![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
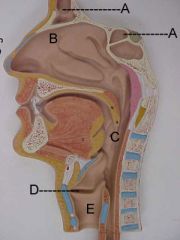
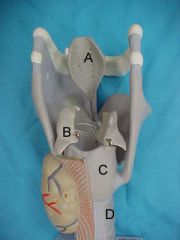
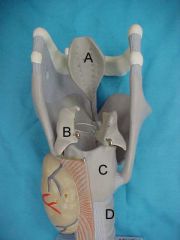
Name A, B, C, D and E
|
A.paranasal sinuses
B.nasal cavity C.pharynx D.vocal cords E.larynx |
|
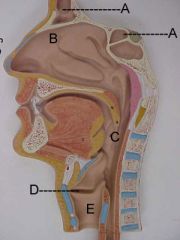
Name A and B
|
A. trachea
B. bronchus |
|
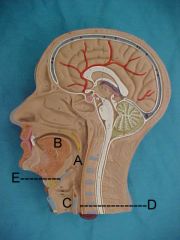
Name A, B, C, D and E
|
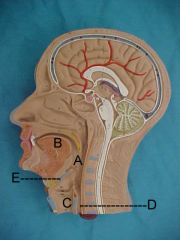
A. pharynx
B. tongue C. larynx D. esophagus E. epiglottis |
|
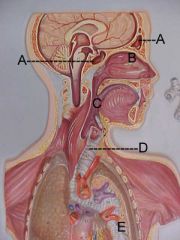
Name A, B, C and D
|
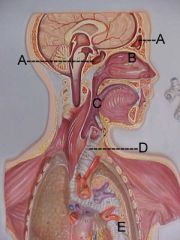
A. paranasal sinuses
B. nasal cavity C. pharynx D. trachea |
|
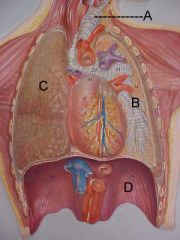
Name A, B, C and D
|
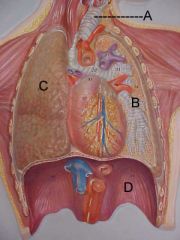
A. trachea
B. bronchus C. lung D. diaphragm |
|
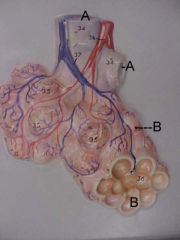
Name A and B
|
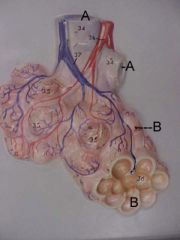
A. bronchiole
B. alviolus |
|
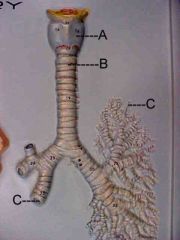
Name A, B and C.
|
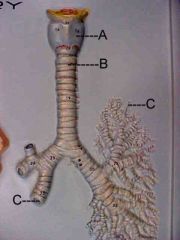
A. larynx
B. trachea C. bronchus |
|
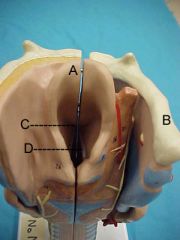
Name A, B, C and D
|
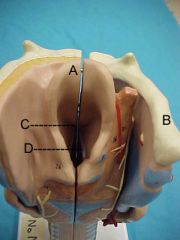
A. epiglottis
B. hyoid bone C. glottis D. vocal cords |
|
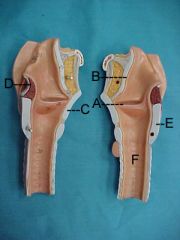
Name A, B, C, D and E
|
A.vocal cords
B.epiglottis C.thyroid cartilage D.arytenoid cartilage E.cricoid cartilage |
|

Name A, B, C, D and E
|

A. thyroid cartilage
B. cricoid cartilage C. epiglottis D. hyoid bone E. trachea |
|
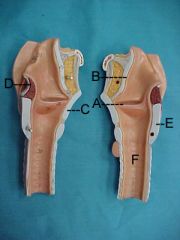
Name A, B, C and D
|
A. epiglottis
B. arytenoid cartilage C. cricoid cartilage D. trachea |
|
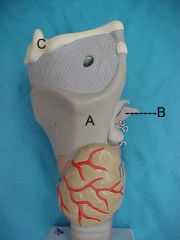
Name A, B and C
|
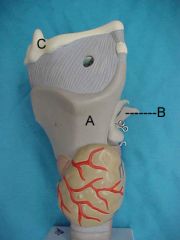
A.thyroid cartilage
B.arytenoid cartilage C.hyoid bone |
|
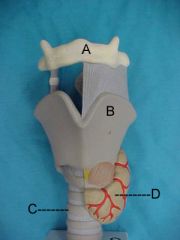
Name A, B, C and D
|
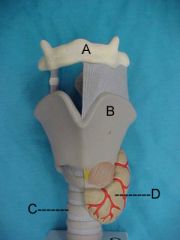
A. hyoid bone
B.thyroid cartilage C.trachea D.thyroid gland |
|
|
What is the function of the sinuses?
