![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a suspension (by definition)? |
A coarse disperse system where an insoluble solid is dispersed in a liquid medium |
|
|
What is the disperse phase made of? |
Solid particles, usually > 0.1µm |
|
|
What is the disperse medium made of? |
Aqueous media (Infrequently also organic or oil) |
|
|
What are the reasons for formulating a suspension? |
-Drug is predominantly insoluble -Drug is more stable in suspension -Need to control the rate of release of the drug -Drug has bad taste> helps to improve compliance by masking taste -Easy to swallow -Can divide and control the dose -Fast pharmaceutical action |
|
|
List some examples of oral suspensions |
Aluminium hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide antacid suspensions |
|
|
State an example of a parenteral suspension |
Insulin zinc suspension BP |
|
|
State an example of a topical application |
Calamine lotion BP |
|
|
State an example of dry powder for suspensions |
Barium Sulphate for suspension BP |
|
|
Why can prednisolone be put in suspension? |
It's poorly soluble |
|
|
Why is Oxytetracycline put in suspensions? |
To prevent degradation of drug/ to improve stability of the drug |
|
|
Why is Chloramphenicol Palmitate put in suspension? |
To mask the taste, it's bitter/unpleasant |
|
|
Why is calamine lotion put in suspension? |
For use as a topical applicant |
|
|
Why are penicillin and procaine put in suspension? |
To control the rate of drug absorption (Parenteral application) |
|
|
Give an example of a vaccine put in suspension |
Cholera vaccine |
|
|
Which x-ray contrast agent is formulated as a suspension? |
Barium Sulphate |
|
|
What are the desirable properties of suspensions? |
-Dispersed particles should settle slowly, allowing accurate and uniform dose -The particles should remain flocculated and be readily dispersed upon shaking (caking/aggregation should be avoided) -Ease of use: viscosity, product must be easily dispersed from its container -Particle size: should remain reasonably constant to assist stability and re-dispersion |
|
|
What does particle size affect? |
-Dose uniformity -Variable dissolution and bioavailability -Sedimentation (physical stability) -Texture (larger particles over 5µm in diameter give gritty texture) |
|
|
Which law do particles follow during sedimentation? |
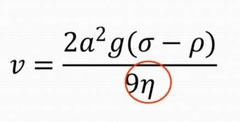
Stoke's Law |
|
|
What is the sedimentation volume, F, defined as? |
The raito of the Height of the sediment/Height of the whole pharmaceutical product Vu/Vo |
|
|
Why do powders float on top of liquids? |
-Presence of an absrobed layer of air -The lipophilic nature of certain materials or contaminants -Poor properties of "wettability"- this generally refers to the contact angle of the particle and the surface |
|
|
What are the properties of hydrophobic powders? |
-Have high contact angle -Not easily wetted and tend to float on the surface of the liquid (eg: sulphur or magnesium stearate) |
|
|
What are the properties of hydrophilic powders? |
-Low contact angle -Readily wetted (eg zinc oxide or magnesium carbonate) |
|
|
How can you improve particle wetting? |
Use wetting agents. This improves wettability of hydrophobic powders by reducing surface tension between the particle and the liquid surface, and therefore reducing the contact angle |
|
|
Why must particles be wetted for suspensions? |
Only wettable and wetted particles can be readily dispersed into the liquid and remain adequately dispersed |
|
|
Which wetting agents are used for oral suspensions? |
Surfactants such as polysorbates sorbitan esters (Tweens and Spans) |
|
|
Which wetting agents are used for IV suspensions? |
Lecithin, polysorbates and poloxamers and related materials |
|
|
In what concentrations are wetting agents used? |
Used in relatively low (ca. 0.1% w/w) concentrations |
|
|
What is a disadvanatge of wetting agents? |
They may cause excessive foaming in product |
|
|
What are some examples of hydrophilic colloids? |
Acacia, bentonite, tragacanth, alginates, xantham gum and carious celluose derivatives |
|
|
