![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List Innate immune system cells
|
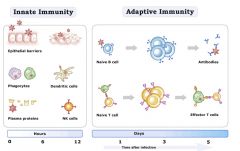
1) mechanical, chemical and microbiological barriers
2) phagocytic leukocytes, 3) dendritic cells, 4) a special type of lymphocyte called a natural killer (NK) cell, and 5) circulating plasma proteins. (Complement system) |
|
|
List adaptive immune system cells
|
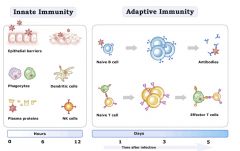
Native B cells, antibodies
Native T cells, effector T cells |
|
|
List the Immunological cells in blood
|
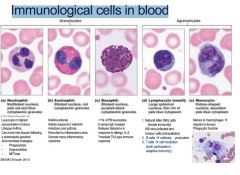
Neutrophil
Eosinophils Basophils Lymphocytes Monocytes |
|
|
Describe neutrophil
|
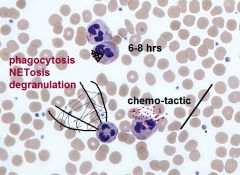
|
|
|
Describe eosinophil
|
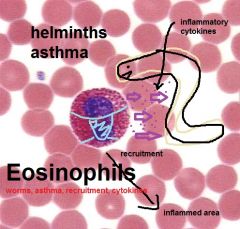
|
|
|
Describe basophils
|
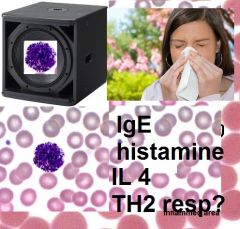
|
|
|
What are the three types of lymphocytes?
|
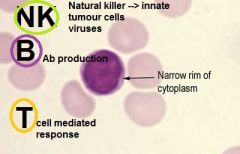
B cell
T cell NK cell |
|
|
Which lymphocyte is in the innate immune system>
|
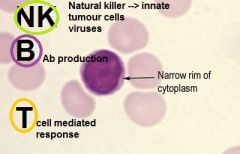
NK cell
|
|
|
Describe lymphocytes
|
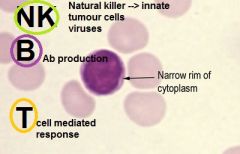
|
|
|
Describe NK cells
|
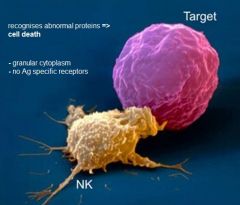
- innate immunity
- no Ag specific receptors - large - granules |
|
|
Describe B cells
|

