DNase agar
|
Emulsion of DNA
Peptides Methyl green dye |
|
|
How mannitol salt agar is used to differentiate among the different Staph species?
|
Differentiates by whether or not the bacteria are able to ferment mannitol
|
|
|
Which Staphylococcus species are positive for MSA fermentation?
|
S. aureus
S. xylosus S. saprophyticus |
|
|
Which Staphylococcus species are DNase-positive?
|
S. aureus
S. intermedius |
|
|
Which Staph species are resistant to the antibiotic Novobiocin?
|
S. saprophyticus
S. xylosus |
|
|
What is the coagulase test and how is it used to identify S. aureus?
|
It tests for the presence of the enzyme coagulase.
Reagent used - citrated plasma |
|
|
What is the catalase test and how can it distinguish strep from staph?
|
Tests for enzyme catalase
Reagent used peroxide |
|
|
Which streptococci are alpha-hemolytic?
|
S. agalactiae
S. bovis S. salivarius S. mutans E. faecalis |
|
|
Which streptococci are beta-hemolytic?
|
S. equi
S. pyogenes S. zooepidermicus |
|
|
Ingredients in Bile Esculin agar
|
Bile salts (oxbile)
esculin ferric ammonium citrate beef and gelatin extracts |
|
|
Which strep species are able to hydrolyze esculin?
|
S. bovis
S. salivarius E. faecalis |
|
|
What is the only member of the strep group that can grow on mannitol salt plates?
|
Enterococcus
|
|
|
Which Streptococcus species does the CAMP test identify?
|
S. agalactiae
|
|
|
Basic principles behind the CAMP test.
|
Relies on the fact tthat most S. agalactiae strains produce a diffusible extracellular compound called the CAMP substance that will conjugate with a specific beta-hemylosin of S. aureus cause a increased hemolytic effect of RBCs in an agar medium.
|
|
|
Is MSA selective, differential, or both?
|
Both.
Selects for halotolerant Differentates for fermentations |
|
|
Ingredients in starch media
|
polysaccharide
|
|
|
What enzymes degrade starch?
|
amylase
maltase |
|
|
What reagent needs to be added to the starch plate?
|
Iodine
|
|
|
What is the lipid substrate in lipid media?
|
Tributyrin
|
|
|
Name the enzyme(s) that degrade lipids.
|
lipase
|
|
|
Know the ingredients in casein media.
|
casein (major-milk protein)
|
|
|
What enzymes degrade casein?
|
casease and protease
|
|
|
What is the peptonization process?
|
Hydrolysis of proteins is called proteolysis.
In proteolysis of casein: Protein is broken down into peoptones, into polypeptides, into dipeptides and finally into amino acids. |
|
|
What is the name of the enzyme which hydrolyzes gelatin?
|
gelatinase
|
|
|
Why was media containing ampicillin used to select for transformants of E. coli?
|
xxx
|
|
|
Why did we streak before and after transformation on media without ampicillin and media with ampicillin?
|
xxx
|
|
|
Be able to calculate transformation efficiency.
|
xxx
|
|
|
What are the 7 ingredients in a TSI slant and what is the purpose of each?
|
1) 0.1% glucose - carb. substrate
2) 1.0% sucrose - carb. substrate 3) 1.0% lactose - carb. substrate 4) peptones - ??? 5) phenol red - pH indicator 6) Sodium thiosulfate - if produces H2S will use this as a substrate and react with Ferrous sulfate to form a black precipitate 7) Ferrous sulfate - see above |
|
|
Name two other types of media that can be used to test for hydrogen sulfide production, and give an example of an organism that produces hydrogen sulfide.
|
SIM Deep Tube, Lysine Iron Agar
|
|
|
What is the name of the enzyme that can hydrolyze urea?
|
Urease
|
|
|
What are the end-products of urea hydrolysis?
|
Ammonia, water and carbon dioxide
|
|
|
What is the pH indicator in the urea broths?
|
Phenol red
|
|
|
Give an example of an organism which is urease-positive.
|
Proteus mirabilis
|
|
|
What are the components of a SIM agar deep tube?
|
Amino acid tryptophan, peptones, sodium thiosulfate and ferrous sulfate
|
|
|
What 3 things does this type of agar test for?
|
Indole production, H2S production and motility
|
|
|
What must be added to the tube following incubation in order to perform this test?
|
Kovac's reagent
|
|
|
What is the MRVP test?
|
Methyl Red Vouges-Proskaur
MR tests for fermentation of glucose with mutiple acid-end products VP tests for fermentation of glucose with only 1 acid-end product ... usually acetic acid |
|
|
What are the components of the MRVP broth, and what is the purpose of each component?
|
Peptones
glucose -substrate phosphate buffer - lowers pH |
|
|
What reagent is added for the MR test?
|
Phenol red
|
|
|
What reagents are added for the VP test?
|
Barritt's reagents A and B
|
|
|
Can an organism be positive for both MR and VP?
|
No
|
|
|
Give an example of an organism that is MR positive and one that is VP positive.
|
MR+ Morganella morganii
VP+ Klebsilla oxytoca |
|
|
What is the purpose of the citrate test, and what are the ingredients in the citrate agar slant?
|
To determine if an organism can use citrate as a carbon source.
The slant contains sodium citrate, brom thymol blue (pH), sodium and water. |
|
