![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The basic theory of turbine operations |
* In a Reaction turbine, ........ * In a impulse turbine,...... |
|
|
|
Fundamental eqn of Reaction turbine |

* Blade force - Have torque(M) * Pressure conical & down ring (M=0) * Water pressure ( M=0) * Gravity ( M= 0) |
|
|
|
Cavitation |
It describes the process of vaporisation, bubble generation and bubble implosion which occurs in a flowing liquid as a result of a decrease and subsequent increase in local pressure. |
|
|
|
Cavitation damage |
* Great deal of noise. * Damage to components * Vibration * Loss of efficiency in the turbine. |
G D V L |
|
|
Classification of cavitation |
* Airfoil(blade) cavitation * Gap cavitation * Cavity cavitation(occur in draft tube) * Partial cavitation |
A G C P |
|
|
Measures to prevent blade cavitation |
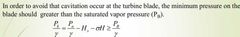
Causes When the water pressure is decrease and less than the saturated vapor pressure, it then causes blade cavitation. |
|
|
|
Suction height, Hs |

Hs = Distance between min. pressure point on blade to d/s water surface. |
|
|
|
Calculation of turbine installation elevation( Za) |

|
|
|
|
Specific speed |

* The specific speed is not the actual speed of a turbine. * The specific speed of high-head turbine with high rotational speed runner is much lower than that of low-head turbines with low rotational speed.
3. Francis turbines 300~80(rpm) |
|
|
|
Turbine characteristics |
The characteristics of Francis turbine hill chart: There are efficiency isolines, guide vane (α0) isolines, cavitation (σ) isolines, and the largest output limit line on the hill chart(shielded line). * The efficiency isolines shapes of Francis turbine are elliptical. * The guide vanes opening and rotate speed of turbine has effect on the discharge. * the efficiency of Francis turbine can keep high over a wide range of water head and flow rate.
The characteristics of Kaplan turbine hill chart:There are efficiency isolines, α0 isolines, σ isolines, and φ isolines on the hill chart. * The efficiency isolines shape nearly round. * There is no largest output limit line on the Kaplan turbine hill chart. * The efficiency of Kaplan turbine can keep high over a wide range of head and flow rate. |
e g e e l e |
|
|
Selection of water turbine |
• Known conditions - The range of heads , - The installed capacity
• Selection Parameters - Turbine type - Number of power-generating units - Runner diameter - Rotational speed - Runner elevation |
T N D R E |
|
|
Steps for the selection of water turbine |
1. Selection of the number of units Factors: - Maximum power for each turbine series - minimum loss of capacity during shutdown for repair or maintenance. - Operation flexibility of units - Higher efficiency operation during low-load demands;
2. Selection of turbine type - both Hmax and Hmin should be included in the head range specified in the tables or in the chart. Eg: HL260 - (Hmax ~ Hmin) = 10~35
3. Slection of runner diameter D= .......
4. Selection of rotational speed n=..... |
M M O H |

