![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
90% of malignant neoplams arising within the oral cavity and pharynx are _____________________
|
SCCA
|
|
|
What are the second most common type of oral cavity cancers?
|
those arising from minor salivary glands
|
|
|
Tobacco and alcohol have a multiplicative rather than additive effect resulting in a ___-fold increased risk for developing these cancers
|
15
|
|
|
Which virus increases risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
|
EBV
|
|
|
Which genetic disease has been implicated in oral cavity carcinoma's?
|
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
|
|
|
What are the borders of the oral cavity?
Anterior Posterior Superior Inferior |
Anterior - cutaneous-vermilion junction of the lips
Posterior - anterior tonsillar pillars Superior - junction of hard & soft palate Inferior - circumvallate papillae |
|
|
What are the subsites within the oral cavity?
|
SEVEN subsites:
Lips Oral tongue, anterior 2/3rds Floor of Mouth Buccal mucossa Gingivas/Alveolar Ridges Retromolar trigone Hard palate |
|
|
What are the borders of the Oropharynx?
Anterior Posterior Superior Inferior |
Anterior - anterior tonsillar pillars
Posterior - soft palate, tonsillar fossa posterior pharyngeal wall & BOT Superior - inferior surface of the soft palate at the junction of the hard-soft palate Inferior - superior surface of the hyoid bone |
|
|
What are the subsites within the oropharynx?
|
FOUR subsites:
Soft palate and uvula BOT Tonsillar fossa Pharyngeal wall (lateral and posterior) |
|
|
What are the borders of the hypopharynx?
Superior Inferior |
Superior - superior border of the hyoid
Inferior - lower border of the cricoid cartilage |
|
|
What are the subsites within the hypopharynx?
|
THREE subsites:
Pyriform sinuses (or fossa), left & right Posterior hypopharyngeal wall Postcricoid region - this region extends from the arytenoid cartilages to the inferior aspect of the cricoid and connects the two pyriform sinuses, thus forming the anterior wall of the hypopharynx. |
|
|
What are the borders of the nasopharynx?
Anterior Posterior Inferior |
anterior - posterior edge of the choanae
posterior - free edge of the soft palate inferior - free edge of the soft palate |
|
|
What are the subsites within the nasopharynx?
|
THREE subsites:
Lateral walls (including the fossa of Rosenmuller (aka posterolateral recess) and eustachian tube orifices) Vault of roof Posterior wall |
|
|
Early stage (stage I-II) carcinoma of the oral cavity and pharynx (excluding nasopharynx) can be tx with what?
|
Surgery or XRT
|
|
|
Early stage (stage III - IV) carcinoma of the oral cavity and pharynx (excluding nasopharynx) can be tx with what?
|
combination of chemotherapy and radiation or surgery and postop radiation
|
|
|
What is the treatment of choice for nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
|
XRT with OR without chemo
|
|
|
What are the options for management of the N0 neck in pts with oral cavity and pharynx cancers?
|
Several tx options are advocated:
1) expectant management 2) elective cervical lymphadenectomy 3) elective radiotherapy of the neck |
|
|
What is the incidence of second primary?
|
Incidence of second primary SCCA is 5-10%
- 50% of second primaries arise in the H&N, while the lung is the next most common site (20%) |
|
|
Distant mets develops in ___% of pts with H&N cancer
|
15%
|
|
|
What are the factors which increase rate of distant mets?
|
Higher nodal stage
Number of luymphatic mets Advanced T stage Hypopharynx as primary tumor site |
|
|
What is the typical follow-up schedule after definitive treatment for H&N cancer?
|
Recurrences usually present in the first 2 years after tx.
For the first year - q4-6 weeks For the second year - q3 months For the third-fifth years - q6 months Then q6-12 months for life |
|
|
What is the most common site of cancer in the oral cavity?
|
lips
|
|
|
What is the most common type of cancer of the lip?