|
|
|
Describe T cells
|
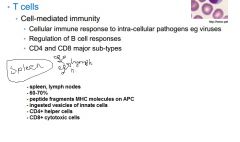
|
|
|
which lymphocytes deal with extracellular pathogens and intracellular pathogens?
|
T cells --> intracellular pathogens
B cells --> extracellular pathogens |
|
|
What are the two classes of T cells?
|
CD4+ and CD8+
|
|
|
Define leucocytosis
|
increase in WBCs stimulated by release of inducing factors from injured cells
|
|
|
How does leucocytosis occur?
|
induction factors are released by injured cells, often due to an inflammatory response
|
|
|
What is margination?
|
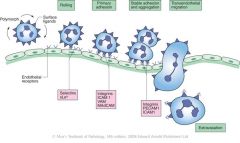
Phagocytes which adhere to the endothelial wall which attach to cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) from injured cells
|
|
|
Define Diapedesis
|
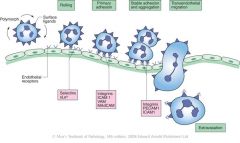
the process of extravasion of phagocytes through capillary wall
|
|
|
Define chemotaxis
|
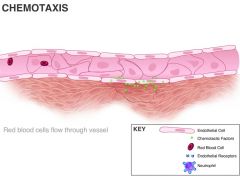
attraction and movement to site of injury
|
|
|
Explain neutrophil migration
|
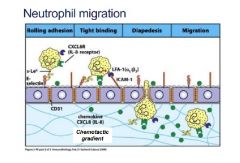
-chemokines which activate local endothelial cells
- CAMs E selectin and ICAM-1 - E selectin bind with a S-Le ligand on the neutrophil -'rolling adhesion' - allows ICAM-1 to bind to LFA-1 - cytokines solidify the binding through IL-8 receptor - moves through endothelial cells called 'diapedesis' - migration occurs through chemotaxis from injures site |
|
|
Describe phagocytosis
|
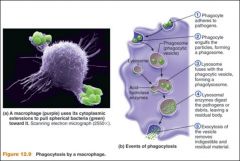
1. active process where an immune cell envelopes a pathogen to create a phagosome,
2. Phagosome merges with lysosome 3. Phagolysosome 4. Lysosomal enzymes digest and destroy 5. Contents removes via exocytosis |
|
|
Describe degranulation
|
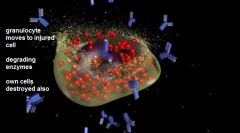
Release of granule contents and activity of nonoxidative and oxidative anti-microbial strategies
|
|
|
Describe NETosis
|
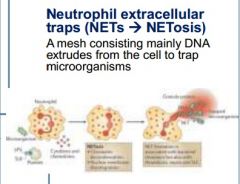
Neutrophils have found that they can cast a net mesh of DNA extrudes which to trap microorganisms
|
|
|
What are the 3 immunological cells in tissues?
|
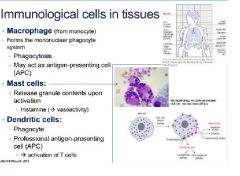
- Macrophages
- Mast cells - Dendritic cells |
|
|
What roles do macrophages perform?
|
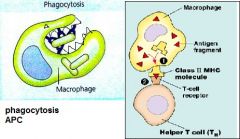
|
|
|
What is a mast cell and what roles does it perform?
|
degranulation
parasitic worms allergies protects surfaces histamine release which increases vasocactivity and induces inflammation |
|
|
What are dendritic cells?
|
Phagocytic cell with finger like processes which perform phagocytosis, macropinocytosis and present antigens to ,and activate, T cells.
|
|
|
What are the four types of dendritic cells?
|

CLFP
Classical Langerhans cells Follicular dendritic plasmacytoid cells |
|
|
Describe Classical dendritic cells
|

- both lymphoid and non lymphoid tissue
- phagocytosis and pinocytosis - APC to T cells - induce immune response to non self Ag - enforce tolerance to self cells |
|
|
Describe Langerhans cells
|
- dendritic cells
- skin - if has an Ag will present at lymph node - APC activity |
|
|
Describe Plasmacytoid cells
|

- production of interfeurons
- distinct lineage from classical dendritic cells - do not really activate naive T cells - weaker expression of MHC molecules |
|
|
Describe Follicular dendritic cells
|
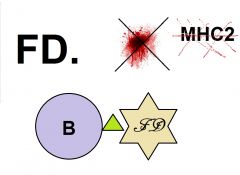
- no MHC II
- B cells - no blood |
|
|
Identify immunological tissue
|
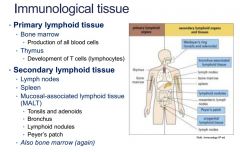
Primary: Bone Marrow & Thymus
Secondary: Lymph nodes, spleen, Malt, bone marrow |
|
|
What are the four types of MALT
|
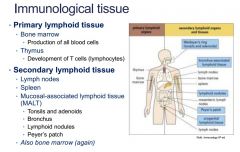
Tonsils
Bronchus Lymphoid nodues Peyer's patches |
|
|
Describe the Thymus
|
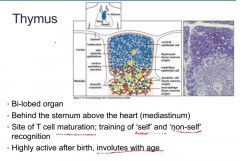
primary immunological tissue
involutes with age matures T cells mediastinum location training of self and non self |
|
|
Describe the lymphatic system
|
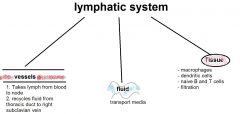
vessels drain lymph from tissues
|
|
|
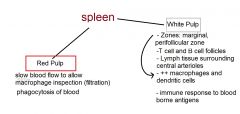
Describe Spleen
|

