![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is in the PT examination? |
Pt. hx (general demographics, lifestyle and functional status, past and current medical hisotry, past and current wound hx) System review Administering tests and measures |
|
|
What are some questions to ask during a wound screening? |
}When and how did the wound begin? }Have any tests been performed? }Current or prior medications for wound? }Wound-related pain? }What is currently being done to wound? }What was tried in the past? }Is wound improving, staying the same, getting worse? |
|
|
What are the things to look at in the cardiovascular/pulmonary system review? |
◦Heartrate ◦Bloodpressure ◦Respiratoryrate ◦Edema ◦Pulseoximetry |
|
|
What are the things to look at in the musculo skeletal system review? |
-Structure -Posture -Range of motion -Strength |
|
|
What are the things to look at in the neuromuscular system review? |
-gait -mobility -transfers -balance |
|
|
What are the things to look at in the gastrointestinal system review? |
-nutrition intake -supplementation -continence -body mass index -nutritional assessment screening tools REAP (Rapid Eating Activity of Patients) WAVE (Weight, Activity, Variety, and Excess) |
|
|
What is the REAP test? |
nutritional assessment Rapid Eating Activity of Patient |
|
|
What is the WAVE test? |
nutritional assessment Weight Activity Variety Excess |
|
|
What are the things to look at in the urogenital system review? |
-incontinence -poorly controlled diabetes -urinary tract infections |
|
|
What are the things to look at in the integumentary system review? |
◦Skin integrity ◦Skin color ◦Scar formation ◦Hair and nail growth – appendeges ◦Brief screen, more detail in the remaining examination |
|
|
What are the routine tests and measures performed on open wounds? |
-Integumentary integrity -circulation -Sensory integrity |
|
|
What is looked at in the integumentary integrity of open wounds? |
intact open color temp etc. |
|
|
What is looked at in the circulation for open wounds? |
can test capillary refill can use pulses can use doppler etc. |
|
|
What is looked at in the sensory integrity circulation for open wounds? |
light tough pressure symmetry etc. |
|
|
What is to be done when documenting or looking at wound location? |
-use anatomically correct terminology -document side and body surface of lesion -document wounds in relation to anatomical landmarks |
|
|
What is to be done when documenting or looking at the wound size? |
-direct measurement -tracings -photography -volumetric measurement -percent of total body surface area |
|
|
What is to be done in the direct measurement of the wound size? |
- Measurelongest length and the widest width - Woundsurface area = length × width - Wounddepth (clock method) (documented as: 'wound depth = 1.4 cm) - Cannotbe used to accurately determine depth in wounds covered with nonviable tissue |
|
|
What is to be done in the direct measurement of the wound size tracings? |
- Two-layeredtransparent film - Moreaccurate representation of wound size - Allowsfor future comparisons - Maybe difficult to visualize wound perimeter through transparency |
|
|
How is a photographic measurement do be done for wound size? |
-Digital images are high quality -Avoids contact with patient’s wound -Provides periwound and wound bed characteristics -Camera angle and focal distance can influence image size -Can be manipulated -Nice adjunct -Must have a measurement tool in the photo and some other identification per protocol. }G |
|
|
How is a volumetric measurement to be done for wound size? |
-Dental, silicone molding, or saline to fill wound -Time consuming and can be painful to patient -Can be detrimental to wound healing *avoid using this techniqu |
|
|
How is total body surface area to be done for wound size? |
-Largesurface area wounds - Percentof total body surface area (TBSA) -Burninjuries – we will discuss this later in the course in depth. |
|
|
What do we do to measure tunneling? |
(sinus tract) -use clock terms to identify position -common in pt. with neuropathic ulcerations and surgical wounds |
|
|
What do we do to measure undermining? |
(shelf) -use clock terms to identify position -common in pt. with pressure or neuropathic ulcerations |
|
|
Example of how to document wound tunneling: |
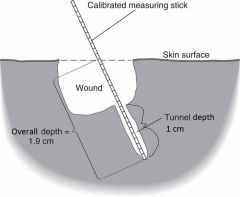
Wound tunnels 1.0 cm at 3-O'clock position, extending the depth to 1.9 cm |
|
|
Example fo how to document wound undermining: |
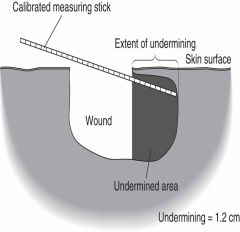
Undermining 1.2 cm from 9-O'clock to 1-O'clock position |
|
|
What needs to be looked at when looking at the wound bed? |
-Granulation tissue -Necrotic tissue -slough -Eschar -other structures within wound bed -fascia, muscle, tendon, joint capsule, bone -foreign bodies or debris |
|
|
What is the wound assessment tool? |
NE1 HATT History Anatomy Tissue type (worst) Touch/view details |
|
|
What is the wound treatment tool? |
DIMES Debridement Infection/inflammation Moisture balance Edge/environment Supportive products |
|
|
What needs to be looked at when looking at the wound edges? |
-distinctness -thickness -color -attachment to base of wound -evidence of epithelialization, scarring, pigment changes |
|
|
What needs to be done when looking at wound drainage? |
Type: serous, saguinous, serosanguinous, purulent, serpurulent Color: clear or pale yellow, red, dark brown, blue/green Consistency: thin or watery, thick Amount: non, trace, minimal to moderate, copious |
|
|
Table for documenting and interpreting wound drainage: |