Is there preference for upper or lower lip? |
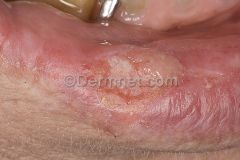
95% are SCCA
95% lower lip, 5% upper lip (BCC in general occurs on the upper lip than lower lip, but SCCA is still the overall most common ca of the upper lip) |
|
|
Is there is sex predilection for cancer of the lip?
|
20-35:1 male to female ratio for the lower lip
5:1 male to female ratio for the upper lip |
|
|
What are the RF for cancer of the lip?
|
Sunlight exposure
Lack of pigmented layer Tobacco smoking |
|
|
How are small (T1, T2) lesions of the lip treated?
How are large (T3, T4) lesions of the lip treated? |
Small = radiation or surgery only
Large = combined modality therapy |
|
|
How is the lower lip closed if the size of the defect is less than 1/4 to 1/3 of the lip?
|
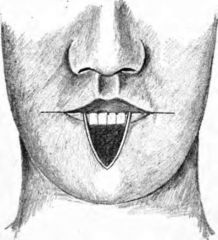
Primary closure, facilipated by V-shaped excision
|
|
|
How is the lower lip closed if the size of the defect is 1/4 to 1/2 of the lip?
|
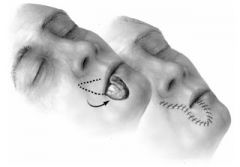
Bilateral advancement flaps or "lip-switch" flaps:
1) Abbe - when close to oral commissure (image) 2) Estlander - when involving the oral commissure |
|
|
How is the lower lip closed if the size of the defect is 1/2 to 2/3 of the lip?
|
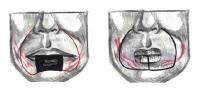
Karapandzic flap
|
|
|
How is the lower lip closed if the size of the defect is 2/3 to total of the lip?
|
Local flap reconstruction (Bernard-Burrow or Gillies fan flap) or free tissue transfer
|
|
|
What is the overall 5-year survival rate for pts with lip cancer?
|
About 91%
- lower as stage increases |
|
|
What is the second most common tumor of the oral cavity?
|
tongue (30%) - most often arises along the lateral borders of the tongue
|
|
|
What are the RF for tongue ca?
|
Tobacco
Alcohol Immunosuppression Possibly poor oral hygiene |
|
|
What is the most common form of early SCCA on the tongue?
|
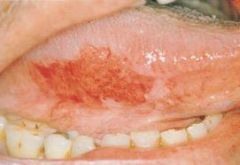
erythroplakia
|
|
|
What are the tx options for T1-T2 tongue ca?
|
Partial glossectomy is indicated with reconstruction by primary closure, secondary intention or skin graft
External beam radiation with or without brachytherapy may be used in these pt's that are not suitable for or refuse surgery. |
|
|
What are the tx options for extensive tongue ca?
|
Near-total or total glossectomy may be necessary
- even with flap reconstruction, there is significant morbidity associated with deglutition and maintenance of an adequate airway - Aspiration may be a chronic problem, thus laryngectomy may be necessary - In select pts, total glossectomy may be possible w/o total laryngectomy Chemo may be considered for T4 tongue cancers, however, bone involvement usually requires surgical excision. |
|
|
How is the mandible managed in pts with tumors extending superficially to the gingiva?
How about if the tumor involves the periosteum? |
periosteum as the deep margin
if tumor involves the periosteum, may require at least a marginal mandiubulectomy with a horizontal cuff of alveolar ridge or saggital resection of the inner or outer cortex. |
|
|
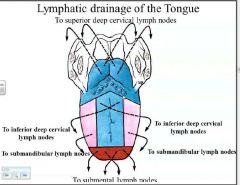
Which nodes does tongue ca typically spread to?
|
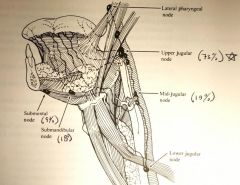
upper jugular nodes (73%) (ie. jugulodigastric)
submandibuar nodes (18%) middle jugular nodes (18%) submental nodes (9%) |
|
|
Elective tx of the neck with either surgery or radiation is recommended for primary tumors of which depth of invasion?
