![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define "kinesiology |

M |
|
|
Explain the relationship between kinesiology and biomechanics. |
Kinesiology explores the muscular involvement in strength exercise and sport-specific techniques,while biomechanics look at the physical factors involved in the movement. |
|
|
List and explain the three types of muscular contractions. |
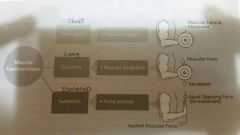
Concentric- muscle shortens Eccentric -muscle lengthens Isometric-fixed position |
|
|
Define "prime mover" (agonist) |
Denoting a muscle in a state of contraction,with reference to its opposing muscle,or antagonist |
|
|
Define "assistant mover" |
Muscle that plays a secondary role to the prime mover involved. |
|
|
Explain the relationship between agonist and antagonist. |
The agonist role is to contract one part of the muscle while the other muscle is relaxed which is antagonist |
|
|
Define the term "stabilizer muscles" and provide an example of how it is used in an exercise. |
Stabilizer muscle that steadies or holds a body part in place.it Archos the bone so that the prime mover has a firm base against which to contract. (I.e. for the muscle pull against.to create precise movements. |
|
|
Explain synergy as it relates to muscle. |
Synergy is use in two ways.it the work of two muscles as they connect . Helping synergy-when two muscles contract to create one movement. True synergy-when a muscle contract to stop the secondary action of another muscle. |
|
|
List and explain the four type of muscular movement. |
Sustained force movement -is movement in which continuous muscle contraction occur in order to keep moving weight. Dynamic balance movement's - are movement in which constant agonist -antagonist muscle contractions occur in order to maintain a certain position or posture Ballistic movement- movement in which inertial movement exist after and explosive or quick,maximum force contraction. Guided movement- is movement that occurs when both the agonist and antagonists contract to control the movement. |
|
|
Define the three imaginary planes of motion and provide and exercises for each plane of movement. |
Sagittal (anteroposterior) plane: separates the body into right and left sections (bicep curls) Frontal (coronal) plane: separates the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts. (Jumping jax). Transverse (horizontal) plane: separates the body superior (top) and inferior (bottom)sections. (Crunches). |
|
|
List and explain the six primary movements that occur in the human body. |
Flexion: a decrease in the angle between two body segments. Extension: an increase in the angle between two body segments,or return from flexion. Abduction: movement of an body part away from the midline. Adduction: movement of an body part toward the midline. Ratation: circular movement of a body segment about long axis. Circumduction: movement of a part,e.g, extremity, in a circular direction. |

