![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is this group called? Why? Which is the most diverse protist? Which is parasitic? Which is an important part of phytoplankton? |
The alveolates because they all possess membrane bound sacs called alveoli under their cell membranes Cilliates, apicomplexa, dinozoa |
|
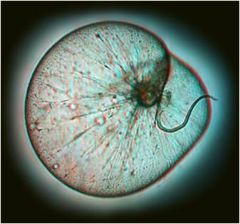
What phylum and genus? What is the tentacle called? Importance? |
Dinozoa, Noctiluca Peduncle Bioluminescent |
|
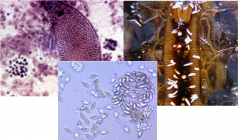
What phylum, group, genus? What location does in infect in which animal, what does it feed on? Draw a sporozoite and diagram the life cycle |
Apicomplexa, gregarinres, monocystis The seminal vesicles of earth worms where it feeds on developing sperm |
|
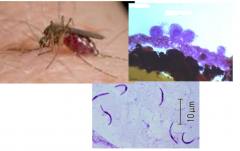
Phylum and genus Clockwise, what is in these pictures Give the lifecycle |
Apicomplexa, plasmodium Anopoles mosquito vector, oocysts in stomach wall, sporozoites |
|
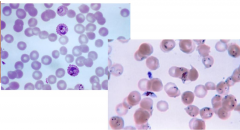
Left to right what are these pictures |
Ring stage trophozoite and gametocyte of p falciparum |
|
|
How do members of cilliophora move? How do they reproduce? What do they have 2 of that most protists only have one of? What are they for? |
Using cilia. They reproduce via conjugation. They have two nuclei micro, for reproduction, and macro for other metabolic functions. |
|
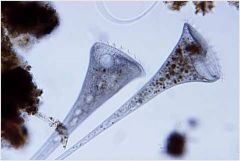
Phylum and genus Identify the cytostome contractile vacuole and nuclei Feeding? |

Ciliophora, stentor Note, the macronuclei are hard to see in this image, in the slides we saw in lab they were pink and in a chain Suspension. |
|
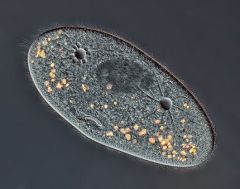
Phylum, genus Label contactile vacuole, macronucleus and cytostome Feeding? |
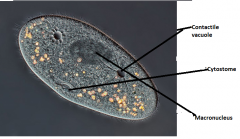
Ciliophra, paramecium Omnivorous |
|

Phylum, genus What is the stalk called? What does it do? Is this colonial? What kind of feeding? |
Ciliophora, vorticella A spasmoneme, it can move up and down like a spring to get away from predators No, but it is gregarious it is a suspension feeder |
|

Genus? Solitary or colonial? Where does it live? |
Epistylis Colonial Commensal on freshwater arthropods |
|
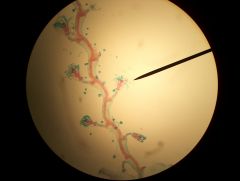
Phylum, genus and group What is it clinging to? Why is this animal different from others in the phylum? What does it lack? What does it have? |
Ciliophora, Ephelota, suctorian An Obelia colony It lacks cilia and has tentacles with haptocysts that it uses to capture food |
|
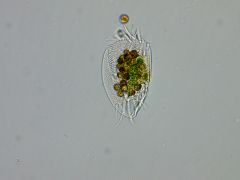
Phylum, genus |
Ciliophora, Euplotes |
|
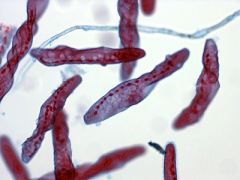
Phylum, genus Label |
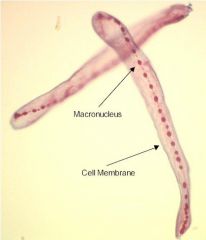
Ciliophora, Spirostomum |
|
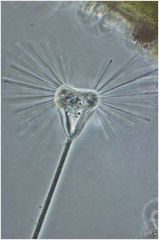
Phylum, group, genus |
Ciliophora, suctorian, Acineta |

