![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Peritoneum |
Kidneys are held in place by... |
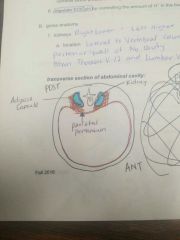
"Around" |
|
|
Kidney Location |
Lateral to vertebral column Posterior wall of abdominal cav Btwn Thoracic V-12 & Lumbar V-3 |
Right lower & Left is higher |
|
|
Urinary System |
Contains Kidney, Ureters, Bladder and Urethra |
|
|
|
Erythropoietin |
Controls RBC formation |
|
|
|
Angiotensin 2 |
Activated by RENIN Controls Aldosterone secretion Controls blood pressure through vasoconstriction |
|
|
|
Trigone |
Area of floor of urinary bladder where ureters and urethra form a invisible triangle. |
|
|
|
Hilum |
Medial indentation on each kidney |
|
|
|
Layers of kidney |
Cortex- superficial, contains renal corpusles& tubules Medulla- not continuous, contains renal pyramids |
|
|
|
Neuron Structure |
Renal Corpusle - contains afferent and efferent arteriole, bowman's capsule TO proximal convoluted tubule TO Loop of Nephron TO distal convoluted tubule TO collecting duct |
|
|
|
Filtration in Nephron |
Excrete 1.5 L/day Reabsorb 178.5 L/day Filter 180 L/day Caused by blood pressure in Glomerular Capillaries |
|
|
|
Materials Reabsorbed |
Glucose Water Amino acids Sodium |
Want to KEEP |
|
|
Materials Excreted |
EXTRA Water Sodium Potassium WASTES Urea Creatinine Uric acid Drugs Vitamins |
|
|
|
Small materials involved in filtration |
Can go through filtrate |
|
|
|
Big materials through Filtration |
Stay in blood Ex: RBC AND PROTIEN |
|
|
|
Levels of Aldosterone |
Affect how much remaining sodium is REABSORBED ^ Aldosterone ^ Na absorption & more excreted K+ |
|
|
|
Level of Anti Diuretic Hormone |
Affects how much of remaining water is reabsorbed |
|
|
|
Bronchi |
Supported by Cartilage Line by suterstratifiesd filiated culombar epi w/ golbit cells |
|
|
|
Alveolar macrophanges |
Wander along Alverio and phagocitize debris |
|
|
|
Right lungs |
3 lobes Sup horizontal fissure Mid oblique fissure Inf |
|
|
|
Left lung |
2 lobes Sup oblique fissure Inf |
|
|
|
Inhaling |
1st: Vol change caused by Contraction of Diaphragm 2nd: pressure change DECREASES 3rd: Pressure Gradient into lungs |
|
|
|
Exhaling |
1st vol change by decreasing thorax 2nd pressure change increase pressure in lungs |
|
|
|
Surfactant |
Prevents lung collapse |
|
|
|
Respir. Membran |
3 layers Type 1 alveolar cells next to air Basement membrane middle Pulm. Cap. Endothe. Cells next to blood |
|
|
|
Mucosa |
Lines nose, nasal cav |
|
|
|
Nasal septum |
Made of ethmoid, vomer and cartilage |
|
|
|
Oxegen |
98.5% goes into blood 1.5% into plasma |
|
|
|
Co2 |
7% in plasma 23% enter the erythrocyte and hemoglobin 70% Rest converted into bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Layers of intestines |
Deep to superficial Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis externa Serosa (visceral periton) |
|
|
|
Lingual fernulum |
Attatches tongue to mouth |
|
|
|
ANS |
Controls digestion in stomach Symp:inhibits activity Parasymp: stimulates activity |
|
|
|
Stomach regions |
Cardiac Fundus Body Pylorus |
|
|
|
Oral phase |
Voluntary (Buccal phase) |
|
|
|
Pharayngeal phase |
Involuntary, pushes food on sensory receptors to medulla center |
|
|
|
Esophageal phase |
Involuntary muscle contracts |
|
|
|
Rugae |
Folds in stomach, allpws expansion |
|
|
|
Small intestines |
5hrs time here Duodenum Jejunum Ileum |
|
|
|
Amylase |
Breaks carbs down |
|
|
|
Protease |
Breaks proteins down |
|
|
|
Lipase |
Breaks Glycerserite down |
|
|
|
Liver section |
Front Right &Left Back Left, caudate, quads are, right |
|
|
|
Cholecystokinin |
Contraction of gall bladder |
|
|
|
Large intestines |
Ascending colon Transverse Descending Sigmoid Rectum |
|