|
Give an example of an organism that is citrate positive.
|
Proteus mirabilis
|
|
|
What are the ingredients in nitrate broth?
|
Beef extract
peptone nitrate |
|
|
What enzymes reduce nitrate? Is this an aerobic or anaerobic process?
|
Nitrate reductase
Anaerobically |
|
|
What reagents need to be added to the nitrate broth following incubation?
|
Nitrate reagent A
Nitrate reagent B |
|
|
What does a positive result following addition of these reagents mean?
|
Color changes to red, means + for nitrate reduction
|
|
|
When would you need to add zinc to the tube?
|
If no color change after Nitrate Reagent B is added, then add zinc.
|
|
|
What does a positive result following addition of zinc mean?
|
Still no color change - then + for nitrate reduction because indicates nitrates were reduced beyond nitrites to ammonia or molecular nitrogen
|
|
|
What does a negative result following the addition of zinc mean?
|
Color changes, means - for nitrate reduction, because the red color means the zinc reduced the nitrates to nitrites, not the bacteria.
|
|
|
Give an example of an organism that is positive for nitrate reduction.
|
E. coli
|
|
|
What are the ingredients in LIA slants and what two biochemical reactions do these slants test for?
|
Lysine, glucose, peptones, brom cresol purple, sodium thisulfate and ferric ammonium citrate.
Tests for lysine decarboxylation and lysine deamination |
|
|
Which reaction is aerobic? Which is anaerobic?
|
Deamination is aerobic
Decarboxylation is anaerobic |
|
|
What are the gram-negative tests used for idenitification?
|
TSI
Urease MRVP SIM Deep - Indole Prod. Citrate Nitrate LIA |
|
|
What test would you use on your gram-positive organism to distinguish Streptococcus from Staphylococcus?
|
Catalase test
|
|
|
Which set of tests would you set up to identify a Strep?
|
MSA growth
Blood Agar (for hemolysis and antibiotic testing (Bactracin and SXT)) Bile Esculin |
|
|
Know the principles behind the rapid Strep test, and be able to identify a positive and negative result.
|
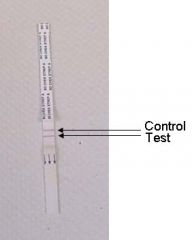
Uses an immunoassay to detect group A strep antigens. The dipstick contains a membrane strip that has been coated with colored anti-Strep A antibodies.
|
|
|
Know the principles behind the rapid Staph test and be able to identify a positive and negative result.
|
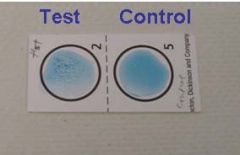
Based on the fact that most pathogenic strains of S. aureus produce a bound coagulase and contain Protein A on their cell surface.
|
|
|
Be able determine using a microscope whether an acid-fast stain of a sputum sample is positive or negative.
|
Look for acid-fast rods and watch for symptoms
|
|
|
Know the basic principles behind the acid-fast stain.
|
Differential stain which stains bacteria, such as Mycobacterium and Nocardia, which have mycolic acids in their cell walls.
|
|
|
Be able determine using a microscope whether a gram stain of a patient specimen is positive or negative, and the morphology and arrangement of the stained organisms.
|
look for clusters, rods, chains, cocci, etc. to help with diagnosis
|
|
|
Know the basic principles behind the gram stain.
|
Differential stains which stains bacteria based on the amount of peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
|
|
|
Name the 2 bacteria used as active cultures in making yogurt.
|
Streptococcus thermophilus
Lactobacillus bulgaricus |
|
|
Know the general process of yogurt production.
|
Boil milk
Cool to 55 degrees Celsius Add scoop of yougurt incubate Refrigerate |
|
|
What plates did we use to test for bacterial contaminants on raw chicken and beef?
|
Salmonella-Shigella Agar plates (SS Agar)
|
|
|
What ingredients do SS Agar plates contain, and what is the purpose of each ingredient?
|
Lactose - Carb. substrate that allows the differentiation between lacotse and non-lactose fermenters.
Bile salts - make agar more selective for gram- enteric bacteria by inhibiting the growth of gram+. Ferric citrate - indictor of H2S production Neutral red - pH indicator for when lactose is fermented. |
|
|
What is the name of the broth media we used to test water purity?
|
Single strength lactose broth with Durham tube and double strength lactose broth with Durham tube
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Durham tube?
|
XXX
|
|
|
Why is this called a presumptive test?
|
Because after incubation, if fermentation plus gas is seen in the tubes then the water tested is PRESUMED to contain fecal coliforms
|
|
|
Which is DNase? Is it a positive or negative rxn.?
|
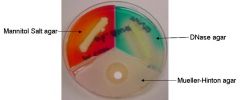
The bluish area, positive
|
|
|
Alpha
Blood agar |
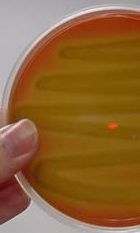
Name alpha, beta and gamma hemolysis. What type of media is this?
|
|
|
Bile esculin slant
Tube 1: Positive for esculin hydrolysis in the presence of bile. Note black precipitate in > 50% of tube. Tube 2: Negative for esculin hydrolysis in the presence of bile. |