|
|
|
What does the red pulp in the spleen perform?
|
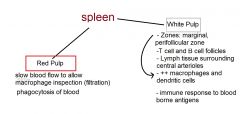
|
|
|
What does the white pulp in the spleen perform?
- zones - follicles - function |
|
|
|
Describe location of MALT
|

|
|
|
Describe lymph nodes
|
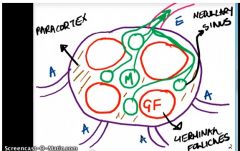
Germinal follicles : B cells --> Plasma cells --> Ab
Medullary sinus: macrophages Paracortex: T cells |
|
|
Describe the initial immune response
|
- macrophage recognises PAMP
- recognised through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) or through TLRs (toll like receptors) |
|
|
What can eventuate from the initial immune response?
|
1. Phagocytosis
2. Initiation of inflammatory response 3. Secretion of cytokines 3. Complement initiation 4. Adaptive immune response |
|
|
What are the interleukons released? (cytokines)
|
IL-1β
IL-6 TNF-α |
|
|
Define cytokines
|
Cytokines: small soluble proteins secreted by one cell that can affect the behaviour or properties of itself or another cell.
• Usually (but not always) given Interleukin number (IL-) |
|
|
Define Antigen
|

|
|
|
Define immunogen
|
Any substance that can elicit an immune response
|
|
|
Define hapten
|
a small molecule that can only elicit an immune response when bound to a larger carrier molecule
|
|
|
What are the 7 factors that influence the immunogenicity of proteins?
|
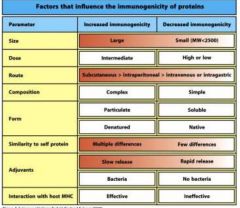
1. size
2. dose 3. route 3. composition 4. form 5. similarity to self 6. adjuvants |
|
|
Rank the route of an protein from its most immunogenic to least immunogenic
|
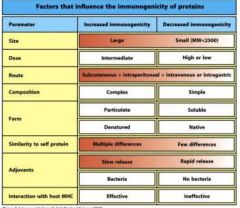
1. subcutaneous
2. intrapetrioneal 3. intravenous 4. intragastic |
|
|
What form is most immunogenic for a protein
|
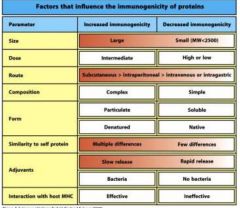
particulate and denatured
|
|
|
What is the least immunogenic form for an immunogen?
|
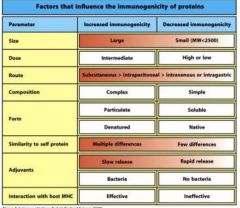
soluble and native protein arrangement
|
|
|
Define epitope
|
Also known as an antigenic determinant, is the discrete site on an Ag where an Ab or an Ag receptor recognises the Ag.
OR That part of an antigen which combines with an antibody or TCR |
|
|
What are the types of epitopes?
|
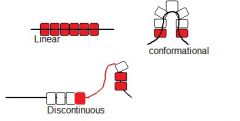
|
|
|
Describe linear epitopes
|
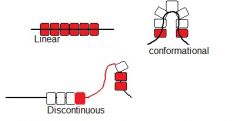
• A single segment of polypeptide
chain • Doesn’t require folding for recognition • T cells can recognise linear epitopes |
|
|
Describe discontinuous epiope
|
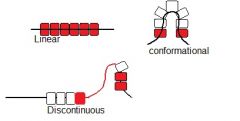
• Amino acids from different parts of
the polypeptide chain are brought together with protein folding • Recognised by antibodies when in their folded conformational shape |
|
|
How does the body recognise non-self?
|

The body’s own cells express molecules to which a healthy immune system shows tolerance.
Recognition of non-self antigens triggers immune response. |