|
warms and moisten air, traps debris in mucus secretions
|
|
|
What is the function of the epiglottis?
|
elastic cartilage flap that covers airway opening during swallowing
|
|
|
What is the function of a bronchiole?
|
it’s a conducting tube able to constrict or dilate (lacks hyaline cartilage)
|
|
|
What is the function of the alveoli?
|
site of gas exchange with capillaries
|
|
|
What is the function of the diaphragm?
|
diaphragm contracts and flattens during inhalation increasing thoracic space, and reverses relaxing during exhalation
|
|
|
The cricoid/thyroid cartilage are made of what kind of cartilage?
|
hyaline
|
|
|
The epiglottis is made of what kind of cartilage?
|
elastic
|
|
|
The C-rings in the trachea are made of what kind of cartilage?
|
hyaline
|
|
|
The bronchus or bronchi are made of what type/s of tissue?
|
PSCCE (pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium) and hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
The bronchioles are made out of what type/s of tissue?
|
simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
|
|
|
The alveoli are made of what type/s of tissue?
|
simple squamous epithelium tissue
|
|
|
The parietal pleura is which?
|
it lines the wall of the thoracic cavity
|
|
|
The visceral pleura is which?
|
covers the lungs themselves
|
|
|
What are the four layers of the trachea?
|
mucosa, submucosa, cartilage, adventitia
|
|
|
What is the submucosa layer of the trachea made of?
|
areolar connective tissue w/glands (simple cuboidal)
|
|
|
What is the cartilage layer of the trachea made up of?
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
What is the adventitia layer of the trachea made up of?
|
areolar connective tissue
|
|
|
What is the function of the mucosa layer of the trachea?
|
moves debris away from lungs and traps microbes
|
|
|
What is the function of the submucosa layer of the trachea?
|
secrete mucus to trap debris
|
|
|
What is the function of the cartilage layer of the trachea?
|
provide patent (open) airway
|
|
|
What is the function of the adventitia layer of the trachea?
|
holds trachea in place
|
|
|
What do the intercostals muscles and rib cage do during inhalation?
|
contract – elevate/expand ribcage
|
|
|
What does the diaphragm do during inhalation?
|
contracts and depresses inferiorly
|
|
|
What does the elastic connective tissue in the lungs do during inhalation?
|
stretches and stretches lungs
|
|
|
What do the pleural membranes do during inhalation?
|
increase the size/volume of the thoracic cavity
|
|
|
What do the intercostals muscles and the rib cage do during exhalation?
|
relaxes and ribs return to original position
|
|
|
What does the diaphragm do during exhalation?
|
relaxes, moves superiorly
|
|
|
What does the elastic connective tissue in lungs do during exhalation?
|
recoils to original size
|
|
|
What do the pleural membranes do during exhalation?
|
recoil and decrease size/volume of thoracic cavity
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the nasal cavities?
|
warms and moistens air, traps debris in mucus secretions
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the pharynx?
|
common pathway for food and air
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the larynx?
|
contains vocal folds, provides a patent (open) airway
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the vocal folds?
|
alter sound pitch when tension or length changed
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the trachea?
|
provides a patent (open airway)
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the lung?
|
organ that contains both conduction and respiratory structures
|
|
|
What is/are the function/s of the bronchi?
