![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pathogen |
An organism capable of disease |
|
|
Inoculate |
To transfer organisms to a medium to initiate growth |
|
|
Sterile |
Free of microorganisms and viruses |
|
|
Ubiquity |
The existence of something everywhere at the same time |
|
|
Alpha hemolytic |
A partial clearing of hemolysis surrounding colonies grown on blood agar plates often appears green |
|
|
Beta hemolytic |
A sharply defined clear zone of hemolysis surrounding colonies grown on blood agar |
|
|
Catalase |
An enzyme found in most aerobic organisms that breaks down H2O2 to water and oxygen |
|
|
Enterococcui |
Cocci found in the intestines |
|
|
Gamma hemolysic |
No blood cells are lysed on blood agar plate so it appears red |
|
|
Glomerulonsphritis |
Inflammation of the kidneys affecting the structure of the renal glomeruli (inflammation of the capillaries caused by toxins produced elsewhere in the body) |
|
|
Inhibition zone |
Lack bacterial growth around an antibiotic disc. The clear zone diameter is a measured in mm. It's where bacteria were killed |
|
|
Inhibition zone |
Lack bacterial growth around an antibiotic disc. The clear zone diameter is a measured in mm. It's where bacteria were killed |
|
|
Nonsnterocci |
Cocci found in other locations besides the intestines |
|
|
Inhibition zone |
Lack bacterial growth around an antibiotic disc. The clear zone diameter is a measured in mm. It's where bacteria were killed |
|
|
Nonsnterocci |
Cocci found in other locations besides the intestines |
|
|
Nutrient Agar |
Complex culture media nutritious with beef extract pepton (digestive protein) 17-20 mL of nutrient agar in each plate 2.5% agar is added to nutrient broth to solidify Solid at 37 degrees Celsius |
|
|
Autoclave |
121 degree Celsius and 15 PSI sterilize the culture media with the temperature and with the pressure |
|
|
Autoclave |
121 degree Celsius and 15 PSI sterilize the culture media with the temperature and with the pressure |
|
|
Moraxella catarrhails Gram negative Cat positive Ox positive |
|
|
Gram positive Cat negative Ox negative Streptococcus |
|

|
Corynebacterium and diphtheroids Gram positive Cat positive Ox negative |
|

|
Staphylococcus Gram positive Cat positive Ox negative |
|

|
Yeast Appear gram positive Cat positive Ox positive |
|
|
Normal biota |
The organisms usually found associated with parts of the body (previously termed normal flora) |
|
|
Moraxella catarrhails Gram negative Cat positive Ox positive |
|
|
Gram positive Cat negative Ox negative Streptococcus |
|

|
Corynebacterium and diphtheroids Gram positive Cat positive Ox negative |
|
|
|
Staphylococcus Gram positive Cat positive Ox negative |
|

|
Yeast Appear gram positive Cat positive Ox positive |
|
|
Encapsulation |
A protective gelatinous material surrounding some bacteria that may also relate to their virulence |
|
|
Oxidase |
A reagent that test for cytochrome C. This reagent reacts with the air so it must be read within a minute to avoid a false positive test Positive test=purple |
|
|
Oxygen-Labile hemolysin |
Hemolysin destroyed by oxygen, this is why the agar is stabbed, to check for oxygen labile hemolysins that would not be decayed otherwise |
|
|
Example of beta hemolysic |
Stapholoccus arueus |
|
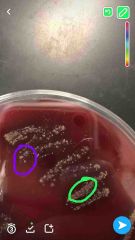
Purple Green |
Purple gamma Green alpha |
|
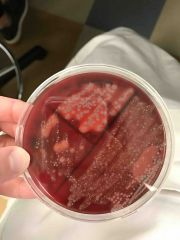
|
Beta, alpha and gamma |
|
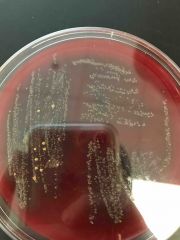
|
Beta and gamma |
|
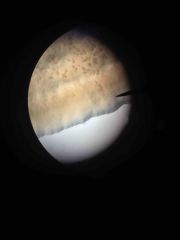
|
Escherichia coli |
|
|
What are the different elevation? |
Flat, conical, Craterlike |
|
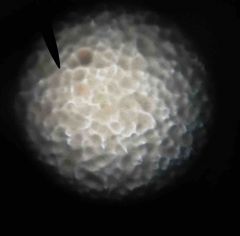
|
Staphylococcus epidermis |
|
|
What is the log phase? |
Where the bacteria is actively growing |
|
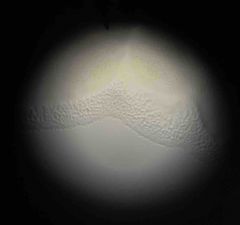
|
Pseudomonas |
|
|
Bacterlostatic |
Prevented from growing but doesn't kill them |
|
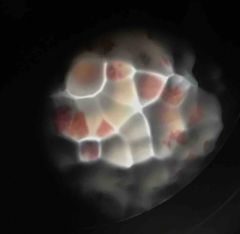
|
Serratia |
|
|
Why isn't there one kind of agar medium that will support the growth of all microorganisms? |
Because microorganisms are present everywhere so there is no one condition medium that will roemit the growth of all |
|
|
|
Beta, alpha and gamma |
|
|
Why do you invert agar plates when placing them in the incubator? |
To prevent condensation from forming on the lid and dripping on the agar below. The moisture would permit colonies of bastetja to run together |
|
|
How does the microscope zoom? |
Once with the ocular lense 4x and once with the scanning lense 10x for a total of 40x |
|
|
|
Beta and gamma |
|
|
|
Escherichia coli |
|
|
Escherichia coli |
Color: goldish brown Surface: shiny Conskdtancy: moist Elevation: conical |
|
|
|
Staphylococcus epidermis |
|
|
Staphylococcus epidermis |
Color: pale yellow Dull Comical Dry |
|
|
|
Pseudomonas |
|
|
Pseudomonas |
Consistency: mucoid Color: white/pale yellow Surface: shiny Elevation: flat |
|
|
|
Serratia |