What are hydrophilic colloids used for? |
-Used to coat particles to make them more wettable -Act as suspending agents due to their viscosity |
|
|
Which solvents are used to improve particle wetting? |
Various alcohols (usually ethanol), glycerol and glycols |
|
|
What are solvents used for in suspensions? |
To penetrate into loose aggregations of particles to displace the air adsorbed within such structures |
|
|
What is the definition of flocculation? |
A process of contact and adhesion whereby the particles of a dispersion form larger-size clusters |
|
|
What is flocculation? |
The removal of a sediment from a fluid. Flocculation can be forced through agitation or the addition of flocculating agents |
|
|
Flocculation vs Deflocculation |

|
|
|
What is the equation for sedimentation volume in a deflocculated system? |
Fu = Vu/V0 |
|
|
What is the equation for sedimentation volume in a flocculated system? |
Ff = Vf/V0 |
|
|
What is the equation for the degree of flocculation? |
β = Ff/Fu = Vf/Vu |
|
|
What does a bigger value of β mean? |
Better flocculation |
|
|
What is Zeta potential? |
The electrical potential in the interfaical double layer at the boundary of different regions of a suspension. The potential difference between the dispersion medium and the stationary layer of fluid attached to the dispersed particle in suspension. |
|
|
What happens if the concentration of electrolytes in suspension is too high? |
Results in charge repulsion and therefore caking of the suspended agent |
|
|
How is flocculation in suspension controlled? |
By buffering the formulation to control the pH and ionisation, and by controlling the electrolyte concentration |
|
|
Which polymers are used in suspensions? |
Starch, alginates, tragacanth, and cellulose derivatives |
|
|
Give two examples of polysaccharides and when they're used |
-Acacia: used with other thickeners in extemporaneous products -Tragacanth: used in extemporaneous products, slow to hydrate, and shows non-Newtonian behaviour |
|
|
List different types of viscosity modifiers |
-Polysaccharides -Alginates -Water-soluble celluloses -Hydrated silicates -Carbomers |
|
|
Why are hydrated silicates used to modify viscosity? |
They're highly absorbent and Non-Newtonian |
|
|
What additives are added to suspensions to improve compliance and shelf life? |
-Buffering agents -Sweeteners -Flavours -Colouring agents -Preservatives |
|
|
Which methods can be used to manufacture suspensions? |
-Extemporaneous methods eg: mortar and pestle -High-shear mixers -Homogenisers -Ball mills |
|
|
What is the definition of Ostwald Ripening? |
The change of an inhomogeneous structure over time. Over time, small crystals (or sol particles) dissolve, and redeposit onto larger crystals or sol particles. |
|
|
What is the equation for the solubility of particles? |
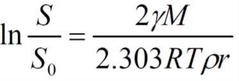
|
|
|
How many common crystal forms does cortisone acetate suspension have? How many of these are unstable, and how do they change into the stable form? |
Five common crystal forms Four unstable> turn to stable form in presence of water (caking is often observed when the crystal form changes) |
|
|
Which additives or conditions can cause the inhibition of crystal growth? |
-Polymers> form a prtoective layer around the particles -Surfactants>reduce crystallisation (some may increase it) -Temperature> influences solubility, which changes the degree of saturation or supersaturation in solution |
|
|
Which tests are carried out to evaluate physical stability? |
-Aesthetic tests (appearance, colour, odour, taste) -pH (zeta potential and solubility) -Sedimentation rate -Particle size and form -Redispersion and centrifugation tests -Rheological measurements -Freeze-Thaw temperature cycling -Compatability with container and cap liner -Dose uniformity -Microbial testing |
|
|
What excipients are in calamine lotion, and why? |
-Calamine 30g -Zinc oxide 10g-Bentonite 6g (thickening agent)-Sodium citrate 1g (controls flocculation)-Liquefied phenol 0.5mL (preservative)-Glycerol 5mL (thickening agent; also helps the product adhere better to the skin)-Water to 200mL |