|
|
|
What if you have a wound with odor? |
possible indicator of wound infection |
|
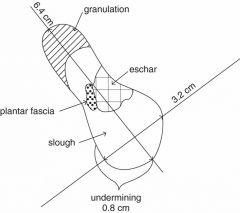
Wound tracing with complete documentation for this picture: |
Patient name: John Doe. Date: January 10, 2010. Clinician: Jane Smith, PT. Wound location: L plantar forefoot over 2nd metatarsophalangeal joint. Wound size: 6.4 × 3.2 cm, depth 1.2 cm. Wound bed: 25% granulation tissue, 50% yellow adherent slough, 20% black eschar, 5% plantar fascia. Undermining: 0.8 cm from 5-o’clock to 8-o’clock positions. Wound edges:unattached, circumferentially hyperkeratotic rim. Wound drainage: minimal, seropurulent. Wound odor: none. Periwound: anhydrous |
|
|
What are the periwound and associated skin characteristics to include within the examination of a pt. with open wound? |
-structure & quality -color -epithelial appendages -edema -temperature |
|
|
What may be in the structure and quality of the periwound and associated skin characteristics? |
Age-related skin changes Periwound hydration Skin turgor: a reflexion of the skin's elasticity, measured by monitoring the time it takes for the skin of the forearm to return to position after it is lightly pinched between examiner's thumb and forefinger (N=3sec) Calluses Scar formation |
|
|
What may be the color of the periwound and associated skin characteristics? |
-normal skin tone -erythema (blancchable/nonblanchable) -pale/blue-circulation concern |
|
|
What may the epithelial appendages be of the periwound and associated skin characteristics? |
hair and nail growth |
|
|
What may the edema be of the peri wound and associated skin characteristics? |
-pitting/nonpitting 1+ to 4+ scale -induration- hard or firm |
|
|
Scale for edema of the pareiwound: |

|
|
|
Written out scale for edema of periwound: |
1+ Barely perceptible depression <2mm 2+ Easily identifiable depression, rebounds in <15sec 2-4 mm 3+ depression rebounds in 15-30 sec 5-7 mm 4+ depression lasts for >30 sec >7mm |
|
|
What may the temperature assesment show of periwound and associated skin? |
-indication of immflamation,, infection, or impaired circulaiton -document as increased, decreased, or normal |
|
|
What may the circulation assessment show of periwound and associated skin? |
Peripheral pulses: dorsalis pedal, posterior tibialis -graded 0-3+ (absent to diminished) -capillary refill (normal <3 sec) -pinch distal tip or nail to blanch the area, but not too severe as to cause pain |
|
|
What needs to be assessed when looking at the sensory integrity of a wound? |
-impaired light touch is a risk factor for ulceration/reulceration -gold standard for aassessment: Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments |
|
|
Normal light touch interpretation of sensory testing: |

|
|
|
***Interpretation of sensory testing(normal light touch) |
4.17 monofilament = 1 gram pressure = decreased sensation 5.07 monofilament = 10 grams = loss of protective sensation 6.10 monofilament = 75 grams = absent sensation |
|
|
How is monofilament sensory integrity done? |
apply monofilament perpendicular to the skin with enough pressure to cause the filament to bend |
|
|
What are the 5 PT systems to facilitate wound etiology? |
-pain -position -presentation -periwound -pulses -Temperature |
|
|
What is involved in the prognosis of a wound? |
-predict optimal level of improvement -determine frequency and duration of treatment -types of interventions required -determine time to reach optimal level |
|
|
Wound healing curve: |

|
|
|
What is a positive indicator a wound is healing? |
20-40% decrease in wound surface area within 2-4 wks |
|
|
What is a negative indicator a wound is healing? |
-no decrease in size or signs of improvement within 2 wks -reassess |