Which cervical levels should be dissected? |
2-4mm depth
typically at least a level I-III dissection is needed bilateral neck dissection should be performed for midline dorsum or ventral tongue cancers |
|
|
What are 5-year survival rates for tongue ca?
|
Stage I, II = 60-75%
Stage III, VI = 25-40% |
|
|
What is the 3rd most common site for oral cavity tumor?
|
floor of the mouth
|
|
|
Cervical mets from the floor of the mouth is typically seen in which nodes?
|
Submandibular (64%)
Upper jugular (43%) Submental nodes (7%) Bilateral spread is not uncommon |
|
|
What is the rate of recurrance of FOM cancers?
|
Recurrence at the primary site (41%) is more than twice as common as failure in the neck (19%)
|
|
|
Retromolar cancers often have involvement of which nerve?
|
Inferior alveolar nerve (V3) due to its close proximity to the mandibular foramen
|
|
|
What is the lymphatic drainage of the retromolar trigone?
|
predominately to the upper jugular LN
|
|
|
What is the tx for stage I and II retromolar trigone tumors?
|
Surgery and radiation are EQUALLY effective
If only soft tissue involvement - radiotherapy may result in less morbidity than surgery, but advanced-stage lesions often require BOTH |
|
|
If retromolar trigone tumor involves the mandible, what are the reconstruction options?
|
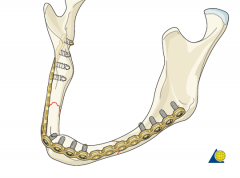
Mandible defects <5cm = mandibular reconstruction bar to span the bony defect and a soft tissue flap
Mandibular defects >5cm - usually require a composite flap such as fibular osteocutaneous free flap |
|
|
What is the lymphatic drainage of cancers of the alveolar ridge?
|
Most often to levels I and II
|
|
|
Why is radiation therapy as the primary modality is not recommended for alveolar ridge tumors?
|
because of the close proximity of tumor to the underlying bone, unless the pt is an unsuitable operative candidate
|
|
|
Which tumor types are present in hard palate cancers?
|
About 50% are SCCA
Minor salivary gland tumors |
|
|
Which benign dz process of the hard palate can be mistaken for malignancy?
|
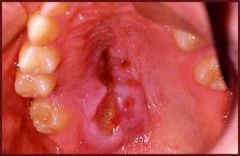
Necrotizing sialometaplasia
|
|
|
What are the tx options for cancers of the hard palate?
|
Although radiation can be used to tx carcinomas of this site, surgery is preferred. Radiation is more commonly reserved for adjuvant
|
|
|
How is the neck managed with hard palate cancer?
|
elective tx of the neck is generally not performed because of the low rate of occult mets
|
|
|
What is the 5-year survival rate for hard palate cancers?
|
44-75%
|
|
|
Which product caused an oral cancer epidemic in India?
|

"Pan" chewing, a combination of betel nut, lime and tobacco
|
|
|
Which varient of SCCA has a predilection for the buccal mucosa?
|
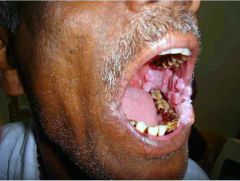
Verrucous carcinoma
|
|
|
What are tx options for ps with carcinoma of the buccal mucosa?
|
Surgical resection is the preferred method
Radiation alone or as adjuvant |
|
|
What are the number one and number two most common types of malignancies in the oropharynx?
|
1) SCCA
2) Lymphoma - due to abudantly present lymphoid tissue in the oropharynx as part of Waldeyer's ring (mc sites are palatine tonsils and the BOT) |
|
|
Which HPV subtype has been shown to be prevalent in oropharyngeal carcinoma?
|
HPV 16
|
|
|
Soft palate tumors most frequently occur where?
|
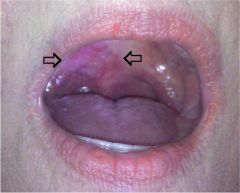
on the oral surface of the soft palate
|
|
|
Where is the lymphatic drainage of soft palate cancers?
