![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
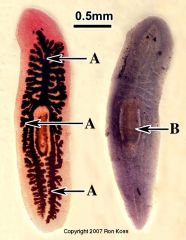
Phylum, class, genus Where does it live? Advances from previous Phyla? Name sensory structures and their function How are they different from other members of the phyla |
Platyhelmintes, Turbellaria, Dugesia This planarian is a free-living freshwater carnivore A: Branched gut B: Protrusible pharynx Bilateral symmetry, acoelomate (triploblastic), d-v flattened, cephalization Auricles; chemosensory, eyespots; photoreception They are free living with a ciliated epidermis and lots of mucus |
|

Phylum, class, genus + species Where does it live? Can other members of this class be symbiotic? |
Platyhelminthes, turbellaria, Notoplana sanguinea (Aka the saddleback flatworm) It lives in the intertidal zone. Yes! they can be ectocommensal or endoparasitic in marine arthropods and echinoderms. |
|
|
What phylum and class are digeneans in? What is their basic lifecycle? |
Platyhelminthes, Trematoda Typically 3 host life cycle; snail-> 2nd intermediate host (prey of def. host)-> vertebrate definitive host Miracidia- sporocyst - rediae -cercaria -metacercaria - adult |
|
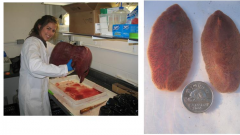
Phylum, class, genus and species What host? |
Platyhelminthes, trematoda, Fascioloides magna Elk (liver) |
|
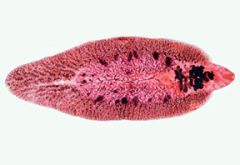
Phylum, class, g + s Life cycle with hosts |
Platyhelminthes, trematoda, Fasciola hepatica -embryonated eggs released in sheep feces -if they reach water, free swimming miracidium hatches -using apical and cephalic glands it bores into appropriate snail -w/in the snail it develops into sporocysts (from germ balls in miracidium) wich give rise to rediae, which give rise to free swimming cercaria -cercaria encyst on vegetation as metacercaria -they are ingested by the sheep when grazing -metacercaria excyst in duodenum and migrate to biliary duct where they mature |
|
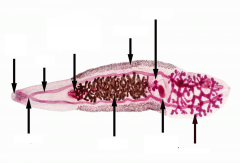
Phylum, class, genus, species Life cycle with hosts |
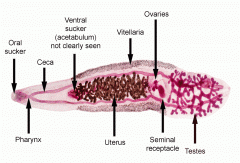
Platyhelminthes, trematoda, Clonorchis sinensis -embryonated eggs released in human feces -eggs are ingested by snail miracidia hatch -miracidia give rise to a single sporocyst which prosuce rediae which give rise to free swimming cercariae -cercariae penetrate 2ndary freshwater fish host, encyst as metacercaria -after human injests fish flesh metacercaria excyst in duodenum and migrate to biliary duct |
|

Phylum, class, g + s How does it differ from other members of the class (2 things) What disease does it cause Life cycle and hosts |
Platyhelminthes, trematoda, Schistosoma mansoni It is dioecious (F and M) and it lacks a metacercaria stage Schistosomiasis, they are also called blood flukes -eggs released in human feces -eggs hatch in water releasing miracidia, which penetrate snail int. host - miracidia -> 1 sporocyst -> many daughter sporocysts -> cercariae -cercaria are released, penetrate skin on human definitive host -cercaria shed tail, become schistosomules in blood stream -mature in hepatic portal vein -paired adults migrate to mesenteric veins of intestine and reproduce |
|
|
What type of genus of trematode causes swimmers itch? What life cycle stage causes it? What it it supposed to end up in? |
Trichobilharzia The cercaria stage, its supposed to end up in ducks |
|
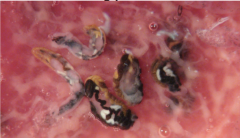
Phylum, class, g + s Life cycle and host |
Platyhelminthes, trematoda, Hematoloechus longiplexus -Embryonated eggs shed in frog feces -eggs hatch in water, release miracidium -miracidium penetrates snail -> mother sporocyst -> daughter sporocyst -> cercaria -Cercaria penetrate odonate nymph and encyst as metacercaria -Metacercaria persist in adult dragonfly and are ingested by frog -Excyst in frog stomach and migrate to lungs where they mature |
|
|
What class are tape worms in? How are they different from trematodes? What are the sections of the body called? |
Cestoda They lack a digestive system and feed across their tegument Scolex (with holdfasts), proglottids (comprise stobilla) |
|

Phylum, class, Family, g + s Life cycle and hosts |
Platyhelminthes, Cestoda, Taenidae, Taenia pisiformis -Proglottids (containing eggs) are shed in canine feces - eggs are released on vegitation and are eaten by a rabbit -oconospere hatches from egg, pentrates the gut wall and enters the blood stream -it migrates to the liver becomes a cysticercus, and migrates to the peritoneal cavity -upon ingestion by dog the cysticercus exvaginates, attaches to the gut wall and matures |
|
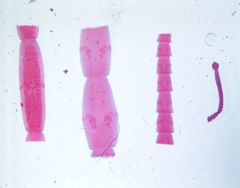
Phylum, class, g + s Life cycle and hosts |
Platyhelminthes, cestoda, Dipyldium caninum -Gravid proglottids released in dog feces -Proglottids rupture releasing egg packets -eggs ingested by larval flea -oconosphere hatches from egg in flea gut, penetrates gut wall and forms cysticercoid -dog eats flea while grooming, cysticercoid exvaginates in gut, attaches to gut wall and matures |

