![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Pedigree |
A record of descent |
|
|
|
Phylogeny |
The evolutionary development and diversification of a species or group of organisms, or of a particular feature of an organism. |
|
|
|
Polytomies |
Polytomy is a term for an internal node of a cladogram that has more than two immediate descendants (i.e, sister taxa). In contrast, any node that has only two immediate descendants is said to be resolved. |
|
|
|
Clade |
Another word for a branch of a phylogeny: a group. |
|
|
|
Pachyderms |
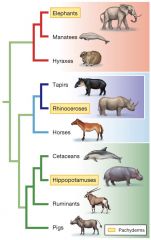
|
Non-monophyletic(polyphyletic) group |
|
|
Monophyletic |
All descendant taxa + most recent common ancestor (located at a node) |
|
|
|
Paraphyletic group |
Non-monophyletic group (Fish: not all descendants of the common ancestor are fish) |
|
|
|
Cladogram |
A phylogeny with the branch tips aligned; indicates only the evolutionary relationships among the species shown |
|
|
|
Phylogram |
Phylogeny that also represents the amount of sequence change along each branch by differing the horizontal branch lengths |
|
|
|
Chronogram |
A sort of phylogeny that indicates the timing of evolutionary events |
|
|
|
Homologous traits |
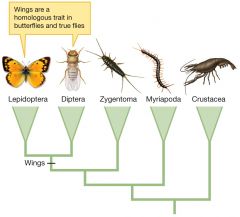
|
When descendants and their common ancestor all share a trait |
|
|
Analogous traits |
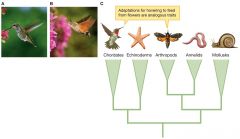
|
When a shared trait evolved separately in two lineages |
|
|
Convergent evolution |
The process whereby organisms not closely related (not monophyletic), independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. |
|
|
|
Aposematic coloration |
Conspicuously recognizable markings of an animal that serve to warn potential predators of the nuisance or harm that would come from attacking or eating it. The bold patterns of skunks and the bright colors of poison arrow frogs are examples. |
|
|
|
Apomorphy |
A novel evolutionary trait that is unique to a particular species and all its descendants. Can be used as a defining character for a species or group in phylogenetic terms. Hence, the possession of feathers is unique to birds and defines all members of the class Aves. |
|
|
|
Synapomorphy |
A Characteristic present in anancestral species and shared exclusively (in more or less modified form) by itsevolutionary descendants. |
|
|
|
Autapomorphy |
A distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon |
|
|
|
Plesiomorphy |
The ancestral trait state, usually in reference to a derived trait state |
|
|
|
Symplesiomorphy |
An ancestral character or trait state shared by two or more taxa (synonym to plesiomorphy) |
|
|
|
Homoplasy |
Correspondence between parts or characteristics acquired as the result of parallel evolution or convergence |
|
|
|
Monophyly |
A group of organisms which forms a clade; consists of an ancestral species and all its descendants |
|
|
|
Pleomorphy |
The ability of some bacteria to alter their shape or size in response to environmental conditions |
|
|
|
Outgroup Criteria |
Using an outgroup to root a phylogeny tree |
|
|
|
Maximum Parsimony Criteria AKA Optimality Criterion AKA Objective Function |
The tree with the fewest "extra" or ad hoc assumptions of character change is the preferred tree |
|
|
|
Phenetics |
Methodology for Building Classification based on overall similarity or difference AKA Numerical Taxonomy |
|
|
|
Simpson's Index |
(# shared characters) / (total number of characters) --> % |
|
|
|
Simple Distance Coefficient |
(# unshared characters) / (total number of characters) --> % |
|
|
|
Long-branch attraction AKA the Long branch problem |
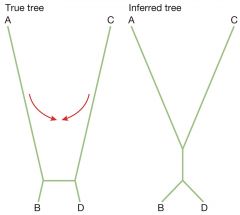
|
|
|
|
3 Strategies for Searching "Tree Space" |
-Exhaustive (impractical, too many possibilities) -Branch & Bound (impractical, too many possibilities) -Heuristic (widely used) |
|
|
|
Heuristic Strategy for Searching "Tree Space" |
Uses algorithms to analyze different trees by grafting different trees to look for the shortest possible tree |
|