|
upper jugular nodes (level II)
|
|
|
What is the most common site for carcinoma of the oropharynx?
|
tonsils
|
|
|
What is the tx of choice for carcinoma of the tonsil and tonsillar pillars?
|
Radiation or combined chemoradiation is generally the tx of choice
|
|
|
What are the surgical options for carcinoma of the tonsil and tonsillar pillars?
|
1) transoral excision - limited to very small lesions
2) anterior mandibulotomy with mandibular swing - useful for tonsil and BOT cancers w/o bony invasion. avoids sacrifice of inferior alveolar nerve and preserves sensation to lip and lower face. 3) composite resection - en bloc resection of posterior mandible and primary tumor. |
|
|
What is more aggressive, carcinoma of the oral tongue or BOT?
|
BOT
|
|
|
What are the mc presenting signs of BOT carcinoma?
|
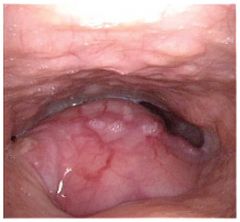
referred otalgia and odynophagia
|
|
|
Which neck zones are most common for the lymph node mets in BOT carcinoma?
|
levels II-IV (20% are bilateral)
|
|
|
What is the primary treatment method for BOT carcinoma?
|
like with other cancers of the oropharynx, XRT or chemoradiation are used
(surgery is used for small primary tumors or for salvage following XRT or chemorads) |
|
|
List some surgical procedures for BOT carcinoma
|
Mandibular swing or composite resection
Median mandibuloglossotomy Suprahyoid pharyngotomy - through a neck incision Transoral laser resection |
|
|
Which syndrome is associated with hypopharyngeal carcinoma?
|
Plummer-Vinson syndrome - IDA, dysphagia, mucosal webs, wt loss, angular stomatitis, and atrophic glossitis. affects women
|
|
|
In the US, cancer of which hypopharynx site predominates?
|
Pyriform sinus carcinoma
|
|
|
A characteristic feature of hypopharyngeal cancer is its tendency for ___________________
|
submucosal spread
|
|
|
What is the primary modality in the tx of T1 and selected T2 lesions of the hypopharynx?
|
XRT alone
(adjuvant postop XRT plays an important role in advanced-stage cancers of the hypopharynx) |
|
|
What role does surgery play if cancer of the hypopharynx involves the posterior hypopharyngeal wall?
|
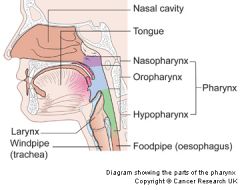
selected tumors can be resected with laryngeal preservation if there is no fixation to the preverterbral fascia
approach via transhyoid or median labiomandibular glossotomy |
|
|
What role does surgery play if cancer of the hypopharynx involves the postcricoid mucosa?
|
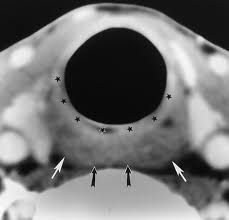
usually present at an advanced stage and therefore require total laryngopharyngectomy
these lesions can involve the cervical esophagus and require laryngopharyngoesophagectomy. |
|
|
What role does surgery play if cancer of the hypopharynx involves the pyriform sinus?
|
Extended partial laryngopharyngectomy
Supracricoid hemilaryngopharyngectomy Total laryngopharyngectomy |
|
|
What are the THREE types of WHO classifications of nasopharynx carcinoma?
|
Type I - keratinizing SCCA (25%)
Type II - nonkeratinizing SCCA (12%) Type III - undifferentiated carcinoma (63%) |
|
|
Which nasopharyngeal carcinoma types are endemic and which are sporadic? What are the risk factors of these groups?
|
Endemic = WHO Type II and III
- EBV, genetic predisposition, environmental factors (certain food preservatives) Sporadic = WHO type I - tobacco and alcohol exposure |
|
|
At which decades does NPC peak?
|
Fifth and sixth decades
20% present in pts under the age of 30 (young pts more likely to have WHO III (undifferentiated)) |
|
|
What is the role of EBV in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)?
|
EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the human herpesvirus family.