What type of media is this? Which is a positive rxn?
|
|
|
CAMP test
The arrows pointing to the "arrowhead effect" as hemolysins from S. aureus interact with hemolysins from S. aureus to produced an enhanced zone of beta-hemolysis. |
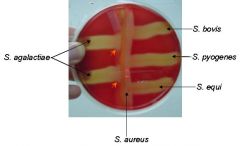
What type of test is this?
|
|
|
MSA plate
Both organisms growing on the plate above are halotolerant. The organism (Staphylococcus aureus) indicated by the orange arrow is capable of mannitol fermentation, signified by the color change in the surrounding media. The organism (Staphylococcus epidermidis) indicated by the blue arrow is not capable of mannitol fermentation. |
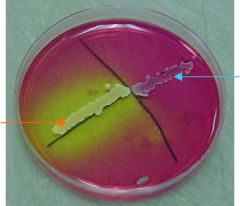
What type of media is this? Which is = or -?
|
|
|
Citrate test
Tube 1: Negative for citrate utilization. Note that there is no color change, and there is no growth on the slant itself. Tube 2: Positive for citrate utilization. Note that the color has changed to "Caribbean blue", and there is also growth on the surface of the slant. |
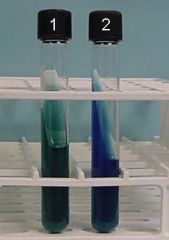
What type of media is this? Which is - or +?
|
|
|
Water Purity test
Media: Single (and Double)strength lactose broth with Durham tube Tube #1: Positive for fecal coliforms. Note (1) the gas present in the Durham tube and (2) the color change from red to yellow as acid end-products react with the pH indicator. Tube #2: Negative for fecal coliforms. Note the absence of gas in the Durham tube. Even though the pH indicator has changed from red to yellow, gas must be produced for a positive result. Tube #3: Negative for fecal coliforms. |
Name the media/test. What are the results?
|
|
|
Extracellular Enzymes:
This plate is positive for starch and lipid hydrolysis, and weakly positive for casein hydrolysis. Note the zones of clearing in the media around the bacterial growth. (Iodine has been added to the starch sector to aid in seeing starch hydrolysis.) |
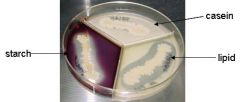
Name the media/test. Is this a - or +?
|
|
|
Extracellular Enzymes
This plate is negative for starch and lipid hydrolysis, and positive for casein hydrolysis. Note the absence of a zone of clearing in the starch and lipid sectors. |
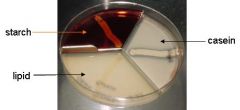
Name the media/test. Is this a - or +?
|
|
|
Gelatin Hydrolysis
Tube #1 is negative for gelatin hydrolysis. Tube #2 is positive for gelatin hydrolysis. |