|
conducting tube which enters lungs
|
|
|
What is the mucosa layer of the trachea made up of?
|
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium w/goblet cells
|
|
|
Describe the effect of hyperventilation on O2 and CO2 levels? Why?
|
O2 levels increase CO2 levels decrease because of inhaling/exhaling O2/CO2 rapidly
|
|
|
Describe the effects of rebreathing on O2/CO2 levels – why?
|
each stays normal, rebreathing is normal breathing
|
|
|
Describe the effect of hypoventilation on O2/CO2 levels? Why?
|
O2 goes down, CO2 goes up – too little O2 is being brought in and too little CO2 is being released
|
|
|
Which vial, green or blue has more CO2?
|
green
|
|
|
Excess CO2 in the blood causes it to be acidic or alkaline?
|
acidic
|
|
|
The Ph of blood that is acidic is high, or low?
|
low
|
|
|
In respiratory acidosis, CO2 _________, O2 ___________, Ph ___________
|
Increases, decreases, decreases
|
|
|
In respiratory alkalosis, CO2 ___________, O2 _________, pH ___________
|
decreases, increases, increases
|
|
|
In metabolic acidosis, HCO3 _____________, pH ________________
|
decreases, decreases
|
|
|
In metabolic alkalosis, HCO3 _____________, pH ______________
|
increases, increases
|
|
|
What are the causes of respiratory acidosis?
|
hypoventilation, emphysema, pulmonary edema
|
|
|
What are the causes of respiratory alkalosis?
|
hyperventilation, anxiety
|
|
|
What are the causes of metabolic acidosis?
|
ketosis
|
|
|
What are the causes of metabolic alkalosis?
|
diuretics, antacids
|
|
|
What is the carbonic acid formula?
|
CO2-->H2O<-->H2CO3<-->H+ + HCO3-
|
|
|
What is H2CO3?
|
carbonic acid
|
|
|
What is HCO3-?
|
bicarbonate
|
|
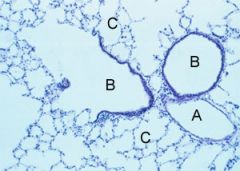
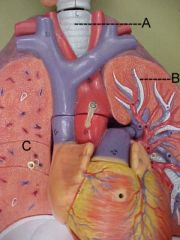
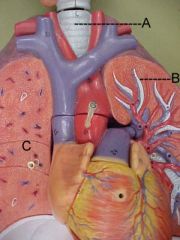
Name A, B and C
|
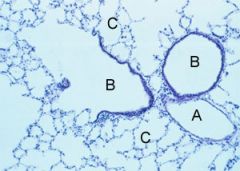
A-vein
B-bronchiole C-alveoli |
|
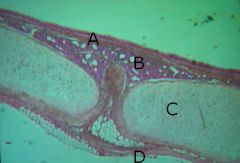
Name A, B, C and D
|
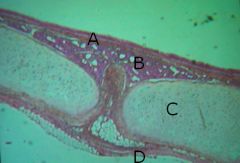
A - mucosa layer
B - submucosa layer C - hyaline cartilage layer D - serosa (adventitia) |
|
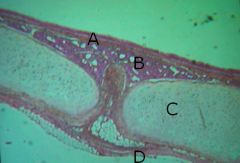
Name the tissues for A, B, C and D
|
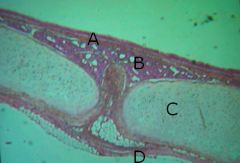
A - pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium (PSCCE) w/goblet cells
B - areolar connective tissue w/glands (simple cuboidal) C - hyaline cartilage D - areolar connective tissue |
|
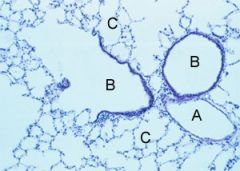
Name the tissues for B and C
|
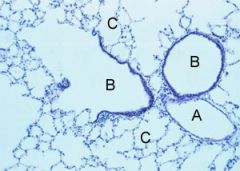
B - simple cuboidal
C - simple squamous |
|
|
what are the conduction portions of the respiratory system?
|
nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
|
|
|
What is the respiratory portion of the respiratory system?
|
alveoli
|
|
|
What does PSCCE stand for?
|
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial tissue
|