It establishes persistent, chronic infection, usually in B lymphocytes. 90-95% of the populations have demonstrable EBV Ab's by adulthood Molecular cytogenetic studies have confirmed that EBV infection is an early, possibly initiating event in the development of NPC |
|
|
What is the primary tx modality for NPC?
|
Radiation therapy or chemoradiation is the primary tx modalities
Chemotherapy concurrently with XRT for NPC has been shown to improve overall survival rates recently |
|
|
What role does surgery place in NPC?
|
Resection is technically difficult due to architecture and inaccessibility of the anterosuperior skull base
Reserved for highly selected pts in cases of radiation failure or tumor recurrence. |
|
|
What are the local and regional control rates of NPC with radiation? How about with radiation with concurrent chemotherapy?
|
XRT - 60%
Radiation with concurrent chemotherapy - 70-80% |
|
|
What are the 5-year survival rates of NPC with radiation? How about with radiation with concurrent chemotherapy?
|
XRT - 36-58%
Radiation with concurrent chemotherapy - 70-80% |
|
|
Which subsite within the head and neck region that has the highest rate of distant mets?
|
Cancers of the nasopharynx - 25-30% of pts
- whereas local and regional failure previously accounted for most morbidity and mortality, distant mets now is a frequent mode of failure and death |
|
|
What types of cancer is prevalent in esophageal cancer?
|
SCCA or adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Where does adenocarinoma occur in the esophagus?
Where does SCCA occur in the esophagus? |
>75% of adenocarcinomas occur in the distal esophagus.
SCCA is more EVENLY distributed throughout the esophagus |
|
|
What is the most common site of primary esophageal cancer?
|
distal third > middle third > proximal third
|
|
|
What are the RF for SCCA of the esophagus?
|
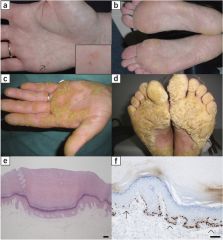
Tobacco
Alcohol use Achalasia Caustic injury Plummer-Vinson syndrome Hx of H&N cancer Hx of radiation therapy to the mediastinum Low socioeconomic status Nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (tylosis; image) |
|
|
What are the RF for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus?
|
Barrett's esophagus
Weekly acid reflux Tobacco use Hx of radiotherapy to the mediastinum |
|
|
What is the annual rate of malignant transformation in Barrett's esophagus?
|
0.5% annually
|
|
|
At the time of diagnosis of esophageal cancer, what % of patients have distant mets or an unresectable primary tumor?
|
50%
|
|
|
What role does surgery play in esophageal cancer?
|
Early-stage dz is tx with a transthoracic or transhiatal approach for partial or total esophagectomy
Transcervical approach for upper cervical esophagus or inferior extension from hypopharynx Laryngectomy with or without partial tracheal resection may be necessary for upper cervical esophageal cancer Endoscopically placed stents may be deployed for palliative tx of dysphagia in advanced dz |
|
|
What role does radiation play in esophageal cancer?
|
Primary radiotherapy may be used an alternative tx in pts with medical comorbidities that prevents surgical resection
No improvement in survival has been demonstrated with preop XRT Postop XRT improved local dz control and is useful in pts at high risk for recurrence, tracheoesophageal fistula, or presence of residual dz |
|
|
What role does chemotherapy play in esophageal cancer?
|
Preop chemo may result in a reduction in primary tumor size as well as tx regional and distant mets, but no survival benefit has been demonstrated
Postop chemo may also tx regional and distant mets but results in increased toxicity, morbidity and no improvement in survival |
|
|
What role does chemoradiation play in esophageal cancer?
|
Increased toxicity bu better tumor response
If utilized preoperatively, the reduction in tumor size may allow for complete surgical resection No clear survival benefit when used preop |
|
|
What is the overall 5-year survival rate for esophageal cancer?
|
14%
|