Name the media/test. Which is + or -?
|
|
|
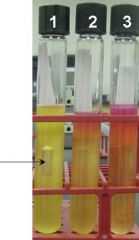
Urease Test
Tube 1: Positive Tube 2: Negative |

Name the media/test. Which is + or -?
|
|
|
Indole prod. - SIM deep tube
Tube 1: (1) Positive for H2S, (2) Negative for Indole production, (3) Positive for motility Tube 2: (2) Negative for H2S, (2) Positive for Indole production, (3) Undetermined motility |

Name the media. What does this test for? Results?
|
|
|
TSI slant
Tube 1: Acid slant/ Acid butt/ Gas/ no H2S Tube 2: Alk slant/ Acid butt/ Gas/ H2S Tube 3: Alk slant/ Alk butt/ no gas/ no H2S Tube 4: Alk slant/ Acid butt/ no gas/ no H2S |

Name the media. Results?
|
|
|
Lysine Iron Agar Slant
Tube 1: Positive decarboxylation (butt), negative deamination (slant) Tube 2: Negative decarboxylation (butt), positive deamination (slant) Gas production - bubbles H2S prod. - black precipitate |

Name the media/test. Results?
|
|
|
Which set of tests would you set up to identify a Staph? What do positive/negative reactions look like for each test?
|
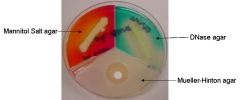
Tri-plate
|
|
|
Beta, blood agar
|

Name hemolysis, and media
|
|
|
Gamma, blood agar
|
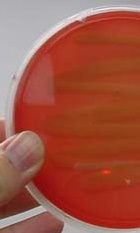
Name hemolysis and media
|
|
|
Salmonella-Shigella (SS) plates are used to detect bacterial contamination on raw meat. Salmonella-Shigella agar plates contain lactose, bile salts, ferric citrate, and neutral red. The bile salts select for Gram-negative bacteria. The other components differentiate among Gram-negative bacteria.
Coliform bacteria such as E. coli will ferment the lactose in the media, resulting in bacterial growth with a pink color. (They do not produce any hydrogen sulfide.) Members of the genus Salmonella will not ferment lactose, but do product hydrogen sulfide gas. The resulting bacterial colonies will appear colorless with black centers. Members of the genus Shigella do not ferment lactose or produce hydrogen sulfide gas, so the resulting colonies will be colorless. |
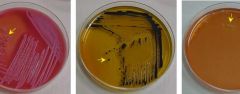
Name the media. Which organisms are on each?
|

